Table of Contents
SSP Full Form Explained
In India, SSP full form is Senior Superintendent of Police. This position plays a crucial role in managing police affairs in a district or urban area. Respecting law and order, reducing crime, and maintaining the public’s safety and security are important responsibilities given to Senior Superintendent of Police.
The Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) position was first established in India during the colonial period. During British rule, this position aimed to establish an organized and efficient police force. In the post-independence era, India retained and restructured its police system, wherein the role of SSPs evolved to meet the diverse and unique challenges of the nation. They have made their responsibilities from regular police by adopting developments in technology and changes in culture. Today’s SSPs actively connect with communities and establish positive public relations while maintaining law and order for the good of the country.
SSP Full Form In Hindi
वरिष्ठ पुलिस अधीक्षक (Vrishth Polis Adhikshak).
SSP Meaning
The Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) is a high-ranking police officer who oversees law enforcement in a town or city. They wear a badge with ‘IPS’ and a star and emblem called the Ashoka emblem. The Senior Superintendent of Police manages bigger districts, while an SP handles smaller ones.
The SSP position dates back to British colonial times, when they set up a structured police system. Since then, SPs have been crucial in keeping people safe and following the law in India. To do their job better, they’ve updated their methods over time, using modern tools and involving the community more.
Rank and Hierarchy in the Indian Police Service
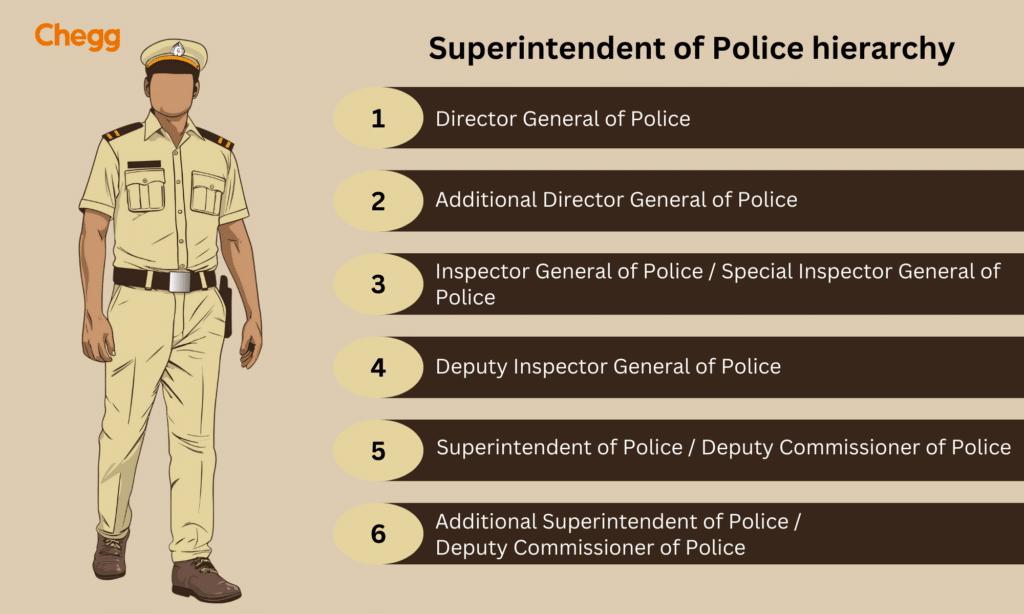
The Indian Police Service (IPS) follows a well-defined hierarchy of ranks, with each level carrying increasing responsibility and leadership. Here’s a breakdown from top to bottom:
1. Director General of Police (DGP):
- Heads the entire state police force.
- Highest-ranking IPS officer in a state.
- Oversees law and order, crime investigation, and police administration.
2. Additional Director General of Police (ADGP):
- Assists the DGP in managing specific areas like crime investigation, intelligence, or training.
- May head specialized wings within the state police.
3. Inspector General of Police (IGP):
- Heads a police zone within a state encompassing several districts.
- Oversees law and order, crime investigation, and police administration for the zone.
4. Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG):
- Heads a police range within a zone, typically comprising a few districts.
- Oversees law and order, crime investigation, and police administration for the range.
5. Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP):
- Heads a district police force.
- Manages law and order, crime investigation, and police administration for the district.
6. Superintendent of Police (SP):
- Heads a smaller district or a police subdivision within a district (depending on the state structure).
- Oversees law and order, crime investigation, and police administration for their jurisdiction.
7. Additional Superintendent of Police (ASP) / Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP):
- Hold positions of responsibility at the district or sub-divisional level, assisting senior officers.
- May head specific units like crime investigation, traffic control, or special branches.
These ranks can be different in each state. Also, officers might have special jobs like Police Commissioner, Deputy Commissioner, or Traffic Superintendent.
Powers and Authority of an SSP
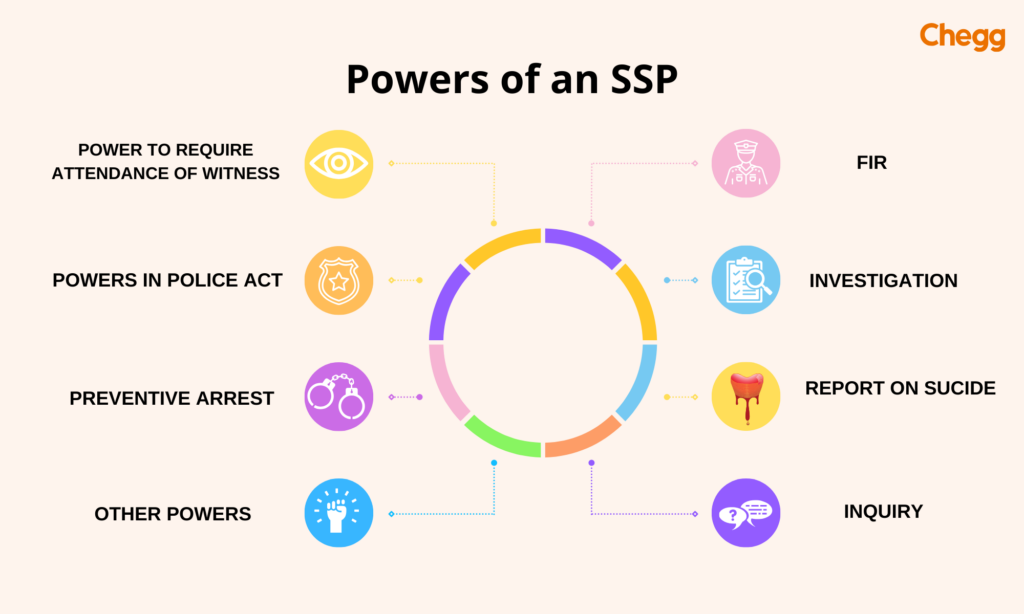
An Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) in India wields significant powers and authority to maintain law and order and ensure public safety within their jurisdiction. Here’s a breakdown of their key responsibilities and powers:
1. Leadership and Management:
- Overseeing multiple police stations within their district.
- Leading and motivating police personnel to ensure efficient law enforcement.
- Delegating tasks and responsibilities to subordinate officers.
2. Maintaining Law and Order:
- Implementing strategies to prevent crime and maintain public peace.
- Supervising investigations of criminal activities.
- Taking necessary actions to control riots or other disturbances.
- Enforcing relevant laws and regulations.
3. Public Safety and Security:
- Developing and implementing plans to safeguard the community.
- Responding to emergencies and crisis situations.
- Issuing orders for preventive arrests in anticipation of trouble (under specific legal provisions).
- Collaborating with other law enforcement agencies and security forces.
4. Magisterial Powers:
- In some cases, SSPs may possess magisterial powers granted under the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- These powers allow them to take actions like:
- Declaring curfews under Section 144 to prevent violence or riots.
- Demanding security bonds from potential or habitual offenders.
- Employing reasonable force to maintain public order during emergencies.
5. Other Responsibilities:
- Addressing public grievances related to police matters.
- Ordering departmental inquiries for misconduct or corruption within the police force.
- Liaising with local authorities and the public.
- Ensuring the proper functioning of police stations and outposts.
