

Quick Summary
Economics has evolved over the centuries due to its presence in every aspect of life. The scope of economics is vast, covering various sectors that impact individuals, businesses, and governments. As a branch of social science, economics helps us understand past, present, and future economic models. It explains how resources are allocated, how markets function, and how economic policies influence growth and stability. By studying economics, we gain insights into the world around us and how economic principles shape societies at local, national, and global levels.
The scope of economics involves analyzing how individuals, businesses, and governments allocate limited resources to meet their needs and desires. It includes both microeconomics, which focuses on individual and business decisions, and macroeconomics, which examines broader economic factors like production, consumption, distribution, and the exchange of goods and services on a national or global scale.
Additionally, the scope of economics extends to various specialized fields, making it a diverse and dynamic subject. It includes international trade and globalization, which analyze economic interactions between countries. Development economics focuses on growth and poverty reduction in low-income nations, addressing issues like inequality and financial inclusion. Behavioral economics integrates psychology into economic decision-making, helping us understand consumer behavior and market trends. These fields show how economics is applied in real-world scenarios, influencing policy decisions and business strategies.
Explaining the full scope of economics is complex because it touches multiple aspects of life and industry. However, exploring its nature helps us appreciate its significance in shaping economies and improving livelihoods. In this article, we will delve into the nature and scope of economics, as well as the various career opportunities available in this field.

The nature of economics has a dual presence, as it is considered both a science and an art. Economist Lionel Robbins defined economics as a science that studies human behavior in relation to scarce resources. He emphasized that economics focuses on making choices to satisfy unlimited wants with limited resources. This view highlights the analytical and systematic approach of economics in understanding decision-making.
On the other hand, economist Alfred Marshall described economics as an art. He believed that economics not only analyzes problems but also provides practical solutions to improve living standards. This perspective shows that economics is not just about theories but also about applying knowledge to real-world economic challenges.
Let us explore the nature of economics as science and art –
British economist Lionel Robbins defined economics as a branch of social science that studies human behavior in relation to scarce resources with alternative uses. Economics is considered a science because it follows systematic principles to analyze financial decisions. The scope of economics includes studying how individuals and societies allocate resources efficiently. It relies on facts, data, and logical reasoning to understand economic activities and their impact on people and markets.
The scope of economics is evident in research methods used to study micro and macroeconomic trends. Like science, economics examines cause-and-effect relationships while collecting, classifying, and analyzing data. Economic research helps in understanding consumer behavior, market fluctuations, and policy outcomes. By applying scientific principles, economics provides valuable insights into solving financial and societal challenges effectively.
Economics is considered an art because it applies various theories, concepts, and findings to achieve practical goals. Economist Alfred Marshall defined economics as the art of applying scientific theories to real-world situations. It helps in decision-making by using economic principles to solve financial and societal problems. The scope of economics as an art lies in its ability to provide solutions for business growth, resource management, and economic stability.
The scope of economics is also seen in the use of graphical representations to explain relationships between economic variables. These models help in understanding concepts like supply and demand, inflation, and market trends. By applying these theories, economics helps in formulating policies and strategies for economic development. This practical application of theories highlights the artistic nature of economics in solving real-world challenges.
