

Quick Summary
In the world of business and finance, understanding costs is crucial for managing budgets, setting prices, and achieving profitability. One of the key concepts in cost management is the idea of fixed cost. But what is fixed cost?
A fixed cost is an expense that does not change regardless of the level of production or sales. These costs remain constant over a while, even if a company produces more or fewer goods. Examples include rent, salaries, insurance, and loan payments, which must be paid regularly, no matter the business activity.
This article will provide a detailed and easy-to-understand explanation, making it simple for anyone to grasp the concept.
What is Fixed Cost? Fixed cost refers to the expenses a business incurs that do not change regardless of the level of production or sales. These costs remain constant whether a company produces 1 unit or 10,000 units.
For example:
These expenses do not fluctuate with the company’s production or sales volumes.
In simple terms, fixed costs are the predictable, steady expenses that businesses must pay, no matter how much they produce or sell.
Understanding what is fixed cost is essential for managing business finances effectively. Fixed costs are expenses that do not change regardless of how much a company produces or sells in the short term. These costs are a crucial part of business operations and play a key role in financial planning.
Fixed costs remain the same even if there is a significant change in production levels. Whether a company manufactures 100 units or 1,000 units, these expenses typically stay unchanged in the short run. For example, rent for office space or salaries of permanent staff will not fluctuate based on output.
A defining feature of fixed costs is that they are independent of how much is produced or sold. Even if the production output drops to zero, businesses must still bear these costs. For instance, equipment maintenance contracts need payment regardless of production activity.
While fixed costs do not change in the short term, they can be subject to revisions over time. Rent agreements, for example, may be renegotiated annually, leading to an increase or decrease. However, within the agreed period, these costs typically remain stable.
Fixed costs often represent critical expenses that allow a business to function smoothly. Examples include utilities, insurance, and salaries for administrative staff. These costs form the foundation of operational continuity, irrespective of production levels.
One of the benefits of fixed costs is their predictability. Businesses can budget these expenses accurately, which aids in financial planning and forecasting. Knowing what is fixed cost helps companies assess their breakeven point and make better operational decisions.
By understanding the characteristics of fixed costs, businesses can better manage their resources, optimize spending, and achieve long-term growth while maintaining essential operations.
To fully understand what is fixed cost, it helps to look at fixed cost examples. Fixed costs are those expenses that remain constant, regardless of how much a business produces or sells. These costs are unavoidable and necessary for maintaining the basic operations of any company.
A business pays rent for its office or manufacturing space regardless of the level of activity happening inside. Even if the office is temporarily closed or production slows down, the rent remains unchanged. This predictable monthly or yearly payment makes rent a classic example of a fixed cost.
Salaries paid to full-time staff are another common fixed cost. These employees receive a set amount each month, no matter how many products are manufactured or sold. For instance, the salary of an HR manager will stay the same, even if the company experiences a dip in sales.
Businesses often purchase insurance policies to protect against potential risks such as theft, accidents, or natural disasters. The premiums for these insurance policies are fixed and must be paid regularly, regardless of the company’s production levels or profitability.
Depreciation is the gradual reduction in the value of assets such as machinery, vehicles, and office equipment over time. Although depreciation is a non-cash expense, it is treated as a fixed cost because it remains consistent and predictable throughout the asset’s lifespan.
Utility bills, such as electricity and water, often have fixed basic charges that must be paid regardless of consumption. Even if the business uses minimal electricity or shuts down temporarily, these minimum charges still apply.
By understanding these examples, it becomes clear what is fixed cost and how these expenses impact business finances. Properly managing fixed costs allows companies to predict their financial obligations and make informed decisions to achieve profitability.
What is fixed cost and how to calculate it is essential for managing business expenses and planning budgets effectively. Fixed costs are the expenses that do not change regardless of the production level or sales volume of a business. Follow these simple steps to calculate fixed costs accurately:
Start by identifying all the expenses your business incurs within a specific period (monthly, quarterly, or yearly). These expenses typically fall under categories like rent, salaries, insurance, raw materials, and utility bills.
Once you’ve listed your expenses, classify them into two categories:
For example:
Related Read – What Is Variable Pay in CTC: Do Incentives Matter?