While SSPs hold considerable authority, they typically report to the District Magistrate, who has overall control of the district administration. The specific powers and responsibilities of an SSP may vary slightly depending on state police laws and departmental policies.
Role of SSP in Maintaining Law and Order
Keeping law and order is a big job. The Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) is the top police officer in charge of making sure people follow the law and stay safe in their district. Here are some of the important things the SSP does:
- Preventing Problems: SSPs look at where crimes happen and plan how to stop them before they start. They focus on risky areas and take steps to keep bad things from happening.
- Working with the Community: SSPs believe in teamwork with the community. They support programs like neighborhood watch groups. These programs help people trust the police and work together to fight crime.
- Acting Fast in Emergencies: When things go wrong, SSPs lead the way. They send officers quickly to handle big crowds, keep order, and make sure everyone stays safe. This includes dealing with riots, accidents, and other emergencies.
- Keeping Things Fair: Under an SSP’s guidance, police officers follow the rules and treat everyone fairly. This stops criminals and makes people feel safe.
- Leading Investigations: SSPs make sure crime investigations are done well. They watch over how evidence is collected and make sure the law catches those who break it.
- Talking with People: During protests and events, SSPs talk with people to keep things calm and safe. They help people share their thoughts peacefully while making sure everyone stays safe.
- Planning Security: SSPs notice places that need more security, like important buildings or events. They plan how to keep those places safe and quickly handle any problems.
In short, SSPs are like the leaders of a safety team for the district. They plan ahead, work with everyone, and take action to keep peace and make your neighborhood safe.
Skills and Qualities of an SSP
To be a good Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form), certain skills and qualities are important. Here’s what they need:
- Leadership: An SSP leads a big team of police officers. They need to inspire and guide their team well.
- Decision-making: SSPs must make quick and smart decisions, especially during emergencies or tough situations.
- Communication: They need to talk clearly with their team, other police, and the public. Good communication helps build trust and solve problems.
- Problem-solving: SSPs should be good at finding solutions to problems. Police work can be tricky, and they need to think fast.
- Empathy: They should understand other people’s feelings and treat everyone fairly. This helps them connect with the community they serve.
- Integrity: SSPs must be honest and follow the law. People trust them to do the right thing.
- Physical Fitness: Being in good shape helps SSPs do their job well, especially during emergencies or when they need to chase someone.
- Knowledge: They need to know a lot about police work and the laws they enforce. This helps them make good decisions and lead their team effectively.
- Experience: SSPs usually have worked in different police jobs before. This experience helps them understand how things work and handle tough situations.
By having these skills and qualities, SSPs can keep the peace, fight crime, and make sure everyone stays safe.
Also Read- पॉक्सो एक्ट क्या है?
How to Become SSP in Police
In India, becoming a Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) involves cracking a tough national exam and dedication throughout your career. Here’s a simplified roadmap:
1: Education & Preparation
- Complete High School: This is the basic requirement.
- Get a Bachelor’s Degree: Any degree is okay, but Social Sciences like Criminology or Psychology are beneficial.
2: Crack the UPSC Exam
- This highly competitive exam selects officers for prestigious services like IPS (Indian Police Service).
- Focus on studying for the UPSC Civil Services Exam (CSE) conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
3: Join the IPS
- If you qualify for the IPS through the UPSC CSE, you’ll undergo rigorous training.
4: Climb the Ranks
- Start your IPS career as an Inspector and perform well.
- Gain experience and showcase leadership qualities.
5: Promotion to SSP (Selection Grade)
- After roughly 13 years in the IPS, with excellent service, you might be promoted to SSP.
This is a long-term goal. Dedication, hard work, and continuous learning are key throughout your journey.
SSC Exam Pattern
To become an SSP, or Senior Superintendent of Police, in India, you typically need to follow a career path in the Indian Police Service (IPS). The IPS is a prestigious and competitive civil service that requires a commitment to law enforcement and public service. Here’s a general outline of how to become an SSP:
To pass the test, you need to complete three ranges:
- Main Examination: This exam consists of nine papers in total, and students who pass it are invited to an interview.
- Preliminary Examination: Exam papers are limited to what the student must pass; the exam’s results are no longer transferred to the main exam.
