Table of Contents
UPS Full Form
UPS full form is an Uninterruptible power supply and it is essential in today’s advanced society. It offers a trustworthy power backup solution, guaranteeing an ongoing power supply to protect equipment, crucial activities, and data.
UPS Full Form in Hindi
UPS Full Form in Hindi is “अबाधित विद्युत आपूर्ति” (Abadhīt Vidhyut Aapoorti).
What is the full form of UPS?
A UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, is a device that provides backup power to electronic equipment during power outages or fluctuations. It acts as a buffer between your devices and the power source, ensuring they continue to operate smoothly even if the main power supply fails.
Types of UPS Systems
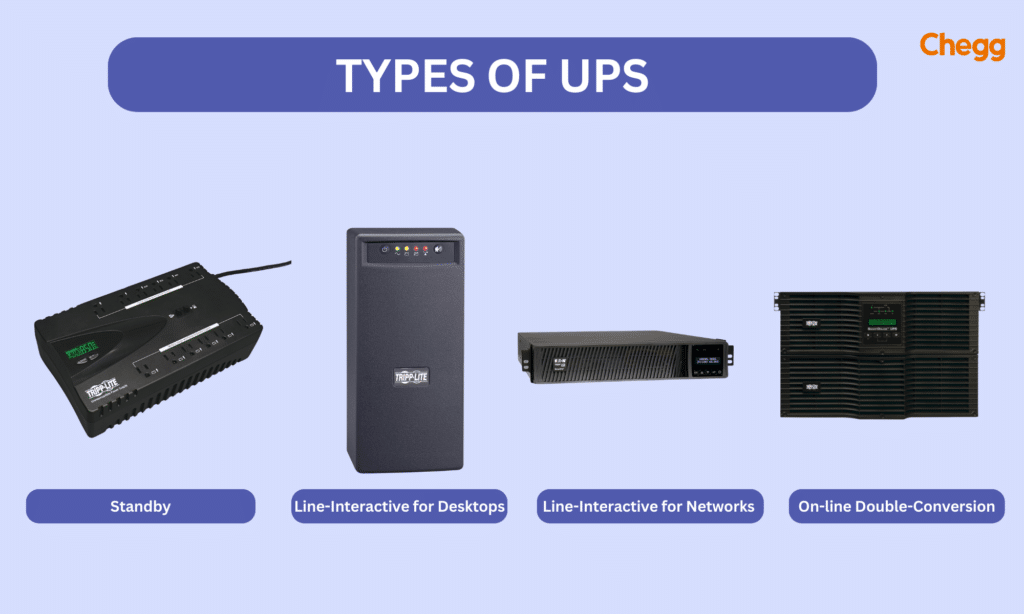
There are different types of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS Full Form) systems available, each designed for specific needs and applications:
1. Standby (Offline) UPS:
- In standby mode during normal operation, directly connects the load to the mains supply.
- Switches to battery power only when a power failure is detected.
- Best suited for small, less critical applications like home computers.
2. Line-Interactive UPS:
- Similar to standby UPS but includes a built-in automatic voltage regulator (AVR).
- Provides better protection against power fluctuations.
- Commonly used for small business and office applications.
3. Online (Double Conversion) UPS:
- Continuously converts incoming AC power to DC, and then back to AC.
- Provides the highest level of protection by isolating connected devices from the mains power completely.
- Ideal for critical applications like data centers, medical equipment, and industrial processes.
Key Points to Remember
Here are some key points to remember about Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- First Invented by John Hanley: John Hanley built the first UPS in 1934.
- Protects Hardware: A UPS helps protect computers and other equipment from being damaged by sudden power spikes and surges.
- Prevents Data Loss: It stops data from being lost or corrupted when the power goes out.
- Reliable and Efficient: UPS systems are known for being reliable and efficient in keeping devices running smoothly.
- Reduces Downtime: They help keep networks and applications running with minimal downtime.
- Small and Cost-Effective: UPS systems are usually compact and don’t cost too much, making them easy to use without taking up a lot of space or money.
These points show why UPS systems are important for keeping electronic devices safe and running.
Why You Need a UPS
Here are the key reasons why an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS full form) is essential for computer systems:
- Preventing Data Loss: A sudden power outage during data writing can lead to file corruption. A UPS provides crucial time to safely save and close files.
- Equipment Protection: Voltage fluctuations and spikes can harm hardware components. The UPS regulates power, safeguarding your electronics.
- Network Continuity: Servers and network equipment need a proper shutdown to prevent crashes. A UPS ensures time for a graceful shutdown.
- Work Continuity: During short power disruptions, a UPS allows computers and monitors to continue operating.
- Battery Backup: The UPS’s battery power enables work continuity on laptops and mobile devices when mains power is unavailable.
