

Quick Summary
Economics is a branch of knowledge that examines a nation’s financial structure and the various factors that influence it. As a social science, it studies how societies produce, consume, and distribute goods and services. Broadly, economics is divided into two major branches: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Adam Smith (1723–1790), widely regarded as the “Father of Economics”, laid the foundation for understanding these concepts through his pioneering work The Wealth of Nations. Later, Alfred Marshall refined Microeconomics, making it a cornerstone of modern economic theory.
From a student and career perspective, understanding these two areas is crucial. For instance, Anjali, an Economics graduate from Delhi University, shared that studying Microeconomics helped her land a role as a Market Research Analyst, where she applies concepts of demand and supply daily to advise clients. Similarly, Rohit, who pursued a Master’s in Economics, found Macroeconomics invaluable for his role in a policy think tank, analyzing India’s GDP growth and unemployment trends.

| Basis | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
| Meaning | Microeconomics is the study of individual units of the economy of a nation. | Macroeconomics studies the aggregate variables of the economy of a nation. |
| Area of Study | The area of study of Microeconomics includes the particular market segment of an economy. | Microeconomics deals with multiple issues such as Demand and Supply, Product pricing, Factor pricing, Production, Consumption, Economic welfare |
| Deals with | Macroeconomics deals with several issues such as National Income, Employment Distribution, General price level. | Macroeconomics deals with several issues such as National Income, Employment Distribution, and General price level. |
| Area of Application | Applied to internal issues. | Applied to external and environmental issues. |
| Concept | Narrow | Wide |
| Scope | Theory of product pricing, Theory of factor pricing, Theory of economic welfare | Theory of economic growth and development, Theory of money, Theory of national income, Theory of international trade, Theory of employment, Theory of general price level |
| Importance | Helps in the determination of prices of products or commodities, along with the pricing of factors of production in an economy. | Helps in dealing with critical issues like inflation, deflation, reflation, unemployment, and poverty in an economy as a whole. |
| Limitations | The study is based on presuppositions. | The study incorporates the misconception of composition. |
Before heading towards the difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics, let us first understand each branch of economics separately.
Microeconomics is the study of the Microelements of the economy. These Microelements can be a single individual, a household, or a business firm. The way these elements maintain their economy, that is, allocate their scarce resources and their interaction with other elements is studied under Microeconomics.
Microeconomics generally analyses the market and determines the prices of goods and services. It studies how individuals or firms allocate their resources, and how it affects the utilization and distribution of their resources.
Macroeconomics is a study of the macro elements in economics. It is the aggregate study of the economy of a nation. Macroeconomics deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of the entire economy as a whole.
It analyses the markets, businesses, industries, and governments on an overall basis. The government policies and the factors influencing the economy of a nation are covered under the scope of Macroeconomics.

