Quick Summary
Table of Contents
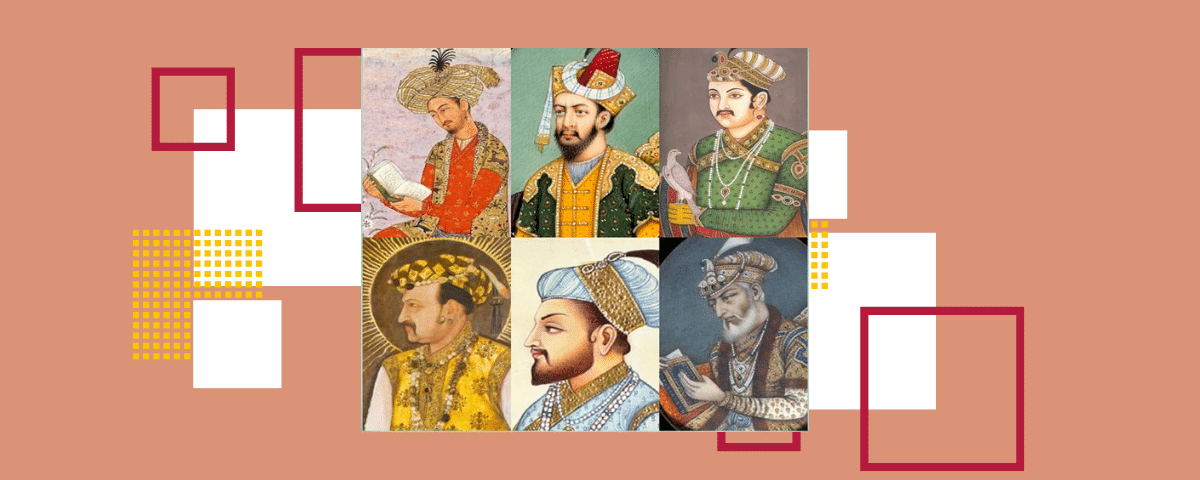
The list of Mughal emperors in India gives glimpses of a fascinating epoch of history. They ruled over India from the 16th to the 19th century, not intending to exercise their dominance but to fashion a national identity. They left behind majestic forts and monuments and a rich heritage of art and culture that inspires admiration today.
From Babur’s victories to Aurangzeb’s growth, each emperor showed how they helped the empire with different changes, ideas from books, and the blending of Persian and Indian cultures. Even though some people did not support their rule, their legacies were strong. Let’s learn about Mughal dynasty emperors, their rise, their reigns, and the impressions they left on the subcontinent.
The Mughal Empire was one of the greatest dynasties in Indian history. Their rulers have left a lasting impact on the country. The following table provides a summary of the list of Mughal emperors in India, when they ruled, their main achievements, and significant contributions:
| Emperor | Timeline | Major Achievements | Contributions |
| Babur | 1526-1530 | Defeated Ibrahim Lodi and won the First Battle of Panipat, Introduced Persian culture | Established Mughal rule in India; defeated Ibrahim Lodi to lay the foundation. |
| Humayun | 1530-1540, 1555-1556 | Introduced Persian art styles, Built Din-Panah | Laid the groundwork for the future stability of the Mughal Empire. |
| Akbar | 1556-1605 | Din-i-Ilahi, Nine Jewels (Navratnas), Married Rajput princess | Established a centralized government; promoted arts and architecture (e.g., Fatehpur Sikri). |
| Jahangir | 1605-1627 | Nur Jahan’s influence, Trade relations with England | Promoted Mughal painting; facilitated trade with European merchants. |
| Shah Jahan | 1628-1658 | Taj Mahal, Red Fort, Peacock Throne | Built iconic structures like the Red Fort and Jama Masjid. |
| Aurangzeb | 1658-1707 | Largest territory, Strict Islamic law | Imposed strict policies; faced rebellions that marked the empire’s decline. |
| Bahadur Shah I to II | 1707-1857 | Promoted Mughal painting and facilitated trade with European merchants. | Bahadur Shah II’s reign ended Mughal rule after the revolt of 1857. |
The Mughal dynasty emperors made a long-lasting impression on India through their building, art, government, and religious work. The first Mughal emperor, Babur, started this legacy, but every ruler added his skills to it, changing the culture and politics of India. Let’s take a closer look at what they contributed:
The grand Mughal emperors are remembered mainly for their architectural excellence. Beyond the famous Taj Mahal, they built entire cities like Fatehpur Sikri, which combined Persian and Indian styles. Their architectural innovations included:
Under the Mughal rulers list, art and culture flourished. Jahangir loved the fine arts. Literature did not lag either, and Persian became the language in court and influenced modern Urdu. Cultural stories were enriched by the poet Amir Khusrau and historians like Abul Fazl.