Economics deals with a wide variety of things. It comprises multiple principles and theories whose implications influence the economy of a country. When it comes to the scope of economics, it can be understood by the two scope of economics – Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Learn more about the nature and scope of economics below –
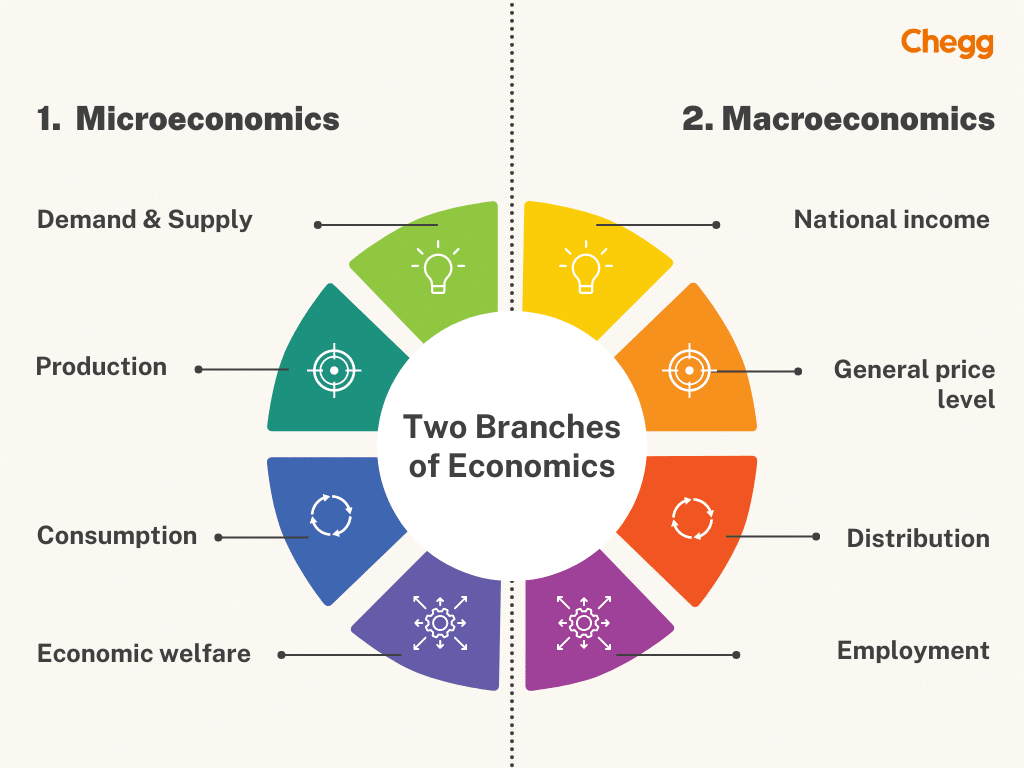
Microeconomics focuses on the smaller elements of a nation’s economy, analyzing how individual units like households, firms, and industries function. It studies product pricing, the cost of production, and the pricing of resources such as labor and capital. By examining these factors, microeconomics helps understand consumer behavior, market demand, and supply patterns. The scope of economics in this field extends to understanding how individuals and businesses make decisions based on limited resources. These insights help in optimizing production, setting prices, and improving market efficiency.
The scope of economics in microeconomic studies also includes resource allocation, income distribution, and the efficient utilization of goods and services. It explains how businesses maximize profits, how consumers make purchasing choices, and how markets maintain equilibrium. By analyzing competition, monopolies, and consumer preferences, microeconomics helps in policy formulation and economic planning. The scope of economics is not just limited to theoretical concepts but also extends to practical applications in business strategies and financial planning. As part of the broader scope of economics, microeconomics plays a vital role in shaping economic policies and guiding decision-making at all levels.
The scope of micro economics includes:
Macroeconomics focuses on the larger aspects of a nation’s economy, studying overall economic performance and trends. It analyzes key factors such as total production, national income, employment rates, inflation, and economic growth. Unlike microeconomics, which studies individual units, macroeconomics examines how these units function collectively. The scope of economics in macroeconomic studies includes understanding aggregate demand and supply, government policies, and international trade. This helps policymakers and economists make informed decisions to maintain economic stability and promote growth.
The scope of economics in macroeconomics extends to analyzing economic fluctuations, business cycles, and the impact of fiscal and monetary policies. It plays a crucial role in understanding how government spending, taxation, and interest rates influence an economy. The scope of economics is also seen in global markets, where exchange rates, trade policies, and international investments shape economic conditions. By studying macroeconomic trends, experts can predict recessions, control inflation, and create policies for sustainable development. The broad scope of economics in macroeconomic analysis helps in ensuring a balanced and growing economy at both national and global levels.