Microeconomics and Macroeconomics are two distinct branches of economics. While microeconomics focuses on the economic behaviour of individuals and firms in the market, macroeconomics examines the overall performance of the economy as a whole. Both microeconomics and macroeconomics are closely related and constantly interact with each other, making them essential for understanding how economies function at both the individual and aggregate levels.
In microeconomics and macroeconomics, the behaviour of individual consumers and firms is studied to determine how they interact in the market to produce and allocate resources. This economic behaviour, analyzed in microeconomics and macroeconomics, is then used to understand the overall performance of the economy. For example, the demand and supply of a certain good can be studied in microeconomics and macroeconomics to see how it affects both individual market prices and the overall price level of the economy.
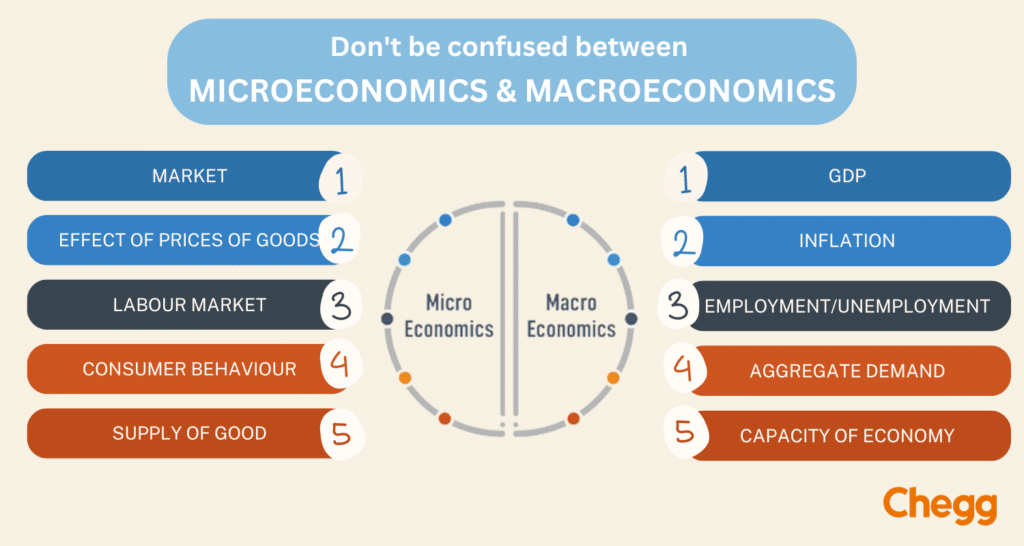
On the other hand, Macroeconomics focuses on the aggregate economic performance of a nation. It examines the factors that affect the overall economic performance such as GDP, inflation, unemployment, and trade balance. It also studies the effect of fiscal and monetary policies on the economy.
The two branches of economics interact with each other. Microeconomic decisions of households and firms affect the Macroeconomic performance of the economy. For example, the decisions of households to consume or save can affect the overall level of economic growth. Similarly, the decisions of firms to invest or not can affect the overall level of investment in an economy.
Both microeconomics and macroeconomics are vital for understanding how economies work at individual and aggregate levels.
Together, microeconomics and macroeconomics provide a complete picture of economic functioning and decision-making.
Microeconomics mainly studies:
Macroeconomics focuses on:
The differences between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics can also be understood by looking at the constraints and challenges each branch faces in practical application.
Economics is indeed a promising career option as the knowledge imparted in this field contributes greatly to a nation’s microeconomics and macroeconomics models. Microeconomics focuses on individual markets, while macroeconomics focuses on whole economies. The main difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics lies in the scale of their study.
Microeconomics studies the behaviour of individual households and firms in making decisions on the allocation of limited resources. Another way to phrase this is to say that microeconomics is the study of markets, demand, supply, and how prices are determined.
On the other hand, macroeconomics is generally focused on countrywide or global economics. Its studies involve total economic activity, dealing with aspects such as national growth, inflation, unemployment, and monetary or fiscal policies. Thus, macroeconomics provides a big-picture view of how economies function at a broader level.
In this article, we have discussed the key differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics. The primary comparison has been made above to help you gain a clear understanding of both branches of economics. As you study these subjects in greater depth, there will be a lot more to analyze and compare.
Both fields are interconnected—microeconomic decisions at the household or firm level shape the broader macroeconomic environment, while macroeconomic policies directly influence individual markets. A balanced understanding of both is essential for students aiming to build a strong foundation in economics and pursue careers in business, finance, or policy-making.
Microeconomics and macroeconomics offer diverse career paths across various industries. While microeconomics focuses on individual businesses and consumer behavior, macroeconomics deals with broader economic factors like national income, inflation, and fiscal policies.
Both fields offer excellent career prospects in government agencies, financial institutions, multinational corporations, and research organizations.
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics are two pillars of economics that together explain how individuals, businesses, and entire nations make choices about resources, production, and growth. While microeconomics zooms in on specific markets and decision-making at the individual or firm level, macroeconomics takes a broader view, analyzing national income, unemployment, inflation, and overall economic stability. Understanding both perspectives provides a complete picture of how economies function, from the smallest household decision to the policies shaping a nation’s future.
For students and professionals, learning these two branches not only builds a strong academic foundation but also opens diverse career opportunities in business, finance, research, and policymaking. Whether you aim to become a financial analyst studying market trends or a policy advisor shaping government decisions, economics offers a pathway to impactful and rewarding roles. By mastering both micro and macroeconomics, learners can better navigate real-world challenges and contribute meaningfully to society’s economic progress.
Microeconomics studies topics such as supply and demand, cost and production, pricing, market structures, and consumer behaviour.
Macroeconomics looks at national and international economic trends such as unemployment, inflation, economic growth, and monetary and fiscal policy.
Microeconomics focuses on the small details, like how people spend their money or how companies decide on prices. It’s about individual choices and specific markets.
Macroeconomics looks at the big picture, like how the entire economy is doing, what causes prices to rise, or how many people have jobs. It’s about understanding the economy of a whole country or even the world.
Limitations of Microeconomics – Assumes people always make logical choices, Ignore other changing factors, Focus only on small parts of the economy, and Often don’t consider changes over time.
Limitations of Macroeconomics – Looks at the big picture, missing details, Hard to predict due to many influencing factors, Policies can have unexpected results, Good data can be hard to find.
Significance of Microeconomics – Understands how people and businesses decide what to buy and sell, explains how prices are set by supply and demand, shows how people maximize satisfaction, helps companies price products and manage costs.
Significance of Macroeconomics – Guides tax and spending decisions, analyzes growth and inflation, aims to control inflation and reduce unemployment, and understands interactions between countries’ economies.
Adam Smith is often regarded as the father of economics as a whole, but Alfred Marshall is specifically considered the father of Microeconomics. His book Principles of Economics (1890) introduced key concepts such as supply and demand, consumer surplus, and elasticity, which form the foundation of modern microeconomic theory.

Authored by, Gagandeep Khokhar
Career Guidance Expert
Gagandeep is a content writer and strategist focused on creating high-performing, SEO-driven content that bridges the gap between learners and institutions. He crafts compelling narratives across blogs, landing pages, and email campaigns to drive engagement and build trust.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.