
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
The White Revolution in India, famously known as Operation Flood, stands as one of the most remarkable and transformative dairy development programs in the world. Launched in 1970 by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) under the leadership of Dr. Verghese Kurien, this revolution played a pivotal role in making India the largest producer of milk globally.
Before the White Revolution, India faced severe milk shortages, relying heavily on imports to meet domestic demand. However, through strategic initiatives such as enhanced milk production, rural dairy development, and the establishment of a nationwide milk grid, the revolution not only boosted dairy farming but also improved the livelihoods of millions of farmers.

The White Revolution in India launched in 1970, was a nationwide initiative to increase milk production, improve dairy farming practices, and make India self-sufficient in milk and milk products. This ambitious project was led by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and spearheaded by Dr. Verghese Kurien, also known as the “Father of the White Revolution.”
The term “White Revolution” signifies the large-scale production of milk and milk products, similar to how the Green Revolution referred to the massive increase in agricultural production. The color white represents milk, which was the focal point of this revolution.
Before the White Revolution, India faced a severe shortage of milk and milk products. The country relied heavily on imports to meet its dairy needs. Dairy farming was unorganized, and traditional methods led to low productivity. The per capita availability of milk was very low, and the quality of milk was often poor.
Operation Flood, the core program of the White Revolution in India, was launched in 1970 by the NDDB. It aimed to create a nationwide milk grid, linking milk producers with consumers across the country. The project was implemented in different phases of white revolution in India know as Operation Flood:

Dr. Verghese Kurien, known as the architect of the White Revolution in India, played a pivotal role in its success. He founded the NDDB and implemented innovative strategies to transform the dairy industry. His leadership and vision helped establish dairy cooperatives and improve milk production, benefiting millions of dairy farmers across the country.
Village milk producers’ cooperatives played a fundamental role in laying the foundation of Operation Flood, which was the driving force behind milk the White Revolution in India. These cooperatives brought together thousands of small-scale dairy farmers, enabling them to collectively produce, process, and distribute milk efficiently.
By adopting modern technology and scientific dairy management practices, these cooperatives improved milk collection, storage, and transportation, ensuring a steady supply to both rural and urban markets. The introduction of bulk milk chilling centers, advanced breeding techniques, and veterinary services further enhanced productivity and quality.
The White Revolution had the following objectives:
When Operation Flood started, Dr. Verghese Kurien was the chairman of the National Dairy Development Board. With his great management skills, Dr. Kurien pushed the cooperatives to succeed in the revolution. He is known as the architect of India’s ‘White Revolution.’
Many big corporations helped transform Operation Flood into the White Revolution. AMUL – Anand Milk Union Limited, a cooperative based in Gujarat, was the main force behind the success of the Operation Flood Programme.

