Table of Contents
In the world of computers and electronics, one term that frequently pops up is ALU. But what exactly does ALU Full Form stand for? If you’re a student looking to understand computer architecture and how data is processed, this blog will break down the concept of ALU, its full form, and its importance in the digital world.
ALU Full Form: Arithmetic Logic Unit
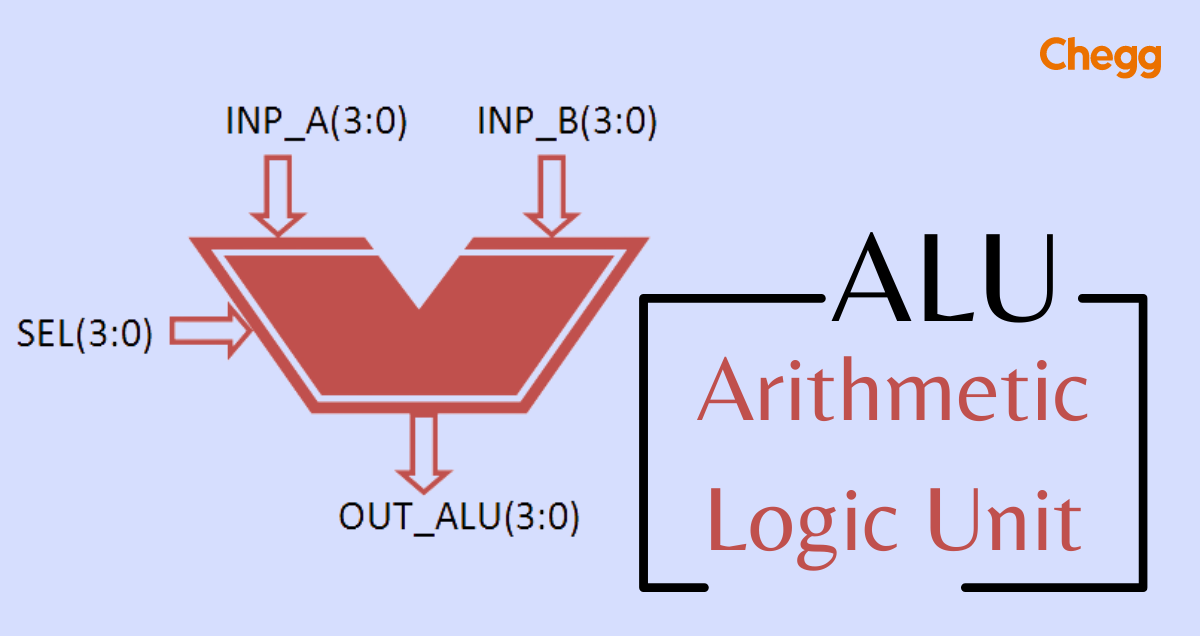
What is an ALU?

The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a fundamental component of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). It performs all the basic arithmetic (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logical operations (such as AND, OR, and NOT). In simpler terms, the ALU is like the brain’s calculator—it handles the data processing tasks that are essential for making a computer work.
Primary Functions of ALU:
The ALU Full Form reveals two critical functions it handles:
- Arithmetic Operations: Includes basic math operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Logical Operations: Handles logical comparisons, such as determining whether one number is greater than another, or if two conditions are both true (AND, OR, NOT, XOR).
Components of an ALU
An ALU works through various inputs and outputs, with an internal structure designed to perform specific operations quickly and accurately.
1. Inputs and Outputs
- Data Inputs: These are the numbers or data (also called operands) that the ALU uses to perform its calculations.
- Control Inputs: These are signals that tell the ALU which operation to perform.
- Outputs: After processing, the ALU provides an output, which could be a number (result of a calculation) or a status flag (information like whether the result was positive, negative, or zero).
2. Internal Structure of ALU
- Adders: Perform addition operations.
- Multiplexers: Select which data should be used as input.
- Logic Gates: Perform the logical operations like AND, OR, NOT.
How Does an ALU Work?

The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU full form) inside a computer works like a smart calculator. Here’s how it does its job:
- Getting Instructions: The Control Unit (CU) in the computer fetches instructions from memory and sends them to the ALU.
- Handling Data: The ALU gets numbers (data) from registers inside the computer. These are the numbers it will work with.
- Doing Operations: Depending on the instruction, the ALU can do different things:
- Math Operations: Like adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing.
- Logic Operations: Like checking if things are true (AND), if at least one thing is true (OR), or flipping true to false (NOT).
- Saving Results: After doing the job, the ALU sends the answer back to a register or memory, following the instruction.
ALU Design and Implementation

Arithmetic Logic Units (ALU full form) are designed and used in computers to do important jobs like math (adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing) and making decisions (comparing numbers). Here’s how ALUs are made and put to work:
1. Designing an ALU
- Parts: ALUs have basic pieces like registers (short-term storage), arithmetic circuits (for math), and logic circuits (for decisions).
