

Quick Summary
Data is at the core of everything today, enabling businesses to make smarter decisions, boost performance, and drive innovation. From e-commerce and healthcare to finance and entertainment, companies increasingly rely on data analysis to stay competitive. With organizations generating vast amounts of data daily, the demand for skilled data analysts continues to rise across various industries.
If you have a passion for working with numbers, identifying patterns, and transforming raw data into meaningful insights, a career as a data analyst could be an ideal choice. This field combines problem-solving with technology, offering countless opportunities to make a significant impact.
This guide is here to help you navigate your journey into data analytics and teach you how to become a data analyst. We’ll break down the essential skills, education, experience, and certifications you need to build a successful career in this fast-growing industry. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your expertise, this step-by-step roadmap will provide the clarity and direction necessary to thrive in the field.
Over the past decade, data analytics has completely changed how businesses operate. Whether a small startup or a global corporation, companies now rely on data to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and stay ahead in a competitive market. By analyzing large amounts of information, businesses can spot trends, anticipate customer needs, and make smarter decisions that drive growth.
Turning raw data into meaningful insights isn’t just a technical process—it’s the key to business success. Companies use data to track financial performance, fine-tune marketing strategies, and enhance customer experiences. By understanding buying patterns and market trends, businesses can predict demand, minimize risks, and increase profits. Data-driven decisions also help allocate resources more effectively, ensuring smoother operations and better results.
As industries evolve in a data-driven landscape, understanding, interpreting, and using data effectively has become a significant competitive edge. Companies that embrace data analytics stay ahead of the curve and unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth.
In today’s digital world, businesses generate more data than ever before. But numbers alone don’t mean much unless they’re analyzed, structured, and turned into clear insights. Professionals who can make sense of complex datasets and transform them into real business strategies are in high demand. Whether forecasting future trends, tracking real-time performance, or optimizing business processes, leveraging data correctly helps companies make smarter choices that lead to long-term success.
This guide provides a clear and actionable roadmap for becoming a data analyst. Whether you’re a high school student exploring career options, a college graduate looking to switch careers, or someone seeking to upskill, this guide will walk you through the necessary steps to embark on your journey to becoming a data analyst.

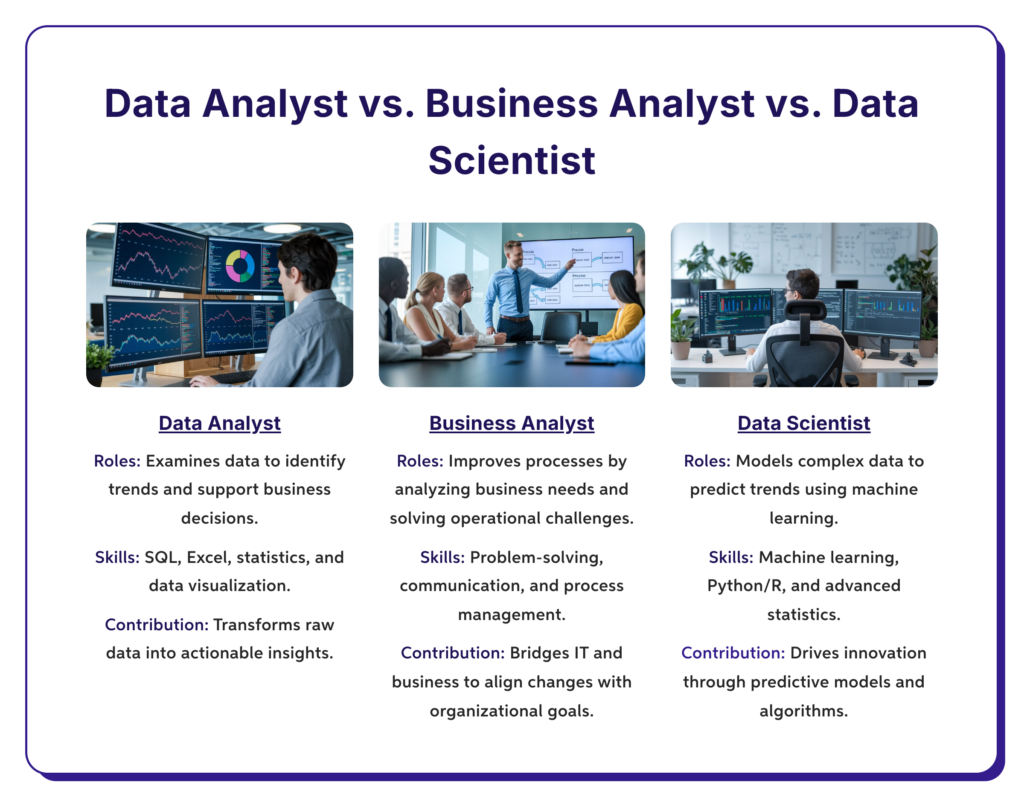
Data analysts are today’s most important assets. Businesses are increasingly operating on insights culled from data to make solid decisions. As a data analyst, one deals with turning unprocessed data into meaningful information so that organizations can improve efficiency, profit maximization, and competitiveness. Let us enumerate the fundamental work of a data analyst and the industries in which these personnel are most demanded.
