Quick Summary
The Khilji Dynasty ruled India during the Delhi Sultanate and was founded by Jalal-ud-Din Khilji.
The most famous ruler, Alauddin Khilji, expanded the empire and reformed its economy.
The dynasty fell due to weak successors and internal conflicts.
Table of Contents
The Khilji dynasty was a significant force in medieval Indian history. Established in 1290 by Jalal-ud-Din Khilji, it ruled large parts of northern India for over three decades. The dynasty is best known for the reign of Alauddin Khilji, who expanded the empire’s territory and reformed the administrative systems. In this article, we explore the history, key rulers, and legacy of the Khilji dynasty.
The Khilji dynasty was one of the most significant ruling families in the history of the Delhi Sultanate, which ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 13th and 16th centuries. The Khiljis played a crucial role in the consolidation of Muslim rule in northern India. Their reign, spanning from the late 13th century to the early 14th century, brought about notable political, military, and administrative developments. Below are the key aspects of their significance:
The Khilji dynasty was a prominent ruling dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate in India, which reigned from the late 13th century to the early 14th century. Founded by Jalal-ud-din Khilji in 1290, the dynasty marked a significant period in Indian history characterized by military conquests, administrative reforms, and cultural developments.
The Khilji dynasty emerged during a time of political instability in Northern India, following the decline of the Mamluk dynasty. Jalal-ud-din Khilji, the founder, came to power after a successful coup against the last Mamluk ruler, and he established the Khilji rule, which would last for nearly two decades.
Key Figures
The most notable ruler of the Khilji dynasty was Alauddin Khilji, Jalal-ud-din’s nephew and successor. Alauddin is renowned for his ambitious military campaigns, including the conquest of Gujarat and the southern territories, which expanded the empire significantly. His reign is also marked by significant administrative reforms, including the introduction of a market regulation system to control prices and ensure the availability of essential goods.
The Khilji dynasty is significant for several reasons:
At the heart of the Khilji Dynasty was a visionary founder named Jalal-ud-din Khilji. He was a seasoned warrior who had big dreams for a better future. Born in 1256, he became the ruler in 1290 after overthrowing the previous rulers, known as the Slave Dynasty. Jalal-ud-din wasn’t just any ruler; he was the very first one from the Khilji Dynasty. He took over Delhi and became its Sultan, but he chose not to sit on the traditional throne. Instead, he ruled from a place called Kilokhari. One of the most important things he did during his time was to launch an expedition to Devgiri, a significant event that shaped his legacy of strong leadership.

Initially, the Khiljis were like the right-hand helpers to the Slave Dynasty rulers. But over time, they found ways to strengthen their position among the nobles of Delhi. Gayasuddin Balban dismantled the ‘Chalisa’ nobility group to solidify his control over the nobles. They gained a chance to strengthen their presence among Delhi’s nobility’. It allowed the Khiljis to establish their influence among the nobles. Then Jalal-ud-din Khilji came, who was initially given an important job by another Sultan. However, his power grew, leading to a big change known as the ‘Khilji Revolution.’
This revolution marked the end of the previous rulers’ time and the beginning of the Khilji Dynasty. This power shift was like a turning point that set the stage for the Khilji rulers that followed. While Jalal-ud-din aimed for stability and won the loyalty of his people, his successors faced their challenges.
The Khilji dynasty, established in Delhi in 1290 AD, produced two particularly noteworthy rulers:
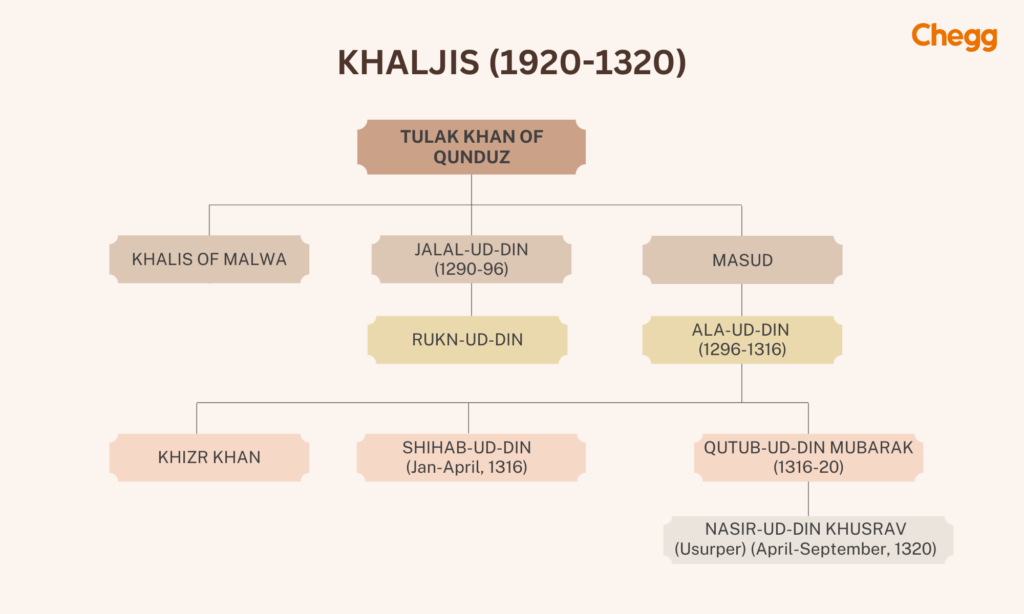
Ala-ud-din’s reign marked a period of power and prosperity for the Khilji dynasty. However, his successors lacked his ability, and the dynasty fell apart within a few years after his death.