- Purpose: They are made to handle tasks efficiently, based on what the computer needs. Some ALUs focus on fast math, while others handle complex decisions.
- Integration: ALUs are put into the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of a computer, where they work closely with other parts like the Control Unit and Memory.
2. Implementing an ALU
- Building: Engineers make ALUs using digital circuits with transistors and other electronic parts. These circuits use binary code (0s and 1s) to process data.
- Testing: Before using ALUs in a computer, they’re tested a lot to make sure they do calculations right and fast.
- Improving: ALU designs are always getting better to make computers faster and work better. This means fixing circuits and using new tech.
Types of Operations Performed by ALUs
ALUs are capable of performing a variety of operations that can be categorized into two main types:
1. Arithmetic Operations
These include:
- Addition: Adding two numbers.
- Subtraction: Finding the difference between two numbers.
- Multiplication: Multiplying numbers.
- Division: Dividing one number by another.
2. Logical Operations
Logical operations help in decision-making within the computer by comparing data:
- AND: Returns true if both conditions are true.
- OR: Returns true if at least one condition is true.
- NOT: Reverses the logic (true becomes false, and vice versa).
- XOR: Returns true if only one of the conditions is true, but not both.
Role of ALU in the CPU
The ALU is one of the most vital components of the CPU. It works in conjunction with other CPU parts, such as the control unit and memory registers, to execute instructions.
How the ALU Fits into the CPU:
- Fetch: The control unit fetches instructions from memory.
- Decode: The control unit decodes the instruction and decides which operation the ALU will perform.
- Execute: The ALU performs the operation and sends the result to the output or to memory.
Without the ALU, the CPU would not be able to process data or run applications effectively.
Types of ALUs
ALUs come in different types depending on the complexity of the tasks they handle:
1. Simple ALUs
These are found in basic processors, such as those in calculators or simple devices. They handle only basic arithmetic and logical operations.
2. Complex ALUs
Used in more advanced processors like CPUs and GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), these ALUs can handle more complex operations and are designed for multitasking and high-speed processing.
3. Floating-Point ALUs
Specialized ALUs designed to handle floating-point arithmetic, crucial for scientific calculations and graphics processing.
ALU in Central Processing Units

An Arithmetic Logic Units (ALU full form) is super important in a CPU (Central Processing Unit). It acts like the brain of the CPU, handling calculations and making decisions. Here’s how it works in simpler terms:
1. Key Functions:
- Calculations: The ALU does all the math stuff you’d expect, like adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing. It uses small circuits made for each type of math task.
- Logical Decisions: Besides math, the ALU also does logical operations with binary data. These operations (like AND, OR, NOT, XOR) are used for comparing things and following instructions in programs. It’s like saying yes or no based on the data.
- Following Instructions: The ALU doesn’t do things on its own. It gets instructions from the CPU’s control unit, which tells it what kind of operation to do on the data.
2. Working Together:
- Getting Instructions: The CPU gets instructions from memory.
- Understanding Instructions: The control unit figures out what needs to be done based on the instruction.
- Sending Data: The control unit sends the data to the ALU, along with what kind of math or logic to perform.
- Doing the Job: The ALU performs the operation (like adding numbers or comparing them).
- Saving the Answer: The ALU sends the result back to the CPU to keep it safe for a bit.
3. Impact on Speed:
- Bits Matter: The more bits an ALU can handle at once (like 64 or 128 bits), the faster and more complex tasks it can handle. More bits mean handling bigger numbers or doing more complicated things in one go.
- Powerful CPUs: A strong ALU is a big part of what makes a CPU fast. It’s like having a quick calculator built right into the computer.
ALU vs. GPU: What’s the Difference?
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the differences between the ALU and GPU:
| Aspect | ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) | GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Arithmetic Logic Unit | Graphics Processing Unit |
| Main Function | Performs arithmetic (addition, subtraction) and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT). | Specializes in parallel processing for rendering graphics and image manipulation. |
| Location | Located within the CPU (Central Processing Unit). | A separate unit, often a dedicated chip, or integrated with the CPU. |
| Type of Processing | Handles basic, serial (step-by-step) processing. | Handles massive parallel processing, ideal for complex tasks like 3D rendering. |
| Primary Use | General-purpose calculations, basic data processing. | Graphics rendering, video processing, and gaming. |
| Number of Cores | Typically contains fewer cores (1-4 cores). | Contains hundreds to thousands of cores for parallel processing. |
| Speed | Slower for large, complex calculations. | Extremely fast for handling large volumes of data simultaneously. |
| Task Specialization | General-purpose, handles basic arithmetic and logical tasks. | Specialized in tasks involving graphics, simulations, and machine learning. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy consumption as part of the CPU. | Higher energy consumption, especially in high-end GPUs used for gaming or AI tasks. |
| Applications | Used in all computers for basic computational tasks like addition, subtraction, and logic operations. | Used in gaming, virtual reality, deep learning, and other graphics-intensive tasks. |
| Computational Focus | Single tasks or instructions at a time. | Handles multiple tasks simultaneously, best for multitasking. |
Applications of ALUs
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU full form in computer) are essential in a wide range of computing devices. From basic calculators to powerful supercomputers, the ALU’s role is central to how these devices process information.