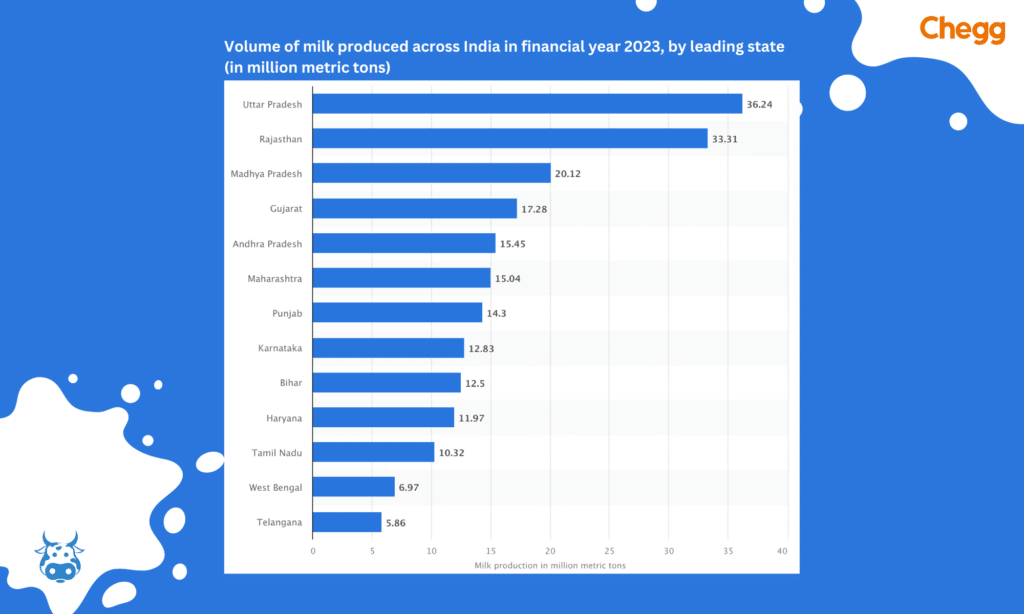
One of the most significant achievements of the White Revolution in India was the dramatic increase in milk production. From a mere 22 million metric tons in 1970, India’s milk production surged to over 132 million metric tons by 2014. Today, India is the world’s largest milk producer, with an annual production of over 200 million metric tons.
The White Revolution in India had a profound impact on the rural economy. It provided a stable source of income for millions of dairy farmers, many of whom were small-scale producers. The establishment of dairy cooperatives ensured fair milk prices, eliminating the exploitation by middlemen. This revolution uplifted the socio-economic status of rural communities and reduced poverty.
The White Revolution introduced modern dairy farming techniques and infrastructure, improving milk quality and productivity. Innovations such as artificial insemination, cross-breeding, and veterinary care enhanced the health and yield of dairy cattle. The establishment of milk processing plants ensured the production of high-quality milk and milk products.
The White Revolution in India played a crucial role in empowering women, especially in rural areas. Women were actively involved in dairy farming and became members of dairy cooperatives. This participation provided them with economic independence and a sense of empowerment.
Initially, the low productivity of dairy cattle was a significant challenge. The introduction of cross-breeding programs and improved veterinary care helped enhance the genetic quality and health of cattle, leading to higher milk yields.
The lack of infrastructure, such as chilling centers and transportation facilities, was a major hurdle. Operation Flood invested in the development of necessary infrastructure, ensuring efficient collection, storage, and distribution of milk.
A major challenge in the success of milk the White Revolution was the lack of knowledge and skills among dairy farmers, which hindered their ability to adopt modern dairy farming techniques. Many farmers relied on traditional methods that resulted in low milk yield, poor cattle health, and inefficient dairy management.
To address this issue, the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) took proactive measures by organizing extensive training programs and workshops across the country. These initiatives aimed to educate farmers on scientific cattle breeding, proper nutrition, disease prevention, hygienic milking practices, and efficient milk storage and transportation.
The NDDB played a central role in implementing the White Revolution in India. It provided technical and financial support to dairy cooperatives, facilitated infrastructure development, and promoted dairy farming practices.
Amul Dairy, based in Gujarat, is one of the most successful examples of the White Revolution in India. Founded by Dr. Verghese Kurien (the pioneer of the white revolution in India), Amul became a model for dairy cooperatives nationwide. Its success inspired the creation of similar cooperatives across the country.
The White Revolution received support from international organizations such as the World Bank and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). These organizations provided funding and technical assistance, contributing to the success of Operation Flood.
The White Revolution in India successfully fulfilled its primary objective of making the country self-sufficient in milk production, drastically reducing its dependence on imports. Before the revolution, India struggled with milk shortages, but through strategic initiatives like Operation Flood, the nation transformed into the world’s largest producer of milk.
Today, India not only meets its domestic dairy demands but has also emerged as a key player in the global dairy market. The country exports a wide range of milk and milk-based products, including skimmed milk powder, butter, ghee, and cheese, to several countries.