| Name of Sultan | Tenure | Achievements/Important Facts |
|---|---|---|
| Jalaluddin Firuz Khilji | 1290-1296 | – Established the Khilji dynasty |
| – Suppressed Malik Chajju’s revolt | ||
| – Captured territories of Ranthambhore state under Hamir Deva | ||
| Alauddin Khilji | 1296-1316 | – Extended Delhi Sultanate to the extreme south |
| – Received monetary tribute from South Indian Kings | ||
| – Maintained a large and regular standing army | ||
| – Introduced market reforms and curbed black marketing | ||
| Shihabuddin Umar | 1316 | – Ascended to the throne at the age of 6 |
| – Real power held by Malik Kafur | ||
| Qutbuddin Mubarak Shah | 1316-1320 | – Last ruler of the Khilji Dynasty |
| – Assassinated by his military commander, Ghazi Malik |
The Khilji rulers embarked on ambitious military campaigns that expanded the empire’s reach. Alauddin Khilji’s campaigns against Mongols and southern kingdoms strengthened the Sultanate’s position and secured its borders. To ensure the protection of his empire, Alauddin Khilji maintained a robust and extensive standing army. Notable reforms include.
Alauddin Khilji introduced horse branding (dagh) and managed descriptive records of soldiers (Yuliya) to counter deceptive enrollments and misconduct. He abolished the Jagir system and implemented a system of cash salaries. The soldier gets paid 234 tankas annually, with an extra 78 tankas for those responsible for two horses. The selection process of soldiers was examined by the Ariz-i-Mumalik.
The Khilji Dynasty (1290–1320) was marked by significant military campaigns and territorial expansion, particularly under Alauddin Khilji, its most powerful ruler. Here’s an overview of their wars and conquests:
The Khilji Dynasty’s administrative structure and rule were marked by significant reforms and innovations that strengthened the Delhi Sultanate. Here’s an overview:
The Khilji Dynasty’s reign occurred during a dynamic period of Indian history. It followed the Slave Dynasty and preceded the Tughlaq Dynasty, contributing to the Sultanate’s evolution.
The Khilji Sultanate marked a transformative era in the history of the Delhi Sultanate, influencing its future development. The Khilji rulers’ contributions influenced subsequent dynasties and shaped the trajectory of the Delhi Sultanate’s growth. Their administrative practices and military strategies set benchmarks for governance and expansion. The Khilji empire was known for its administrative and economic reforms, which had a profound impact on the Delhi Sultanate.
The Khilji Sultans adhered to Sunni Islam, the dominant branch of Islam at the time. However, their approach to religious matters wasn’t entirely straightforward.
This seemingly contradictory situation reflects the complex social dynamics of the era. While the Khiljis favored Islam, they were also pragmatic rulers who recognized the value of a capable administration.
The Khilji Dynasty’s territorial expansion extended from North India to the Deccan. Their victory changed the political demography of subcontinental areas.
The dynasty’s dominion covered a vast expanse, demonstrating their military might and strategic vision in controlling diverse regions.