These points highlight the indispensable role of a UPS in ensuring smooth and safe computer operations.
History of UPS
The history of Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS full form) shows how they have become essential for keeping electronics running smoothly. Here’s a simplified timeline of important milestones:
1950s: Early Beginnings
- First Ideas: The concept of UPS starts taking shape. Companies like Fuji Electric work on early versions around 1954.
- First UPS Models: By the mid-1950s, the first commercial UPS systems are introduced. These early models mainly use batteries to provide backup power.
1960s-1970s: Growing Need
- Mainframe Computers: As businesses start using big mainframe computers, the need for reliable power grows. UPS systems become more advanced to protect these important machines.
- Transistor Technology: The invention of transistors makes UPS systems smaller and more efficient, replacing older, bulkier vacuum tube designs.
1980s-1990s: Widespread Adoption
- Personal Computers: With the boom in personal computers, UPS systems become more common in homes and offices. They become smaller and more affordable.
- Better Power Quality: As more people rely on electronics, UPS systems evolve to not only provide backup power but also to smooth out voltage changes and protect against surges.
2000s-Present: Modern Innovations
- Digital Age: The rise of the internet and data centers means we need very reliable UPS systems. Modern UPS systems can be monitored and managed remotely, ensuring they work well in critical places like data centers and hospitals.
- Technological Advances: New battery technology and improvements in power conversion make UPS systems more efficient, smaller, and less expensive.
Today, UPS systems are crucial for keeping important devices running without interruption in all kinds of places, from data centers and hospitals to homes and businesses.
How Does UPS Work?
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS Full Form), acts as a behind-the-scenes protector for your electronics during power fluctuations. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Normal Operation:
When everything is functioning normally with a steady AC power supply, the UPS performs these actions:
- The rectifier converts incoming AC power to DC power.
- A portion of this DC power is used to charge the battery and maintain its health.
- The remaining DC power is then inverted back to clean AC power that supplies your connected equipment.
Power Outage Scenario:
When a power outage occurs:
- The AC power from the wall outlet ceases.
- The inverter immediately switches on and starts using the DC power from the battery.
- The inverter converts the DC battery power to clean AC power, ensuring a seamless transition for your connected devices. They continue to operate without interruption.
UPS Components
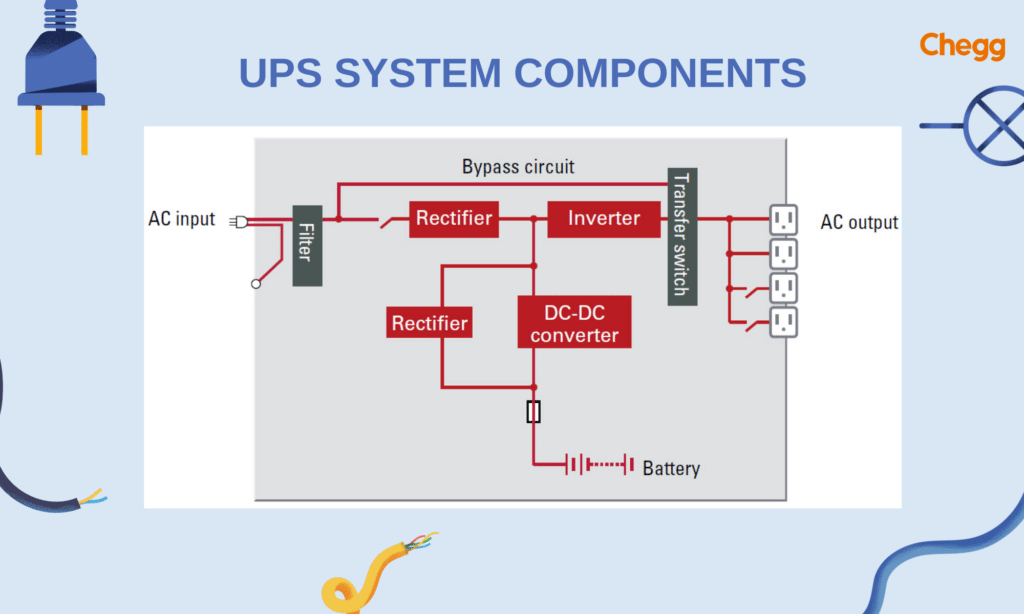
A Uninterruptible Power Supply system (UPS full form) consists of four major components: a rectifier, UPS batteries, an inverter, and a static bypass switch. Here are the four main components:
1. UPS Rectifier
- Function: Converts incoming AC power to DC power.
- Roles:
- Charges the UPS batteries.
- Supplies DC power to the inverter.
- Notes:
- Can handle voltage fluctuations, preventing unnecessary battery use.