The scope of macroeconomics includes:
The career scope of economics provides students with vast opportunities across various industries. Economics graduates can explore careers in banking, finance, policymaking, research, and corporate sectors. With a strong foundation in economic principles, students can analyze market trends, manage resources, and contribute to economic development. This field offers diverse roles that cater to different interests and skills.
Multiple career options are available for those who choose economics as a profession. They can work as economists, financial analysts, data analysts, policy advisors, or researchers. Opportunities exist in government agencies, multinational corporations, and financial institutions. With growing demand, economics continues to be a promising career path with stability and long-term growth potential.
Here are the top 10 career opportunities in the scope of economics:
An economist is responsible for conducting research on the economic model of the country, identifying issues through surveys, and analyzing the collected data through mathematical models and strategic techniques. They conclude research reports and forecast the issues that may arise in the future.
The average salary of an economist is INR 6.6 LPA (Data Sourced from PayScale).
A financial researcher is responsible for accessing and analyzing the financial statements of a company and predicting the company’s future performance in the working sector. Their work includes forecasting future revenues and expenditures and keeping track of the company’s financial plan.
The average salary of a financial researcher is INR 8 LPA (Data Sourced from Glassdoor).
Consumer credit managers research and evaluate the creditworthiness of customers. Their work involves reviewing consumers’ credibility through the creation of credit scoring models. They are responsible for predicting risks and approving or rejecting loans.
The average salary of a consumer credit manager is INR 7.7 LPA.
Personal financial advisors assist their clients in reaching their financial goals. They help individuals or companies achieve their financial goals by providing various strategies and techniques. They provide advice on reducing costs, eliminating debts, and creating more wealth.
The average salary of a personal financial advisor is INR 4.56 LPA.
An economics professor or teacher is responsible for teaching undergraduate or postgraduate students at universities or institutions. They prepare and deliver lectures to students on the subject of economics.
Skills Required:
The average salary of a professor is INR 10 LPA.

The Indian economic services officer or IES officer is responsible for maintaining and regulating the economic affairs in the social or government sectors. Their work includes managing the government’s functioning and making crucial contributions to formulating policies.
The average salary of an IES officer is INR 9.60 LPA (as per the 7th Pay Commission).
Income tax officers are responsible for regulating the taxation procedure of a country. They examine and analyze the tax assets and liabilities to determine delinquent tax issues. They communicate with the members and intermediaries involved in the taxation process to evaluate the tax problems.
The average salary of an income tax officer is INR 7.5 LPA.
A statistical investigator is responsible for planning and executing all the work relating to the census. They monitor and coordinate the training functionaries and collect, process, and disseminate data. They conduct numerous data collection surveys for performing intensive field duties.
The average salary of a statistical investigator is INR 9.36 LPA.
The responsibility of an audit officer includes reviewing and examining the financial reports and records. They check the reports to identify their accuracy and reliability. Audit officers ensure that the assets remain protected. They analyze the processes to find issues and make necessary changes.
The average salary of an audit officer is INR 3.6 LPA.
A probationary officer is responsible for regulating and handling the banking transactions of customers. They retain the authority to issue checkbooks, pass cheques, and manage cash. Probationary officers can also work in private or public sector companies for financial or accounting matters.
The average salary of a probationary officer is INR 7.5 LPA Data Sourced from AmbitionBox).


Economics has become a crucial aspect of both individual life and the professional world. The scope of economics is vast, covering various sectors such as finance, business, policymaking, and governance. Whether in daily decision-making or large-scale economic planning, economics plays a key role in shaping financial stability and growth. As a result, students pursuing economics have numerous career opportunities across multiple industries.
The scope of economics is not limited to traditional job roles. Graduates with a BA in Economics can explore careers in banking, corporate sectors, data analysis, and market research. Many students also choose to prepare for civil services, where knowledge of economics is highly valuable. With a strong foundation in economic principles, students can contribute to financial policies, business strategies, and social development. The scope of economics extends to research institutions, where economists analyze global trends and provide insights for economic progress.
