

Quick Summary
Have you ever wondered how to become a lawyer in India?
According to recent statistics, the legal profession in India is thriving, with over 1.4 million registered lawyers nationwide. If you have a passion for justice and a desire to advocate for others, the legal profession might be the perfect fit for you.
In this comprehensive guide, we will not only provide you with valuable information on how to become a lawyer in India, but also delve into the intricacies of pursuing an LLB after graduation, navigating law exams, and exploring the diverse career prospects that await you after completing your degree.
Join us as we navigate the fascinating world of the legal field and unveil the steps to embark on a successful legal career in India. Whether you’re seeking insights into the qualifications required, the top law colleges, or the various specializations available, we have all the answers you need to unleash your potential in the dynamic field of law.
|
Industry type |
Law, Legal Profession |
Eligibility Criteria to enroll for College |
10+2 (any stream) with a minimum of 60% aggregate marks |
|
Qualify law entrance exams |
Common Law Admission Test (CLAT), All India Law Entrance Test (AILET), and other state-level exams |
|
Admission Process |
Based on merit and performance in law entrance exams |
|
Specializations |
Civil, Criminal, Corporate, Tax, Intellectual Property, Family Law, Environmental Law, and more |
|
Average Starting Salary |
INR 4-6 lakhs per annum |
|
Highest Salary |
INR 80 lakhs to 1 crore per annum |
|
Job Opportunities |
Lawyer, Judge, Legal Advisor, Corporate Lawyer, Criminal Lawyer, Family Lawyer, and more |
Lawyers are legal professionals trained and licensed to provide advice and representation in legal matters. Beyond their courtroom appearances, lawyers play a vital role in upholding justice, protecting rights, and ensuring compliance with the law. They possess in-depth knowledge of legal principles and procedures, enabling them to guide clients through complex legal processes and provide expert advice.
Advocacy is a central aspect of a lawyer’s work. They act as champions for their clients, working tirelessly to protect their rights and ensure fair treatment under the law. Lawyers also contribute to the development of legal precedents and the interpretation of laws through their legal analysis and arguments.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, lawyers help resolve conflicts, provide legal guidance, and maintain the integrity of the legal system. Their expertise and dedication to justice make them indispensable in safeguarding the rights and liberties of individuals, organizations, and entities.
Also Read: Difference Between Lawyer and Advocate
To become a Lawyer, you need to fulfil the following requirements:
Additionally, to practice law in the Supreme Court and certain High Courts, you may need to appear for an examination conducted by the respective courts.
Becoming a lawyer in India is a rewarding career path that requires dedication, education, and practical experience. Here’s a stepwise process to guide you through the journey of becoming a lawyer in India:
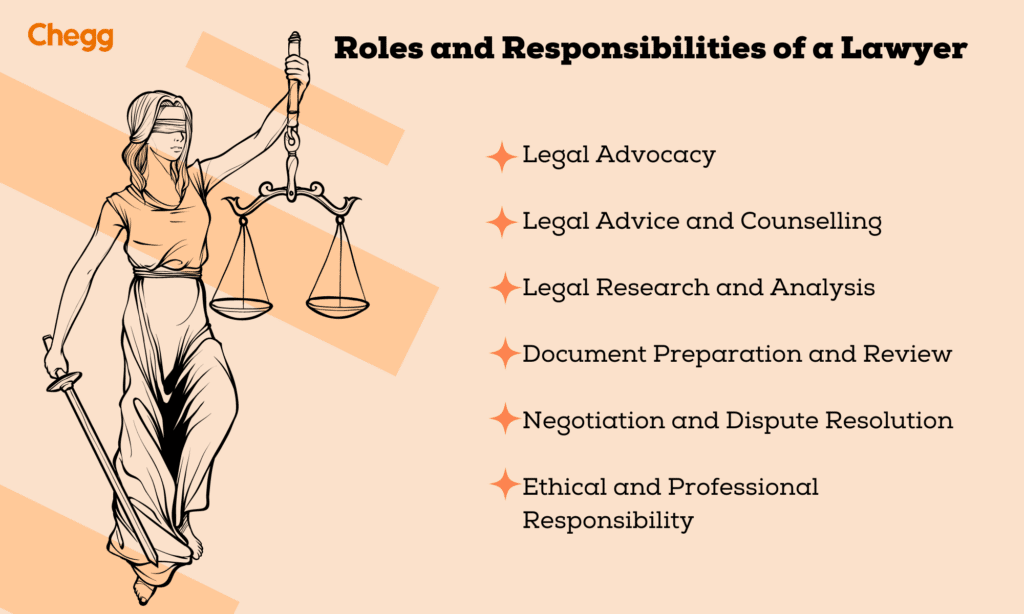
Lawyers apply their legal expertise to guide clients through various legal issues. Their responsibilities vary based on their specialization, but common duties include:
Lawyers specialize in various fields based on their interests and expertise. While some focus on litigation, others opt for corporate or regulatory law. Here are some of the most popular law specializations:
To become a lawyer in India, several qualifications and educational pathways are available. Here are the Lawyer course:
Recommended Read: All You Need to Know about LLM Course in India
By pursuing an LLB or integrated BA LLB program, individuals can acquire the foundational legal education required to become a lawyer in India. Those seeking specialization can pursue an LLM degree to deepen their expertise. Each qualification pathway has its own duration, admission process, and eligibility criteria. Choosing the right qualification depends on individual preferences and career goals.

