
Quick Summary
Managerial economics connects economic theory to business practice, enabling decision-makers to solve real-world issues effectively. Looking ahead, 2025 will be challenging, as markets are highly complicated and technology is changing rapidly. This makes the application of managerial economics dimensions to business models and situations even more critical. Managerial economics provides managers with methods and tools to analyze and estimate demand, set prices, allocate resources, and forecast. By applying economic principles to managerial decision-making, firms are better positioned to make profits while minimizing risks and competition.
Now, suppose you are a future or intended business executive or member. In that case, mastering managerial economics will set you up as a leader who makes informed, data-driven decisions and adapts to changes in the business world. Are you ready to uncover information behind sound business decisions? Let’s examine how managerial economics relates to and impacts successful firms and how this course prepares you as a leader in a constantly changing economy.

Managerial economics is a stream of management studies that focuses primarily on solving business problems and making decisions by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Managerial economics uses economic concepts and tools to support smart business decisions. It is a specialized stream that deals with an organization’s internal issues using various financial tools. Economics is an indispensable part of any business. This single concept derives all the business assumptions, forecasting, and investments. It helps managers analyze costs, demand, competition, and market trends to allocate resources effectively and boost profitability. In short, it connects economic theory with real-world business challenges.
You need to know about the nature of managerial economics to gain more knowledge about it. Let’s read in detail about the nature and scope of managerial economics. The concept of the nature of managerial economics includes the following:
| Feature | Description |
| Interdisciplinary Nature | Combines economics and management for practical decision-making. |
| Microeconomic Foundation | Focuses on firm-level decisions like pricing, production, and market behavior. |
| Decision-Oriented | Uses analytical tools to support rational managerial decisions. |
| Practical Focus | Addresses real business challenges considering risk and uncertainty. |
| Optimization Focus | Maximizes efficiency and profitability while minimizing costs. |
| Dynamic Nature | Adapts to market trends, consumer behavior, and technology changes. |
| Descriptive & Prescriptive | Explains economic behaviors and suggests actionable strategies. |
| Behavioral Insights | Integrates psychology to understand decision-making biases. |
The scope of managerial economics covers two main areas of decision-making:
These are decisions within the organization’s control and include:
These include factors outside the firm’s control but that significantly impact business decisions:
Managerial Economics helps understand business environments and strengthens decision-making in cost control, budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning, making it a crucial discipline for every aspiring manager or business leader.
The branch of managerial economics comprises various concepts:
Opportunity Cost refers to the value of the next best alternative forgone when making a decision. It is a fundamental concept in managerial economics, guiding managers to evaluate trade-offs and make optimal resource allocation choices.
Demand and Supply Analysis examines the interaction between consumer demand and market supply. It provides critical insights for managers to make informed pricing, production planning, and inventory management decisions.
Measures how demand or supply responds to changes in price, income, or other variables. It’s crucial for pricing strategies, revenue management, and market analysis.
Managerial Decision-Making Models employ mathematical and statistical techniques to solve business challenges, providing a structured, data-driven, and analytical framework for making complex managerial decisions.
Behavioral Economics integrates psychological insights with economic principles to explain real-world decision-making, enabling managers to design effective incentives, improve organizational policies, and predict consumer behavior more accurately.
Analyzes strategic interactions among individuals or firms, helping predict competitor behavior and improve strategic business decisions.
Managerial economics is guided by core principles that support its practical application across various business scenarios. It blends theoretical concepts and quantitative analysis to address real-world challenges. Businesses often face imbalances between economic conditions and managerial decisions this is where managerial economics steps in. Applying analytical tools and frameworks helps identify problems, assess their impact, and develop practical solutions.
The key principles of managerial economics include:
Managerial economics is a practical tool for supporting strategic business decisions in areas such as production, pricing, investment, and resource planning. It helps managers make logical, data-driven choices that are aligned with business goals.
With limited resources such as labor, capital, and time, businesses must choose wisely. Managerial economics helps evaluate options and trade-offs to ensure optimal resource use for maximum output and efficiency.
A key focus of managerial economics is helping businesses increase profitability. It involves analyzing cost structures, pricing strategies, and market behavior to determine the most profitable path forward.
This principle provides tools to assess market dynamics, including consumer demand, supply trends, competition, and pricing behavior. These insights help shape effective marketing strategies and sharpen competitive positioning.
Managerial economics offers techniques to identify, evaluate, and manage risks in uncertain business environments. It equips managers to make informed decisions even under unpredictable conditions.
Managerial economics aids in crafting effective internal policies by evaluating the economic outcomes of various strategic choices. This supports expansion, investment, pricing, and production planning decisions.