Now, sum up all the expenses identified as fixed. This total represents your business’s fixed cost.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say the following are your business expenses for a month:
The total fixed cost would be:
₹15,000 + ₹5,000 + ₹25,000 = ₹45,000
Another way to calculate fixed costs is by using the formula:
Fixed Cost = Total Cost − Total Variable Cost
Example Calculation Using the Formula:
Suppose a company’s total cost for a month is ₹80,000, and the total variable cost is ₹35,000.To calculate the fixed cost:
Fixed Cost = 80,000 − 35,000
Fixed Cost = ₹45,000
This means the fixed cost for this business is ₹45,000.
By understanding what is fixed cost and knowing how to calculate it, businesses can better predict financial obligations, set pricing strategies, and manage overall profitability more effectively.
It is important to understand the difference between fixed costs and variable costs.
| Aspect | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs that do not change with production levels | Costs that change with production levels |
| Examples | Rent, salaries, insurance | Raw materials, packaging, shipping |
| Dependence on Output | No | Yes |
| Time Stability | Stable over time | Fluctuates |
Example for Clarity:
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of production levels or sales volume. They play a significant role in business operations and decision-making processes. Let’s explore why they are important:
Fixed costs provide a stable foundation for creating accurate budgets. Since these expenses remain unchanged over a specific period, businesses can forecast their financial obligations and allocate funds effectively.
Example:
A company renting an office space for ₹50,000 per month knows this amount won’t change regardless of production. This predictability allows them to plan other expenses more accurately.
When setting prices for products or services, businesses must ensure that both fixed and variable costs are covered to maintain profitability.
Why it Matters:
If a business doesn’t account for fixed costs when pricing its products, it may suffer financial losses even if sales volumes are high.
Example:
If manufacturing a product costs ₹500 in variable expenses and the business has a fixed cost of ₹1,00,000, the product pricing must be set high enough to recover these fixed expenses over time.
Knowing what is fixed cost helps businesses calculate their break-even point—the point where total revenue equals total costs, including both fixed and variable expenses.
Why it Matters:
This analysis helps determine how much a company needs to sell to start making profits.
Example:
If a company incurs ₹2,00,000 in fixed costs, it must generate sales that cover this amount before any profit is realized.
Effective management of fixed costs can help ensure a business remains financially stable, even during periods of low sales.
Why it Matters:
High fixed costs can strain a business if revenue fluctuates. Businesses with controlled fixed costs are better equipped to handle market uncertainties.
Example:
During an economic downturn, a company with lower fixed costs may survive better than one with high fixed obligations.
By managing fixed costs businesses can maintain better control over their finances, set competitive prices, and achieve long-term financial stability.
The break-even point is when a company’s revenue equals its total expenses, resulting in no profit and no loss. It helps businesses understand how many units they need to sell to start generating profits.
The formula for calculating the break-even point is:
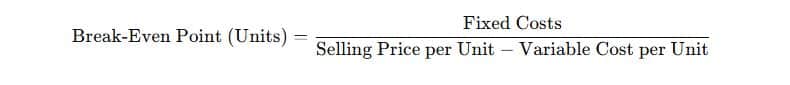
Break-Even Point (Units) = ( Fixed Costs / Selling Price per Unit − Variable Cost per Unit )
Let’s break it down step by step for better understanding:
200 − 100 = 100
This means each unit sold contributes ₹100 toward covering fixed costs.
50,000 / 100 = 500
The business must sell 500 units to break even.
Mastering break-even analysis, businesses gain a valuable tool for managing expenses and achieving profitability.
Understanding Operating Leverage
Operating leverage is an important financial concept that helps businesses understand how fixed and variable costs impact their profitability. It measures how efficiently a company can increase profits by producing and selling more units.
When a company has high operating leverage, it means that a large portion of its costs are fixed. This allows it to generate more profit per additional unit sold. On the other hand, low operating leverage means that most costs are variable, making it harder to boost profits significantly with higher sales.
Operating leverage can be calculated using the formula:
Operating Leverage = Q×(P−V)(Q×(P−V))−FOperating \, Leverage = \frac{Q \times (P – V)}{(Q \times (P – V)) – F}
Where:
Understanding operating leverage is essential for businesses looking to optimize costs, maximize profits, and stay competitive in the market.
Understanding what is fixed cost isn’t just for textbooks—it affects our daily lives! Let’s explore how fixed costs work in real-world Indian scenarios, from your home to local businesses
Imagine your family’s monthly budget:
Why it matters: Fixed costs help families plan savings. For example, if your parents know rent is ₹18,000, they’ll set aside that money first.
