

Quick Summary
Chartered Accountancy in India: CA professionals manage financial reporting, auditing, taxation, and compliance, regulated by ICAI with a structured path involving exams and articleship.
CA Roles: CAs handle financial accounting, tax planning, audits, and corporate governance, ensuring transparency and providing strategic advisory.
Career and Challenges: CAs have diverse career opportunities across sectors, with competitive salaries. Challenges include adapting to technological changes, global regulations, and emerging specializations.
In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of the CA profession in India and answer questions like: What is CA? How can I become a Chartered Accountant in India? What are CAs’ roles and responsibilities? What is the importance of practical training and articles? And how do they contribute to economic development and nation-building?
The CA profession in India has a rich history that dates back to 1949 when an Act of Parliament established the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI). Since its inception, the profession has continuously evolved to meet the changing demands of the business world. The ICAI, entrusted with regulating and nurturing the CA profession, has played a pivotal role in ensuring its growth and relevance in the fast-paced financial landscape. Understanding how to become a Chartered Accountant in India is essential for those looking to enter this prestigious field.

The answer to the question What is a CA simple yet challenging to explain. The CA profession in India holds immense significance in the country’s economic landscape. Chartered Accountants act as financial guardians, offering their expertise to individuals, businesses, and the government. They are instrumental in promoting transparency, maintaining financial integrity, and fostering investor confidence. Moreover, CA professionals are critical in tax planning, auditing, and financial reporting, crucial for sustaining a robust and stable economy. Understanding how to become a CA in India is essential for those interested in this vital role.
Becoming a Chartered Accountant requires dedication, hard work, and a clear understanding of the steps involved. Here’s a breakdown of the process to become a CA in India:
The first step to becoming a CA is ensuring you meet the educational eligibility criteria of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI).
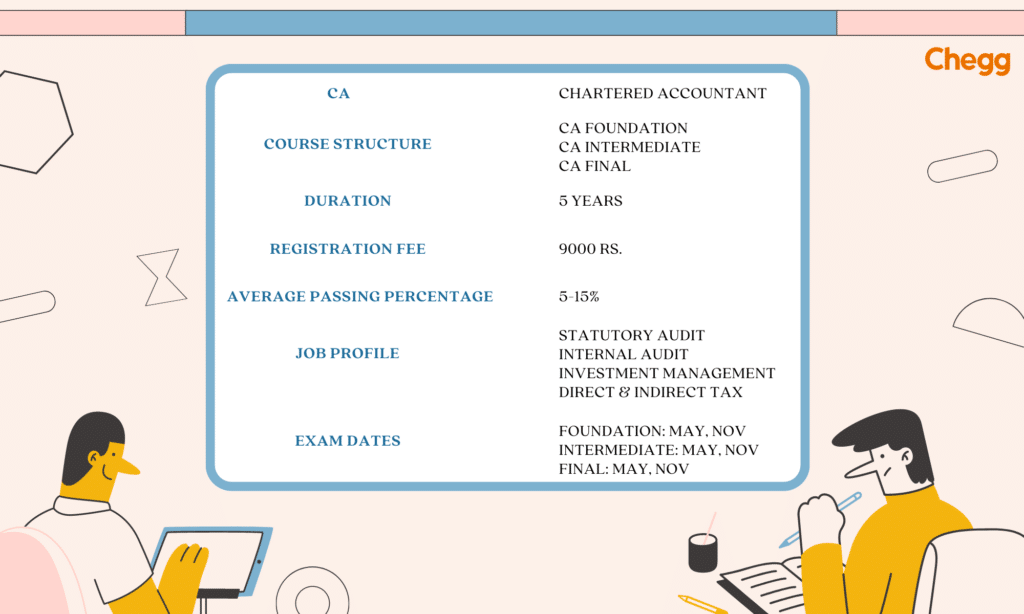
The next step is to register for the CA Foundation course. This preparatory course teaches the basics of accounting, business law, economics, and quantitative techniques.
You can attempt the CA Foundation exams in May or November every year.