The timeline of Mughal emperors reveals their sophisticated methods of managing the government. Akbar established a robust central government and distributed the empire into provinces led by the most trusted leaders. He collaborated with Raja Todar Mal to design a fair and effective tax system. Some other key insights on the Mughal administration are:
The Mughal dynasty had emperors who had different religious rules. Akbar is known to be tolerant and founded the Din-i-Ilahi, which blended all religions. In contrast, Aurangzeb’s strict laws resulted in problems since he reinstated the jizya and curbed cultural freedom. The notable developments in religious policy during the Mughal era were:
The list of Mughal emperors in India shows a family that greatly influenced India’s history. Their impacts go beyond the time they ruled, starting with the first Mughal emperor, Babur, and ending with Bahadur Shah II. Their cultural legacy is easy to see in India’s lively traditions. Mughal art and literature mixed Persian, Indian, and Central Asian styles that still affect today’s designs. Politically, their centralised administration introduced structured governance. The land revenue system served as a model for subsequent rulers. Even the judicial reforms laid the groundwork for India’s current legal system.
Modern Indian culture, including language and food, is influenced by the Mughals. The popularity of Urdu, Mughlai food, and Basant festivals show that Mughal traditions have become a part of people’s lives. The emperors of the Mughals connected the past to the present, leaving behind a rich legacy of beauty, variety, and complexity.
A list of Mughal emperors in India illustrates how they transformed the nation. From Babur’s wins to Akbar’s astute changes and Shah Jahan’s magnificent structures, each emperor made a distinct impact.
Their influence goes far beyond the buildings and legislation. They helped form India’s identity by combining various cultures and traditions. The Mughals taught the world about governance, art creation, and strength. We not only remember them as leaders but also as builders of India’s spirit. The history of Mughal emperors shows us a dynasty that valued creativity, strength, and diversity—qualities that still represent India today!
The first Mughal emperor was Babur. This emperor founded the Mughal Empire and established himself in India by defeating Ibrahim Lodi in the First Battle of Panipat in 1526. He was a master military tactician and introduced gunpowder into Indian warfare, thus starting the rule of the Mughal Empire in India.
Shah Jahan built the Taj Mahal, one of the world’s most iconic monuments. He commissioned it in memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal, in 1632. The Taj Mahal is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture, blending Persian, Islamic, and Indian styles. It stands as a symbol of eternal love.
Bahadur Shah II, commonly known as Bahadur Shah Zafar, was the last Mughal emperor. He ruled during the 1857 revolt, which ended the Mughal dynasty. After the British suppressed the uprising, Bahadur Shah Zafar was exiled to Rangoon, where he lived the rest of his life in captivity.
Akbar was an established visionary leader who also encouraged religious tolerance through means like Sulh-e-Kul (universal peace). He reformulated administration through a centralized government and an efficient tax policy. He also patronized art, literature, and architecture, leaving behind monuments like Fatehpur Sikri and the Akbarnama.
There were many reasons behind the decline of the Mughal Empire. The successors of Aurangzeb after the great emperor turned out to be weak. The rebellions by provincial powers and the unprecedented surge of British power further weakened their rule, concluding in their final downfall in 1857.
The Mughal Empire was governed by a total of 16 emperors between the years 1526 and 1857.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.