Management economics is an essential method for assessing the company’s priorities and objectives, the organization’s current role, and what the management can do to fill the void between the two.
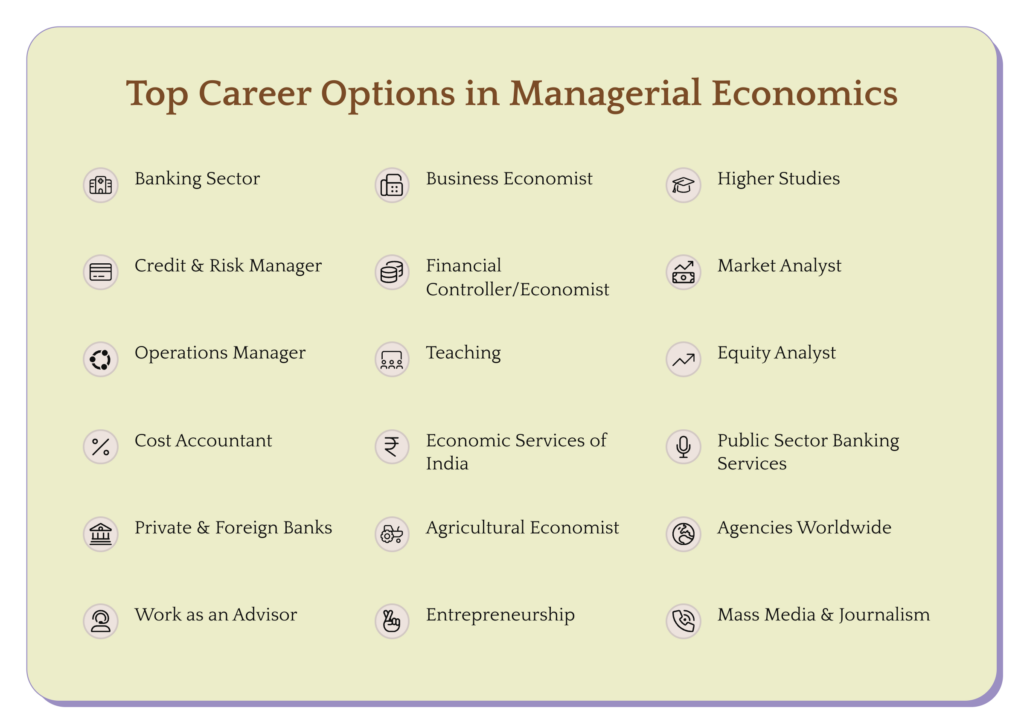
Based on the definition of managerial economics, we have listed the best options you can pursue in this field.
Banking sector job profiles include financial analysts, consultants, financial advisers, investment bankers, environmental policymakers, development officers, or part of the Research and Development. The job in the banking sector comes to the top when we think about the scope of managerial economics.
They deal with various sectors and companies; their primary role is to serve as an intermediary between the corporate world and the outside world.
There are several programs and courses to procure a degree in managerial economics. You can acquire in-depth knowledge in this field through higher studies. Many renowned institutions offer such programs and good placements. Having high-level knowledge can fetch you impeccable opportunities.
They analyze the company’s financial details and calculate the default risk to help the lender and the buyer.
A financial controller, or economist, is concerned with analyzing the day-to-day financial operations of an organization. He/she supervises the finance and accounting department and prepares financial reports.
A market analyst analyzes the market so their employers can make better decisions concerning product launches or rendering services.
From output to the statistics review to educating new staff, an operations manager manages all day-to-day activities in the company and needs to ensure that the organization runs optimally.
If you want to be a lecturer or become a senior economics teacher in private schools, apply for the NET / CTET exam in the field of education. After completing an M.A. in Economics with a mark of at least 55 percent, an applicant can seek a Ph.D. at any college or appear for UGC-NET. The NTA administers the exam.

An equity analyst extracts equity information for investment purposes and explores stock market insights to identify where to invest, whether to proceed, or sell on the market.
A Cost Accountant plans, studies, and records the costing concepts of an organization. He/she analyzes the fixed and variable costs to obtain the company’s total cost. A cost accountant is one of the exciting career options under managerial economics.
You can join India’s Economic Services. To join this service, you must appear for the Indian Economic Service Exam. You should have completed an M.Sc. or MA. in economics with at least 55 percent marks. The age range is 21-30 years. UPSC administers the test.
The Reserve Bank of India also recruits banking-sector economists through various recruitment exams. The age limit is 21-28 years.
An Economics degree holder can apply to both private and foreign banks. The Banking job categories are branch managers, clerks, economic analysts, planning and development officers, etc.