- In smaller UPS systems (below 3 kVA), the rectifier and battery charger may be separate components.
2. UPS Batteries
- Function: Provide backup power when the mains supply fails.
- Charging: Kept charged by the rectifier or a separate charger.
- Configuration:
- Batteries are arranged in series strings.
- Failure of one battery can affect the entire string.
- Smaller systems have internal batteries; larger systems use standalone battery cabinets.
3. UPS Inverter
- Function: Converts DC power back to AC power to supply the load.
- Role: Ensures clean, stable power by filtering out spikes, sags, surges, and noise.
- Output: Produces a pure sine wave for reliable power delivery.
4. Static Bypass Switch
- Function: Acts as a backup in case the UPS fails.
- Role: Automatically switches the load to the mains supply if there’s a UPS fault.
- Note: Direct mains supply isn’t filtered, but this allows equipment to keep running during UPS maintenance or replacement.
Additional Components
- Fans: For cooling the UPS.
- Capacitors: For power regulation.
- External Maintenance Bypass: Allows the UPS to be serviced without disrupting the load.
- Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors (TVSS): Protect against power surges.
- SNMP Monitoring: Enables network-based UPS monitoring and management.
These components work together to provide reliable, continuous power and protect critical equipment from power disturbances.
Benefits & Limitations of UPS
Benefits of UPS
- Emergency Power Supply: A UPS provides an immediate power source during power outages, ensuring continuous operation of devices.
- Surge Protection: It offers robust protection against power surges, safeguarding sensitive electronic equipment from damage.
- Extended Battery Life: UPS systems come with a built-in battery, providing extended power backup during blackouts.
- Cost-Effective Maintenance: The maintenance cost of a UPS is relatively low, making it a cost-effective solution for power management.
- Data Loss Prevention: By providing uninterrupted power, a UPS shields against unexpected data loss, a critical feature for data centers and computer systems.
Limitations of UPS
- Higher Replacement Cost: UPS batteries typically have a lifespan of 5 to 10 years. After this period, they need to be replaced, which can incur a significant cost.
- Complex Installation: Installing a UPS system is not a straightforward task. It often requires the expertise of professionals, adding to the overall cost and effort.
- Runtime & Capacity: UPS batteries provide temporary power during outages. Runtime (how long) and capacity (how much power) are crucial. Choose a UPS that can handle your equipment’s power draw for your desired runtime.
- Battery Degradation: UPS batteries degrade over time, reducing runtime. Consider battery replacement costs when choosing a UPS.
- Surge Protection: Not all UPS models offer surge protection. Use a separate surge protector for comprehensive protection.
- Heat & Maintenance: UPS systems, especially larger models, generate heat and require proper ventilation and maintenance (battery testing, cleaning vents) for optimal performance.
Common Applications of UPS Systems
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS full form) systems are used in many places to keep devices running when the power goes out. Here are some common applications:
- Home and Office:
- Protecting Electronics: UPS systems are used at home and in small offices to protect devices like computers, TVs, and Wi-Fi routers from power surges and outages.
- Keeping Devices On: If the power goes out, a UPS can keep these devices running long enough to save work or finish a task.
- Data Centers and IT:
- Continuous Power: Data centers, which house lots of computers and servers, need a steady power supply. UPS systems ensure they keep running even during power outages.
- Preventing Data Loss: They protect against data loss and downtime by providing backup power, allowing systems to keep operating or shut down safely.
- Healthcare Facilities:
- Supporting Medical Equipment: In hospitals, UPS systems are critical. They provide backup power for life support machines and other vital medical equipment.
- Maintaining Patient Data: UPS systems ensure that important patient information systems stay online and accessible, even during a power outage.
These examples show how UPS systems are essential for keeping things running smoothly in different settings.
How to choose the right UPS?
Choosing the right Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS full form) is important to keep your devices safe and running during power outages. Here are some simple steps to help you pick the right UPS:
1. Power Capacity:
- Know Your Devices: Check the total wattage (power) of all the devices you want to connect to the UPS. This info is usually on the device’s power supply or in the manual.
- Add a Safety Buffer: Add 20-25% more to the total wattage to account for future devices or extra power needed when devices start up.
- Select the Right Capacity: Choose a UPS with a power capacity (measured in VA) that is higher than the total wattage of your devices.
2. Runtime Needs:
- Think About Outage Duration: Consider how long you usually lose power or how long it takes for your backup generator to start.
- Choose the Right Runtime: Pick a UPS that can provide power for the amount of time you need during an outage. The longer the runtime, the longer your devices will stay on.
3. Additional Features:
- Surge Protection: This feature protects your devices from sudden voltage spikes that can cause damage.
- Communication Ports: These ports let you monitor and control the UPS remotely, which is handy for managing power settings.