Collecting and cleaning data is a data analyst’s earliest and most fundamental duty. Data is derived from various sources, and each source will likely have issues, such as missing, erroneous, or inconsistent data. Whether the data is drawn from company databases, web-based surveys, or extracted using web scraping methods, the analyst must clean it before any practical analysis can occur.
This step, commonly called data wrangling or data preprocessing, is essential because the quality of the insights drawn from the data depends directly on its integrity. Data cleaning eliminates duplicates, corrects formatting errors, replaces missing values, and resolves inconsistencies or outliers. Even the most excellent analysis can result in false conclusions without cleaning, so this is an essential initial step in the process.
After cleaning and structuring data, analysis is the next step. This is where the data analyst applies their skill to reveal patterns, trends, and insights that can guide business decisions. Analysis techniques depend on the nature of the data and business requirements.
For instance, a data analyst may utilize statistical techniques for hypothesis testing or regression analysis to ascertain relationships between varying variables. A data analyst would also use correlation analysis to determine how some factors, like customer age or location, relate to purchase behavior. It is about taking raw data and making actionable insights with helpful business intelligence.
After analysis comes communicating the findings clearly and understandably; data, especially when complex, can be difficult for non-technical stakeholders to interpret. That’s where that visualization comes in.
Data analysts use tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Excel to create charts, graphs, and dashboards presenting visually appealing insights. These visualizations can represent trends, patterns, or key performance indicators (KPIs) and help decision-makers quickly grasp the meaning behind the numbers.
Compelling visualizations allow businesses to spot opportunities, risks, and trends in seconds. For example, a data analyst working for a retail company might create a dashboard showing daily sales, stock levels, and customer traffic, allowing management to make quick decisions about promotions or inventory restocking.
With data becoming integral to business success, the demand for skilled data analysts continues to rise across industries.
High School Preparation: If you’re still in school and interested in becoming a data analyst, focus on developing a strong foundation in mathematics, computer science, and statistics. These subjects will set you up for success in more advanced data analysis courses later on. Consider participating in related extracurricular activities or coding clubs to strengthen your technical skills.
Undergraduate Degrees: Obtaining a relevant undergraduate degree is essential to pursue a career as a data analyst. Common degrees include:
You will likely take courses in data structures, probability, statistical methods, database management, and machine learning during your degree. These courses will equip you with the technical knowledge and analytical skills required for data analysis.
Postgraduate Education: A master’s in data science, analytics, or a related field can help you specialize and advance in your career. Postgraduate education offers more profound insights into machine learning, big data analytics, and data modeling, allowing you to pursue high-level positions such as a data science manager or senior data analyst.
Alternative Learning Options: If formal academic paths are not possible, numerous online data analyst courses, boot camps, and certifications can speed up your learning. Sites such as Coursera, Udemy, and edX provide specialized courses in data analysis tools, including SQL, Python, Tableau, and Power BI. These courses enable you to learn skills fast and frequently include hands-on projects to enhance your portfolio.