Agricultural Economics is an advanced branch of Economics. An agrarian economist optimizes food and fiber products’ production, distribution, and consumption.
Experienced and professional economists in well-known international organizations such as the World Bank and the International Labor Organization (ILO) can get great employment opportunities.
Graduates in Economics can work as economic consultants independently. Companies can ensure optimal job opportunities through scientific research and private sector consulting. The position includes Economic Researcher, Business Economist, Investment Analyst, etc.
Economists possessing a profound understanding of the market can create their start-ups. They can evaluate the industry dynamics and competitive business sectors and, based on this, design their business processes. Ultimately, they can achieve exponential growth by starting their own business. Besides, it will also aid the country’s unemployment problems by generating work opportunities.
You can join the news media by becoming an economic or editorial journalist. You can complete your graduation or post-graduation in mass communication and head towards joining the mass media. You can take advantage of this option even if your educational discipline differs. You can grow your career exceptionally by having the required knowledge and skills relating to this field.
Learn with Chegg and get expert help for your studies online. Chegg is a globally recognized educational provider that is highly acknowledged by students worldwide.
Students worldwide trust Chegg for helping them with their studies. You can simplify your complex topics with the help of experts at Chegg. Chegg comprises an efficient team of Subject-Matter Experts (SMEs) who assist in clearing your concepts. They break down complex topics into simple terms and create straightforward explanations with the help of definitions, videos, illustrations, and much more.
Are you interested in the subject of Economics? Do you want to learn more about it? Our experts will help you out. Get broad exposure to the world of economics and clarify various concepts from your home. All you need to do is sign up.
Managerial economics is essential for developing an effective business strategy and maintaining sustainable growth. Combining economic concepts with the realities of management problems allows managers to be informed and deliberate in their strategic decision-making. As we move forward into 2025, businesses that adopt managerial economics concepts will be able to anticipate market shifts better, align their operations to be more efficient, plan strategically focused decisions, and enable long-term success in what will likely be a post-pandemic period of turbulence. You will remain agile and resilient by continually learning and applying these concepts, which is essential in an ever-evolving space.
Whether you are beginning a new business venture or leading a well-established large organization, understanding and practicing managerial economics will highlight you as a proactive, innovative leader. Many businesses and business leaders fail to adopt change. Still, if you are aware of and familiar with this discipline, you can become a value-creating value leader and embrace the future prospects of business and innovation.
Read more:
Managerial economics is the use of economic principles and tools to aid business decision-making. It helps managers make well-informed decisions about pricing, production, investment, and resource allocation.
For example:
A company uses demand forecasting (a managerial economics concept) to determine how much product to produce in the next quarter.
Tip:
When you think about managerial economics, consider how it is “economics in action”; it takes the theory and applies it to a real-world business strategy.
The three primary types of managerial economics are:
Normative Economics – centers on deciding what needs to be determined (decision making and goal setting),
Positive Economics – describes what is happening (facts and cause-and-effect relationships), and
Applied Economics – applies economic theories and models to resolve real business problems.
Example: A manager using applied economics may analyze market evidence to determine whether to bring a new product to market.
Tip: Remember all three types as they work hand-in-hand to assist managers in making data-backed decisions.
It entails demand analysis, cost control, pricing, profit planning, and making decisions in business.
Example: Used to determine how and why to price a product based on cost and market demand.
Tip: Emphasis on using economics to address real-world business problems.
This is because it gives managers a foundation for making strategic choices using economic concepts such as demand, cost, and profit.
Example: A manager uses cost analysis to make a bi/make-or-buy decision.
Tip: It connects economics with business and can enhance efficiency and profitability.
Demand refers to the volume of a product or service that consumers can purchase at a given price and during a given period.
Example: When smartphone prices fall, demand generally increases, helping firms plan production.
Tip: Understanding demand can help with pricing, forecasting, and inventory decisions.
A utility function describes a consumer’s satisfaction or utility from consuming goods or services, typically presented in mathematical form.
Example: With a utility function U(x,y) = x + y, the consumer receives equal utility from one unit of good x and a unit of good y.
Tip: Utility functions can help managers and firm executives understand consumer preferences and make more informed decisions about product and price.
Think of managerial economics as a practical guide for making smarter business decisions. It takes powerful ideas from economics and applies them to the real-world challenges managers face, like setting the right prices or managing costs. Essentially, it helps you analyze what’s happening both inside your company and out in the market, so you can make the best choices to help your business thrive.

Authored by, Gagandeep Khokhar
Career Guidance Expert
Gagandeep is a content writer and strategist focused on creating high-performing, SEO-driven content that bridges the gap between learners and institutions. He crafts compelling narratives across blogs, landing pages, and email campaigns to drive engagement and build trust.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.