- LCD Display: An LCD screen shows the UPS status and battery level, so you know how much power is left.
Resources for Choosing the Right UPS:
Choosing the right UPS means your important devices will stay protected and functional, no matter what happens with the power.
Future Trends in UPS Technology
The future of Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS full form) will be shaped by new technologies that make them more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly. Here’s what to look out for:
1. Better Batteries:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries: More UPS systems will use Li-ion batteries because they last longer, charge faster, and weigh less than older types of batteries.
- Solid-State Batteries: New research on solid-state batteries might lead to UPS systems that are even more powerful, charge quicker, and are safer than Li-ion batteries.
2. More Efficient and Compact:
- Higher Efficiency: UPS systems will get better at converting power, meaning they will waste less energy and produce less heat.
- Smaller Size, More Power: Thanks to better electronics and cooling methods, UPS systems will become smaller but still handle lots of power, making them perfect for places with little space.
3. Smart and Connected UPS:
- IoT Integration: UPS systems will connect to the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing users to monitor and manage them remotely, which helps in fixing issues before they become problems.
- Cloud-Based Analytics: By using cloud services, UPS systems will analyze power use and predict problems, leading to less downtime and more reliable operations.
4. Integration with New Energy Sources:
- Microgrids and Renewables: As more homes and businesses use solar, wind, and other small-scale energy sources, UPS systems will need to work well with these.
- Bidirectional UPS: Some UPS systems will not only provide backup power but also be able to send extra power back to the grid.
5. Eco-Friendly Practices:
- Green Technologies: Future UPS systems will use materials and designs that are better for the environment and more energy-efficient.
- Battery Recycling: There will be a focus on recycling batteries and safely disposing of them to protect the environment.
In summary, the UPS systems of the future will be smarter, more efficient, and better for the planet. With advancements in battery technology and connectivity, these systems will continue to support our growing need for reliable power, especially as we move towards more sustainable energy solutions.
Conclusion
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS Full Form) systems are essential for a world that depends on staying connected and having things work smoothly. They protect our devices and data and keep operations going in different industries. Through this blog, we explored the full form of UPS, its importance, and its functionalities.
UPS Full Form: Key Takeaways
- UPS full form is Uninterruptible Power Supply, a device that provides emergency power to electronics during a power outage.
- Keeps devices running temporarily during power cuts, preventing data loss and equipment damage.
- Includes a battery, power inverter, and charging system to supply and regulate backup power.
- Commonly used with computers, servers, and critical systems to ensure uninterrupted operation.
- Types of UPS:
- Standby: Basic backup for brief power outages.
- Line-Interactive: Adjusts to minor power fluctuations and outages.
- Online: Provides continuous, clean power and handles long outages and severe voltage drops.
- Protects sensitive electronics from power interruptions and surges.
- Allows safe shutdown of systems to prevent data corruption and hardware damage.
- Understanding UPS is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic devices during power disruptions.
- Investing in a UPS can safeguard your data and equipment from unexpected power issues.
Along with the UPS Full Form Learn more about some other full forms too by visiting the below links:
| DHCP Full Form | RDBMS Full Form | ENIAC Full Form |
| GPU Full Form | LAN Full Form | DOS Full Form |
| RADAR Full Form | CFL Full Form | HDMI Full Form |
| URL Full Form | VPN Full Form | MRP Full Form |
Ready to learn more? Click on below button to get the complete list of Full Forms!
UPS Full Form: FAQs
What is UPS full form?
UPS full form is Uninterruptible Power Supply.
What is a UPS used for?
A UPS provides backup power to electronic devices during power outages, protecting them from data loss and damage.
How does a UPS work?
A UPS stores energy in a battery and supplies it to connected devices when the main power fails, ensuring continuous operation.
How long can a UPS provide power during an outage?
The backup duration depends on the UPS capacity and the power consumption of the connected devices. It can range from a few minutes to several hours.
Can a UPS protect devices from power surges?
Yes, most UPS systems include surge protection to safeguard against voltage spikes.
How do I choose the right UPS for my needs?
Consider factors like the total power requirement of your devices, the desired backup time, and the level of power protection needed.
Can a UPS be used with a generator?
Yes, a UPS can be used with a generator to provide immediate power during an outage while the generator starts up.
Do UPS systems require maintenance?
Yes, UPS systems need regular checks to ensure the battery and components are in good condition. Battery replacement is typically required every few years.
What is the difference between a UPS and a power strip?
A UPS provides backup power and surge protection, while a power strip mainly offers additional outlets and may include basic surge protection without backup power.
Can I connect multiple devices to a single UPS?
Yes, as long as the combined power consumption of the devices does not exceed the UPS’s rated capacity.
Got a question on this topic?