The establishment of dairy cooperatives and the promotion of modern farming practices ensured the sustainability of dairy development. The White Revolution created a robust dairy industry that continues to thrive and grow.
The success of the White Revolution in India serves as an inspiration for future agricultural and rural development initiatives. It demonstrates the power of collective efforts, innovation, and visionary leadership in transforming a sector.
The White Revolution was a transformative initiative in India’s agricultural history, revolutionizing the dairy industry and significantly impacting both the national economy and rural livelihoods. By increasing milk production, strengthening dairy cooperatives, and reducing dependence on imports, it played a crucial role in making India the largest milk producer in the world.
However, like any large-scale initiative, it came with both advantages and disadvantages. While it boosted rural employment, improved nutrition, and strengthened the economy, it also led to challenges such as over-reliance on crossbred cattle, environmental concerns, and unequal benefits for small-scale farmers.
The White Revolution brought many positive changes, but addressing its challenges and ensuring the dairy sector’s sustainability is important for India’s future.
The White Revolution, also known as Operation Flood, was a transformative initiative that catapulted India from a milk-deficient nation to the world’s largest milk producer. Spearheaded by Dr. Verghese Kurien, it stands as a testament to cooperative federalism and rural development.
Understanding the White Revolution is essential for UPSC aspirants, as it holds multifaceted significance in various aspects of Indian history, economy, agriculture, and rural development. It played a transformative role in making India self-sufficient in milk production, reducing import dependency, and boosting the livelihoods of millions of dairy farmers.
By understanding these key points about “What is White Revolution in India” and practicing with relevant questions, you can effectively address White Revolution-related queries in the UPSC exam.
Click here to get the: White Revolution Short Note
The White Revolution in India, also known as Operation Flood, is a landmark achievement in the country’s history. It transformed India from a milk-deficient nation into the world’s largest milk producer, benefiting millions of dairy farmers and improving the rural economy. Led by visionary leaders like Dr. Verghese Kurien, the White Revolution introduced modern dairy farming practices, enhanced milk production, and empowered rural communities.
By understanding the significance of the White Revolution, students can gain valuable insights into the importance of agricultural development, rural empowerment, and the role of innovation in transforming lives. This revolution not only made India self-sufficient in milk production but also uplifted millions of dairy farmers by providing them with better income opportunities and access to modern technology.
The White Revolution in India stands as a remarkable example of how strategic planning, scientific advancements, and collective efforts can drive a nation toward economic self-reliance and food security. It highlights the power of cooperative movements, technological progress, and visionary leadership, demonstrating that dedication and innovation can lead to extraordinary achievements in national development.
Click here to get: White Revolution in India PDF.
The village of Anand, Gujarat, is known for the White Revolution in India.
The White Revolution, also known as Operation Flood, was a large-scale dairy development program initiated in India during the 1970s. Its primary goal was to make India self-sufficient in milk production and to improve the livelihoods of dairy farmers.
The White Revolution started by Dr. Verghese Kurien is widely recognized as the “Father of the White Revolution” in India.
The main goal of the White Revolution was to make India a self-dependent country when it came to milk production. The revolution put efforts to increase milk production in the country and made cooperative efforts to distribute it among the consumers.
The Green Revolution focused on increasing crop production (wheat & rice).
The White Revolution focused on increasing milk production (Operation Flood).
The father of the Green Revolution is Dr. M.S. Swaminathan.
The father of the White Revolution is Dr. Verghese Kurien.
Operation Flood was started in 1970.
Dr. Verghese Kurien is also known as the “Milkman of India” for his pivotal role in transforming India’s dairy industry.
The White Revolution is a crucial topic for UPSC aspirants due to its significance in agriculture, rural development, the economy, and government policies. Understanding the concept, its impact, and the challenges faced by the dairy sector is essential for answering UPSC questions related to these areas.
The White Revolution was started by Dr. Verghese Kurien.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.