Fun Fact: Your monthly pocket money isn’t a fixed cost—it’s a variable cost because parents might reduce it if you forget chores!
Application: The owner knows he must earn at least ₹27,000/month (rent + salary) just to cover fixed costs. Only after that can he make a profit
Challenge: During holidays, orders drop, but fixed costs stay the same. The owner might offer discounts to attract customers and cover these costs.
Your school has fixed costs too!
What is fixed cost’s role here? Schools must collect fees to cover these expenses, even during summer breaks.
Indian farmers face fixed costs like:
Problem: If crops fail due to droughts, farmers still pay these fixed costs. This is why farming can be risky.
Pro Tip: Fixed costs are like your phone’s monthly plan—predictable but unavoidable. Plan for them wisely!
Now you know what is fixed cost and how it applies to real life! Whether it’s your home Wi-Fi bill or a farmer’s tractor loan, fixed costs are everywhere. By understanding them, you can make smarter money decisions—just like a pro!
Now that you understand what is fixed cost, let’s learn how to manage these expenses smartly. Whether you’re a student, a family, or a business owner, these tips will help you save money and avoid stress!
Fixed costs like rent or internet bills can sometimes be reduced with a little effort.
Pro Tip: Long-term contracts (like 2-year internet plans) often have lower monthly rates than short-term ones.
Replace expensive fixed costs with cheaper alternatives.
Remember: Always calculate total savings before switching.
Split fixed costs to reduce your burden.
Bonus Idea: Use co-working spaces to avoid high office rents.
Write down all fixed costs in a simple table. This helps you:
Example for Families:
| Fixed Cost | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| Rent | 15,000 |
| School Bus Fees | 1,500 |
| Electricity Bill | 2,000 |
Pro Tip: Use free apps like Moneycontrol or Excel to track expenses.
Fixed costs don’t stop during tough times. Save money in advance to cover them.
Golden Rule: Save at least 10% of your income for fixed costs.
Some fixed costs are necessary for safety or quality. For example:
Managing what is fixed cost is like planning your school timetable—know what’s coming, prepare for it, and avoid last-minute panic! By negotiating, sharing, and tracking expenses, you can control fixed costs instead of letting them control you.
Action Step: List your fixed costs today and see where you can save!
Understanding what is fixed costs and how it impacts business operations is essential for financial success. By knowing how to identify, calculate, and manage fixed costs, businesses can make informed decisions, improve profitability, and achieve long-term stability. Whether you are a student, entrepreneur, or financial professional, mastering this concept will benefit you in many ways.
Innovative, low-investment ideas for the hidden entrepreneur in you! Explore our guide on Business Ideas.

A fixed cost is an expense that does not change with the level of production or sales. Examples include rent, salaries, and insurance premiums.
Variable cost is an expense that changes directly with the level of production or sales. Examples include raw materials and labor costs.
A fixed cost is described as an expense that remains constant regardless of the amount of goods or services produced. It’s a predictable and stable expense.
Fixed price is a set price that does not change, while cost price is the amount it costs to produce or purchase an item.
Companies consider salaries a fixed cost. Employees receive the same pay regardless of the company’s performance.
Total fixed costs are the total of a company’s continuous, non-variable expenditures. Assume a corporation pays $10,000 per month for office space, $5,000 per month for machines and $1,000 per month for utilities. In this example, the total fixed expenses for the firm would be $16,000.
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of changes in production volume. These expenses are time-dependent rather than dependent on the quantity of goods or services produced or sold by your company. Examples include rent, leasing charges, salaries, insurance premiums, and loan repayments.
In economics, a fixed cost is a cost that does not vary with the level of output. Examples include rent and salaries.
Fixed cost is an expense that stays the same regardless of production levels, like rent. Variable cost changes with production levels, like raw materials.
In cost accounting, a fixed cost is an expense that does not change with the level of production or sales, such as rent or salaries.
Fixed costs: rent, salaries. Variable costs: raw materials, labor.
The fixed cost formula is: Fixed Costs = Total Costs – Variable Costs.
In accounting, fixed cost refers to expenses that remain constant regardless of production or sales levels, such as rent and salaries.
In business, fixed cost is an expense that does not change with the level of production or sales. Examples include rent, insurance, and salaries.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.