Once you have cleared the CA Foundation exam or have a degree that qualifies you for direct entry into the Intermediate level, the next step is to register for the CA Intermediate course.
The CA Intermediate exams are held twice yearly (in May and November).
After clearing the CA Intermediate exams, the next step is to undergo articleship training. This mandatory practical training period of 3 years allows you to work under a practicing CA in an office or firm. The training provides hands-on experience in auditing, taxation, accounting, and other core areas of the profession.
After completing your articleship, you can appear for the CA Final Examination. This is the last step before you officially become a Chartered Accountant.
After clearing the CA Final exams, you will officially be eligible to be a member of ICAI, and you can begin your career as a Chartered Accountant.

The CA course is designed to provide comprehensive knowledge and practical training to aspiring Chartered Accountants. The duration typically ranges from three to five years, depending on the candidate’s progression and pace. The curriculum covers accounting, auditing, taxation, financial management, corporate law, and ethics, equipping candidates with a holistic understanding of the financial domain. Understanding how to become a CA in India involves navigating this curriculum and gaining the necessary skills for success in the profession.
One of the defining aspects of the CA course is the mandatory practical training, known as articles.
This training period lasts for a specified duration, allowing candidates to gain hands-on experience in diverse accounting, auditing, and taxation areas. Articleship provides invaluable exposure to real-world scenarios, enhances professional skills, and prepares individuals for the challenges they will face as Chartered Accountants.
As experts in financial accounting, Chartered Accountants play a crucial role in maintaining accurate and transparent financial records for businesses and organizations. Their responsibilities include:
Chartered Accountants are responsible for preparing financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Maintaining records and keeping track of financial statement receipts are usually CA requirements. These statements provide a snapshot of an organization’s financial health and performance.
CAs ensure that financial statements adhere to the relevant accounting standards and regulatory requirements, ensuring transparency and consistency in reporting.
Chartered Accountants analyze financial data, identify trends, and provide insights into an organization’s economic performance. This analysis aids decision-making processes and helps stakeholders understand the financial implications of various strategies.
Auditing is a critical function performed by Chartered Accountants to assess the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. Their responsibilities in this area include:
CAs conduct audits by applicable laws and regulations to ensure compliance and provide an independent opinion on the fairness and accuracy of financial statements.
Chartered Accountants perform internal audits to evaluate an organization’s internal control systems, risk management processes, and compliance with policies and procedures.
CAs ensure financial information, internal controls, and other aspects of an organization’s operations to enhance stakeholders’ confidence and credibility.
Taxation and planning are usually CA’s daily tasks. Chartered Accountants are well-versed in tax laws and regulations, making them essential for effective tax planning and compliance. Their responsibilities in this domain include:
CAs help individuals and businesses optimize their tax liabilities through effective tax planning strategies, taking advantage of tax incentives, exemptions, and deductions.
Chartered Accountants ensure that individuals and organizations comply with tax laws, file accurate tax returns, and meet their tax obligations within the prescribed deadlines.
CAs provide guidance on complex tax matters, assist in tax dispute resolutions, and help clients navigate the ever-changing tax landscape.
Chartered Accountants possess a deep understanding of financial management principles and provide valuable advisory services to organizations, including:
CAs assist in developing financial strategies, budgeting, forecasting, and economic modeling to optimize resource allocation and support business growth.
Chartered Accountants analyze investment opportunities, evaluate risks, and provide advice on investment decisions to maximize returns and mitigate financial risks.
CAs help organizations analyze and manage costs, identify areas of inefficiency, and implement cost-saving measures to improve profitability.
Chartered Accountants are crucial in promoting corporate governance and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Their responsibilities include:
Corporate governance: CAs help establish robust governance frameworks, ethical practices, and internal control mechanisms to enhance transparency, accountability, and stakeholder confidence.
Compliance and regulatory reporting: Chartered Accountants ensure that organizations comply with company laws, corporate governance norms, and regulatory reporting requirements, avoiding legal and financial penalties.