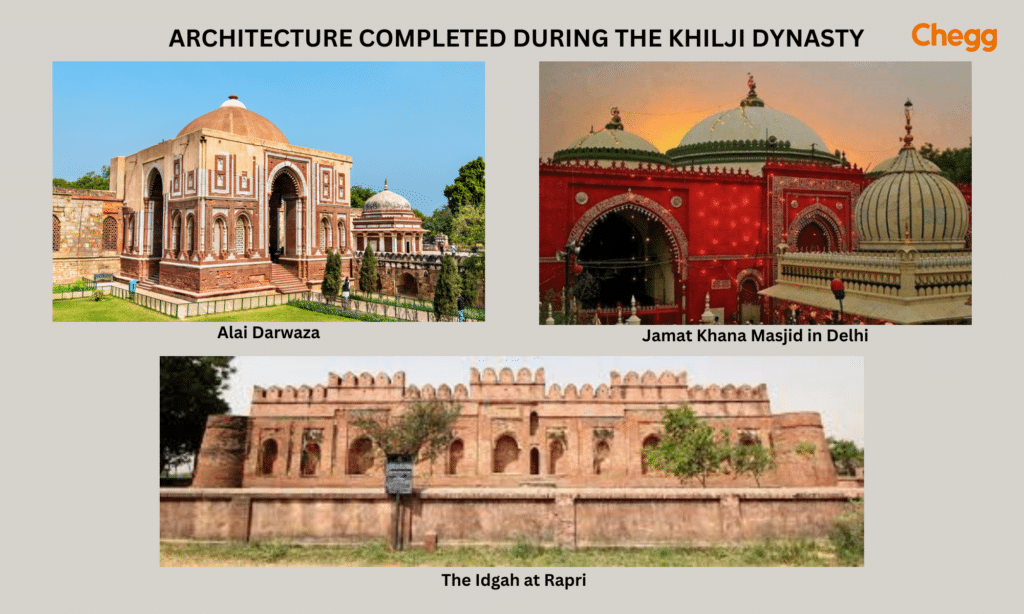
While primarily known for their military and administrative achievements, the Khilji Dynasty also made cultural contributions. The Alai Darwaza, an exquisite architectural gem, reflects their distinctive style and aesthetics.
The Alai Darwaza, situated within the Qutub Minar complex, showcases the dynasty’s architectural finesse. Its intricate carvings and ornate embellishments exemplify the fusion of Indo-Islamic styles that defined the era.
The Khilji Dynasty’s timeline is marked by key events such as Alauddin Khilji’s rise, expansion into the Deccan, and administrative reforms. These milestones illustrate their multifaceted impact on the Sultanate.
The Khilji Dynasty’s transition from one ruler to another shaped its trajectory. The reigns of different rulers underscored their unique contributions and challenges faced during their rule.
The Khilji rulers’ patronage of culture, arts, and literature enriched the Sultanate’s legacy. Their court attracted scholars, poets, and artists, fostering a vibrant cultural milieu.
The dynasty’s influence extended beyond politics and culture, impacting society as a whole. Their rule witnessed the intermingling of diverse cultures and traditions, contributing to social cohesion.
The death of Alauddin Khilji in 1316 AD marked a turning point for the Khilji dynasty. His reign of expansion and reform wasn’t matched by his successors, leading to a rapid decline within a few years.
Weak Leadership: The rulers who followed Alauddin lacked his political acumen and military prowess. Their incompetence created instability and internal conflicts, weakening the dynasty’s grip on power.
Ghazi Malik’s Rise: Capitalizing on this disarray, Ghazi Malik, a governor under the last Khilji sultan, Qutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah, seized power in a coup d’état. In 1320 AD, he assassinated Mubarak Shah and ascended the throne, taking the name Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq. This marked the end of the Khilji Dynasty and the beginning of the Tughlaq Dynasty.
The Khilji Dynasty concluded with Qutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah, who faced challenges to maintain the dynasty’s authority. His rule marked a period of decline and internal strife and following Mubarak Shah’s rule, the Khilji Dynasty witnessed fragmentation and external pressures. The dynasty’s legacy lived on through its architectural marvels and cultural contributions.
Thinking about the Khilji Dynasty gives us a peek into a time of battles, ideas, and complicated situations. They achieved so much, from spreading their rule to making their land stronger and supporting art and culture. Their legacy lives on through their beautiful buildings and the way they influenced the world around them.
A man named Jalal-ud-din Khilji began the Khilji Dynasty in 1290.
Alauddin Khilji was known for being a strong leader in battles, changing how things were run, and supporting art and culture.
Important Khilji Dynasty buildings include Alai Darwaza, the first true dome in India; Siri Fort, a fortified city; and Hauz-i-Alai, a grand reservoir.
The dynasty supported things like art, literature, and culture. They also changed how the land was used and how taxes were paid.
The Khilji Dynasty faced problems like fights over who should rule next, and it ended in 1320.
Alauddin Khilji’s demise in January 1316 remains shrouded in mystery, with speculation suggesting his slave general, Malik Kafur, might have been involved.
Yes, Alauddin Khilji defeated the Rajputs during the Siege of Chittorgarh in 1303, capturing the fort after an eight-month-long battle.
Also Read:-
Pallava Dynasty: Political Background, Territory, and Rulers
Chalukya Dynasty: Exploring Indian History, Architecture, and Facts
Lodi Dynasty: Exploring History, Rulers, and Delhi Sultanate
Razia Sultana (1236-1240): Delhi Sultanate
Ahom Dynasty: Exploring History, Capital, and the First King

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.