- Interview: Since the UPSC verifies the outcome after the interview, the interview serves as the final level of the examination. The interview consists of two hundred marks, and college students are required to respond to questions about their country, politics, intellectual capacity, and areas of interest.
SSP Salary
The exact salary of an Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form) in India can vary slightly depending on factors like state, allowances, and experience. However, we can get a good idea of the range:
- Average: The average salary for an SSP/SP is around ₹1,25,000 per month.
- Pay Scale: As per the 7th Central Pay Commission, the base salary for an SSP might be around ₹78,800 per month.
Additional factors influencing salary:
- Years of Service: Experienced SSPs with more years of service might see a higher base salary.
- Allowances: SSPs are entitled to various allowances that can add to their total compensation. These allowances may cover housing, transport, uniforms, and other job-related expenses.
Exploring SSP Full Form in Different Contexts
SSP Full Form in Education:
- SSP (Student Support Program): This can refer to various support programs or initiatives aimed at assisting students academically, emotionally, or socially within an educational institution.
SSP Full Form in Agriculture:
- SSP (Single Super Phosphate): In agriculture, SSP is a type of fertilizer used to improve soil fertility by providing essential nutrients like phosphorus.
DSP Full Form:
- DSP (Deputy Superintendent of Police): In Hindi, it’s उप पुलिस सुपरिंटेंडेंट. This is a rank in the police department below the SSP, responsible for assisting in various policing activities.
SSP Full Form in Railway:
- SSP (Sub-Sectioning and Paralleling Post): An SSP in railway is a switching station used in electric railway traction systems. It plays a critical role in managing the flow of high voltage electricity that powers trains.
Conclusion
SSP full form the Senior Superintendent of Police, is a key figure in the police department who is in charge of maintaining peace and order in our communities. They are there to protect the public’s safety and security and work tirelessly to control riots, handle demonstrations peacefully, protect us during civil unrest, and manage police stations, making sure everything runs smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- SSP full form is Senior Superintendent of Police.
- It’s a high-ranking position in the Indian police force.
- SSPs manage law enforcement in large districts or major cities.
- Responsibilities include:
- Maintaining law and order
- Overseeing investigations
- Leading police teams
- Handling administrative tasks
- To become an SSP, you typically need to:
- Crack the UPSC Civil Services Exam
- Join the Indian Police Service (IPS)
- Work your way up through the ranks
Learn about some other full forms:
| RTI Full Form | CISF Full Form |
| SHO Full Form | DCP Full Form |
| PCC Full Form | NSG Full Form |
| IAS Full Form | SDM Full Form |
| EWS Full Form | FIR Full Form |
Ready to learn more? Click on below button to get the complete list of Full Forms!
SSP Full Form : FAQs
What is SSP full form in the police department?
SSP full form is “Senior Superintendent of Police.
What is an SSP’s function within the police force?
An SSP is a senior officer in charge of managing law enforcement actions within a district or city region.
How does an SSP ensure public safety and order?
SSPs work with their team to control riots, handle demonstrations, and maintain peace in the community.
Can someone become an SSP directly after school?
No, becoming an SSP requires gaining experience through entry-level positions like police officers and climbing the ranks.
What skills does an SSP need?
A successful SSP requires strong leadership, decision-making, communication, and crisis management abilities.
How much does SSP earn? Or What is the salary of SSP in India?
The average monthly salary of SSPs in India is ₹1.18 lakhs – ₹2.10 lakhs (approx.) with benefits.
Who has more power DCP or SSP?
Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP full form) has more powers than Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP full form)
Is SSP an IPS officer?
Yes, SSP (Senior Superintendent of Police) is typically an IPS (Indian Police Service) officer who holds a high-ranking position in the police department.
Who is bigger, SP or SSP?
SSP is higher in rank and authority compared to SP (Superintendent of Police). The SSPs are in charge of larger districts or more populated areas, while the SPs manage smaller districts or subdivisions.
Who is senior, SSP or DCP?
SSP is generally senior to DCP (Deputy Commissioner of Police) in terms of rank and authority. SSP is responsible for a larger jurisdiction, often encompassing multiple districts, while a DCP typically oversees law enforcement in a specific area within a city.
Got a question on this topic?