For students aspiring to build a stable and rewarding career, the scope of economics offers numerous possibilities. From government jobs to private sector roles, the demand for economic experts continues to grow. With the rise of technology and global trade, the need for skilled economists is increasing. The scope of economics ensures that students not only prosper in their careers but also make meaningful contributions to society. As industries evolve, economics remains a field with immense potential and long-term growth.
The study of economics opens doors to numerous career opportunities and plays a vital role in shaping industries, businesses, and government policies. With its application in finance, trade, healthcare, and development, the scope of economics continues to expand. Graduates with a strong foundation in economic principles can contribute to decision-making at various levels, from managing businesses to influencing national policies. The demand for economic experts is increasing across sectors, ensuring stable and rewarding career paths. Whether in banking, research, corporate roles, or public administration, economics provides diverse opportunities for growth and success.
As economies evolve with advancements in technology and globalization, the need for skilled economists becomes even more significant. The ability to analyze trends, predict market behavior, and develop financial strategies makes economics a valuable field. With numerous professional avenues, including civil services, academia, and consultancy, students can choose careers that align with their interests and expertise. The scope of economics is limitless, offering both financial stability and intellectual fulfillment. In the future, as economic challenges and opportunities continue to arise, professionals in this field will play a key role in shaping policies and driving progress at local, national, and global levels.
The scopes of economics include:
Microeconomics
Macroeconomics
International economics
Development economics
Labour economics
Environmental economics
Public economics
Behavioural economics
Health economics
Agricultural economics
The general scope of economics includes the study of resource allocation, production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It includes microeconomics, focusing on individual choices, and macroeconomics, examining aggregate economic phenomena.
The four main parts of the scope of economics are:
1. Microeconomics – Studies individual markets, consumer behavior, and business decisions.
2. Macroeconomics – Focuses on national and global economic trends, inflation, and GDP.
3. International Economics – Examines trade, globalization, and exchange rates.
4. Development Economics – Analyzes economic growth, poverty, and policies for sustainable development.
The father of economics is often considered to be Adam Smith. His seminal work, “The Wealth of Nations,” published in 1776, laid the foundations for classical economics and introduced key concepts such as the division of labor, free markets, and the “invisible hand” that guides economic activity.
The scope of business economics are:
1. Demand Analysis – Understanding consumer needs.
2. Production & Cost – Managing resources efficiently.
3. Pricing Strategies – Setting competitive prices.
4. Profit Management – Maximizing revenue.
5. Business Environment – Adapting to market trends and policies.
Economy of scope refers to the cost advantage that a business experiences when it produces multiple products together rather than separately. It means that it’s more efficient (and often cheaper) to produce a variety of goods or services jointly because they share resources, processes, or technologies.
The scope of economics typically includes three main areas: microeconomics, macroeconomics, and international economics.
The scope of Class 11 Economics typically includes the following topics:
Introduction to Economics
Consumer Behaviour and Demand
Producer Behaviour and Supply
Forms of Market and Price Determination
Simple Economics of Production
National Income
Money and Banking
Government Budget and the Economy
Balance of Payments
Economic Development and Economic Growth
These topics provide a foundational understanding of key economic principles and frameworks.
The scope of economics on Wikipedia covers various topics including microeconomics, macroeconomics, economic theory, economic policy, economic systems, and the history of economic thought. It includes articles on key concepts, models, theorists, and empirical studies, along with discussions on contemporary issues, economic indicators, and institutions. The content is structured to provide a comprehensive overview of the field, catering to both beginners and advanced readers.

Authored by, Gagandeep Khokhar
Career Guidance Expert
Gagandeep is a content writer and strategist focused on creating high-performing, SEO-driven content that bridges the gap between learners and institutions. He crafts compelling narratives across blogs, landing pages, and email campaigns to drive engagement and build trust.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.