1. Programming Languages
Should be proficient in programming languages like Python, R, and SQL. These languages are essential for manipulating data, performing statistical analysis, and querying databases.
2. Data Visualization Tools
Familiarity with tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel is crucial for creating impactful data visualizations that stakeholders can easily understand.
3. Data Management Tools
Knowing how to manipulate and query large data sets is an important skill. SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL are examples of tools employed to extract and manipulate data from databases.
4. Analytical and Statistical Skills
You must understand probability, regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and other statistical techniques to analyze and interpret data. These skills allow you to detect trends, forecast future results, and solve business issues.
Data analysts must effectively communicate complex insights to non-technical stakeholders. This involves simplifying technical data, using visualizations like charts and graphs, and presenting findings through clear reports or presentations. Strong communication ensures that decision-makers understand and act on the insights.
6. Attention to Detail
Analyzing large datasets requires precision; even minor errors can lead to incorrect conclusions. To maintain accuracy, a data analyst must be meticulous in data cleaning, analysis, and reporting. Double-checking calculations, identifying inconsistencies, and validating results are essential for reliable decision-making.
7. Problem-Solving
Data analysts tackle business challenges by analyzing data for solutions. The process involves:
Strong problem-solving skills help analysts interpret data effectively and drive impactful business solutions.
Certifications
Certifications help boost your credibility and make you more competitive in the job market. Some applicable certifications include:
These certifications show potential employers that you have the skills necessary to excel in the data analyst role.
Why Certifications Matter
Certifications validate your skills, enhance credibility, and make you stand out in the competitive job market. They provide hands-on experience in SQL, Python, Tableau, and Excel tools. Industry-recognized certifications from Google, IBM, or Microsoft boost career prospects, helping you land high-paying data analyst roles faster.
The demand for data analyst’s in India is robust and continues to grow across various industries. As of March 2025, job portals such as Indeed and Glassdoor list over 6,000 data analytics job openings nationwide.
1. Current Job Openings:
2. Notable Hiring Trends:
Several multinational companies are expanding their operations in India, contributing to the increasing demand for data analysts:
3. Job Search Platforms:
To explore data analyst opportunities in India, consider visiting the following job portals:
A career in data analytics offers a dynamic and rewarding path with plenty of growth opportunities. As you gain experience and refine your skills, you can advance to higher roles, take on leadership positions, or specialize in a niche area that aligns with your interests.
You might want to specialize in areas that align with your passion and strengths as you grow. Here are some options:
Online Data Entry Jobs without Registration
10 Best Data Science Institutes in India in 2024
A data analyst career is full of challenging opportunities in the finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and marketing sectors. With businesses making decisions based on data, the need for talented analysts is increasing. A solid mathematical, computer science, or data science background and proficiency in programming, visualization tools, and statistical analysis are necessary. Practical experience and certifications enhance credibility. With problem-solving abilities and ongoing learning, you can excel in this fast-paced field.
To become a data analyst in India, a bachelor’s degree in mathematics, statistics, computer science, or data science is preferred. Proficiency in SQL, Python, Excel, and data visualization tools is essential. Certifications and hands-on experience through internships boost career prospects.
Yes, data analysts in India earn competitive salaries. Entry-level analysts earn ₹4-6 LPA, while experienced professionals can make ₹10-20 LPA or more. Salaries vary by industry, skills, and location, with top companies offering higher pay for specialized expertise.
The best courses for data analysts include Google Data Analytics (Coursera), IBM Data Analyst (Coursera), Data Analyst Nanodegree (Udacity), and Harvard Data Science (edX). These cover SQL, Python, Excel, statistics, and visualization, essential for a successful data analytics career.
A bachelor’s degree in mathematics, statistics, computer science, data science, economics, or engineering is preferred to become a data analyst. However, relevant certifications and practical experience in SQL, Python, Excel, and data visualization can also help you enter the field.
The best branches for a data analyst career include Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, Data Science, Economics, and IT. These fields provide strong analytical, programming, and data interpretation skills, essential for working with databases, visualization, and business intelligence tools.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.