Note: It’s important to note that the sections, number of questions, duration, and marking scheme may be subject to change as per the respective exam conducting authorities. It is advisable to refer to the official websites and notifications of the exams for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
|
Law College |
Fees (Approx.) |
Duration |
Rankings |
Courses Offered |
National Law School of India University |
₹1,60,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 1 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National Law University, Delhi |
₹2,15,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 2 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
NALSAR University of Law |
₹1,70,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 3 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Symbiosis Law School |
₹2,25,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 8 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, BBA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Jindal Global Law School |
₹5,25,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 9 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, BBA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Gujarat National Law University |
₹2,75,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 12 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, BCom LLB, BSc LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National Law Institute University, Bhopal |
₹2,45,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 14 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences |
₹1,80,000/year |
5 years |
Rank 15 (NIRF) |
BA LLB, BSc LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National Law University, Jodhpur |
₹1,66,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, BBA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Rajiv Gandhi National University of Law |
₹2,10,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, BCom LLB, BSc LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University |
₹1,55,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, BSc LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National University of Advanced Legal Studies |
₹1,90,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, BCom LLB, BBA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National Law University and Judicial Academy, Assam |
₹1,20,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, BSc LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
Hidayatullah National Law University |
₹2,30,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
|
National Law University, Odisha |
₹2,20,000/year |
5 years |
– |
BA LLB, LLM, PhD |
Note: Please note that the fees mentioned are approximate and subject to change. Rankings may vary depending on the publication or ranking system used. It’s always recommended to visit the official websites of the respective law colleges for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding fees, duration, rankings, and courses offered.

|
Career Prospects |
Job Roles and Responsibilities |
Average Annual Salary (in INR) |
|
Corporate Lawyer |
Legal advice, contracts, mergers and acquisitions |
6-10 lakhs |
|
Litigation Lawyer |
Representing clients in courts, legal research |
3-8 lakhs |
|
Criminal Lawyer |
Defending accused, investigations, trial representation |
4-9 lakhs |
|
Intellectual Property (IP) Lawyer |
IP advice, filings, infringement cases |
5-12 lakhs |
|
Family Lawyer |
Family legal matters, divorce, child custody |
3-7 lakhs |
Please note that the lawyer salary ranges provided are approximate and can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and organization. Read more about the Salary of Corporate Lawyers in India.
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide has shed light on the process of becoming a lawyer in India. It has covered the essential steps, including eligibility criteria, clearing entrance exams, pursuing a law degree, gaining practical experience, and enrolling with the Bar Council. By following this step-by-step approach, individuals can embark on a successful legal career.
Additionally, the guide has highlighted the diverse career in law field, including roles such as corporate lawyer, litigation lawyer, criminal lawyer, intellectual property lawyer, and family lawyer. With dedication and continuous learning, aspiring lawyers can make a positive impact in the legal profession and society as a whole.
Unleash your legal career potential with our comprehensive Career Advice section, thoughtfully curated to provide valuable insights and guidance for aspiring lawyers in India.
Ans. Becoming a lawyer typically takes 5-7 years:
1. 5 years if you pursue a BA LLB, BBA LLB, or BCom LLB after 12th.
2. 7 years if you complete a 3-year LLB after a bachelor’s degree.
Additional time may be required for internships, bar exams, and specialization.
Ans. To become a lawyer after 12th:
1. Choose a Law Course – Enroll in a 5-year BA LLB, BBA LLB, or BCom LLB program.
2. Clear Entrance Exams – Appear for CLAT, AILET, or LSAT India.
3. Complete Your Degree – Study legal subjects and gain internships.
4. Pass the Bar Exam – Clear the AIBE to practice law in India.
5. Start Practicing – Join a law firm, work under a senior lawyer, or enter corporate law.
Ans. The fastest way to become a lawyer is by completing a 5-year integrated law course (BA LLB, BBA LLB, BCom LLB) right after 12th. After graduation, you must clear the All India Bar Examination (AIBE) to start practicing.
In total, it takes 5-6 years, including internships, to become a lawyer in India.
Ans. A lawyer’s salary in India varies based on experience, specialization, and location.
1. Freshers: ₹3-5 LPA
2. Mid-level (5-10 years): ₹6-15 LPA
3. Senior Lawyers: ₹20 LPA+
4. Top Corporate Lawyers: ₹50 LPA+
5. Independent Advocates: Earnings depend on cases and reputation.
High-profile lawyers and those working in top law firms can earn crores annually.
Ans. To become a lawyer in India, complete 10+2, clear entrance exams like CLAT, and pursue either a 5-year integrated LLB after 12th or a 3-year LLB after graduation. Then, register with the State Bar Council and pass the AIBE to practice law.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.