The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is the regulatory body and professional institute responsible for the Chartered Accountancy profession in India. With over 3.75 lakh members and over 7.80 lakh students, ICAI is the world’s second-largest accounting body. It was established under an Act of Parliament and is the authoritative body for CA education, training, examination, and professional standards.
The ICAI has several key functions and responsibilities, including:
Chartered Accountants are bound by a strict Code of Ethics established by the ICAI. The code outlines the fundamental principles of integrity, objectivity, confidentiality, and professional behavior that CAs must uphold in their practice. It provides guidelines for ethical conduct in areas such as independence, professional competence, and client confidentiality.
The ICAI mandates continuing professional development (CPD) requirements to ensure the ongoing professional development of Chartered Accountants. CAs must engage in lifelong learning and regularly update their knowledge and skills. They must participate in training programs, seminars, workshops, and other learning activities to stay abreast of developments in accounting standards, laws, and industry practices. For those considering how to become a Chartered Accountant in India, understanding the importance of CPD is essential for a successful and sustainable career in this profession.
Suggested Read:
Navigating Your Next Move: What to Do After CA?
Salary of a Chartered Accountant in India
|
Challenges and Trends |
Description |
|
Technological advancements | Rapid technological changes, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, impact the profession. CAs need to embrace these advancements and develop new skills to stay relevant. |
|
Globalization and cross-border regulations | With business globalizing, CAs face challenges in understanding and complying with international accounting standards, cross-border transactions, and complex taxation laws. |
|
Changing regulatory landscape |
Regulatory frameworks are constantly evolving, requiring CAs to stay updated on changes in laws, regulations, and reporting standards. Compliance requirements are becoming more stringent, necessitating thorough knowledge and adherence to ensure ethical practices. |
|
Emerging areas of specialization | The CA profession is expanding into specialized areas such as forensic accounting, sustainability reporting, risk management, and data analytics. To meet evolving client demands, CAs must acquire new expertise and adapt to these emerging fields. |
In conclusion, Chartered Accountancy is an ever-evolving profession that offers a rewarding career path for those with a passion for numbers, a commitment to integrity, and a desire to impact the financial world significantly. As we move forward, the role of Chartered Accountants will continue to be instrumental in driving economic progress and building a secure future for businesses and individuals alike. For those interested in pursuing this fulfilling career, understanding how to become a Chartered Accountant in India is crucial to achieving success in this dynamic field.
As a chartered accountant, you will offer guidance, audit financial records, and disseminate reliable information. This might entail accounting systems and procedures, taxation, auditing, financial reporting, forensic accounting, corporate finance, company recovery, or bankruptcy. Chartered accountants deal with economic planning, finance, capital formation, management accounting, and all taxation procedures. For those interested in pursuing this career, understanding how to become a chartered accountant in India is essential to effectively navigate these diverse responsibilities.
Candidates who get placed in the top recruiting firms get astounding salary packages. The salary package of a CA ranges from INR 2 lakhs per annum to INR 14 lakhs per annum. However, the average salary of a CA is around INR 8.19 lakhs per annum.
According to the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), the 7 subjects in the CA course syllabus are:
1. Business & Accounting Law
2. Auditing and Assurance
3. Direct & Indirect Tax
4. Ethics and Communication
5. Advanced Accounting
6. Cost Accounting
7. Financial Management
Understanding these subjects is crucial for those learning how to become a Chartered Accountant in India, as they form the foundation of the profession.
The Chartered Accountancy program is one of the most reasonable certificate programs compared to other courses. The course offers students a rewarding career with exciting salary packages. The approximate cost of chartered accountancy, including course fees and all other expenses, is within INR 3 lakhs. They cover the estimated price of tuition, enrolment fees, and textbooks. For those interested in this path, understanding how to become a Chartered Accountant in India is essential, as it includes navigating the financial aspects of the course.
The Chartered Accountancy course is highly oriented towards accounting and financial planning. However, students who wish to pursue higher studies can consider the following courses after CA.
1. DISA (Diploma in Information System Audit)
2. ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants)
3. CISA (Certified Information System Auditor)
4. CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst)
5. CIA (Certified Internal Auditor)

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.