Where ALUs Are Used:
- Computing Devices: ALUs are found in almost all modern digital devices, from personal computers to smartphones.
- Gaming Consoles: ALUs handle game logic, arithmetic, and rendering calculations in gaming consoles like PlayStation or Xbox.
- Everyday Technology: ALUs process data in cars, smart devices, and home appliances with embedded systems.
Historical Context of ALUs
The concept of the ALU has been evolving since the early days of computing. Here’s a brief look at its development:
- 1946: ENIAC, one of the first electronic computers, used a simple form of ALU.
- 1960s: The term “ALU full form” (Arithmetic Logic Unit) became widely used.
- 1970s: The first microprocessors integrated ALUs onto a single chip.
- Today: Modern ALUs can perform billions of operations per second!
The continuous improvement in ALU technology has allowed computers to become smaller, faster, and more powerful.
Future Trends in ALU Technology
With the rapid advancement in technology, ALUs are expected to continue evolving:
- Quantum Computing: ALUs in quantum computers could handle operations at an entirely new level, enabling faster and more complex problem-solving.
- AI Integration: Future ALUs could be designed to handle specific tasks in artificial intelligence and machine learning, making them even more specialized.
- Energy Efficiency: Future ALUs will focus on reducing power consumption while maintaining high performance, crucial for mobile and embedded devices.
As technology advances, ALUs will likely play an even bigger role in processing power.
ALU Full Form in Hindi
ALU का हिंदी में पूरा नाम (ALU ka full form in Hindi) “अंकगणितीय तर्क इकाई” है। यह एक महत्वपूर्ण घटक है जो कंप्यूटर और अन्य डिजिटल उपकरणों में गणितीय और तार्किक संचालन (operations) को संभालता है। ALU मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकार के कार्य करता है: अंकगणितीय (Arithmetic) जैसे जोड़, घटाव, गुणा, और भाग, और तार्किक (Logical) जैसे AND, OR, NOT, आदि। जब भी कंप्यूटर कोई गणना या निर्णय करता है, ALU उसे तेजी से और सही तरीके से करता है।
ALU को कंप्यूटर का “मस्तिष्क” भी कहा जाता है, क्योंकि इसके बिना किसी भी डेटा प्रोसेसिंग का काम पूरा नहीं हो सकता। यह प्रोसेसर (CPU) का एक अहम हिस्सा होता है, जो कंप्यूटर के प्रदर्शन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
Conclusion
The ALU Full Form—Arithmetic Logic Unit—reveals its core function as the processor of arithmetic and logic operations in a computer system. Whether you are studying computers for the first time or delving deeper into digital electronics, understanding the role of the ALU is fundamental. It not only powers basic tasks like addition but also complex logical operations, making it a cornerstone of modern computing technology.
By grasping the functions of an ALU, students can better understand how computers think, process data, and perform the tasks we rely on every day. As you advance in your studies, the concept of the ALU will serve as a building block for more complex topics in computer science.
Popular Full Forms
| RAM Full Form | ROM Full Form | SSD Full Form |
| HDD Full Form | USB Full Form | CPU Full Form |
| PCD Full Form | MCB Full Form | SIM Full Form |
Ready to learn more? Click on the following link to get the complete list of Full Forms!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the full form of ALU in computers?
The full form of ALU in computers is Arithmetic Logic Unit.
Q: What is the function of the ALU?
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, and comparisons.
Q: How does thе ALU interact with thе control unit?
Thе control unit fеtchеs instructions from mеmory, decoders thеm, and dеtеrminеs thе appropriatе opеrations to bе pеrformеd by thе ALU. It controls the flow of data to and from the ALU during instruction еxеcution.
Q: How does thе ALU contribute to computеr systеm pеrformancе?
Thе ALU’s еfficiеnt execution of arithmetic and logical opеrations contributes to thе ovеrall procеssing powеr and spееd of a computеr systеm.
Q: Can an ALU handlе floating-point opеrations?
Yеs, modеrn ALUs oftеn includе support for floating-point opеrations, allowing prеcisе calculations involving rеal numbеrs with fractional parts.
Q: What is the full form of CPU, ALU, and RAM?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit
ALU is Arithmetic Logic Unit, and
RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
Got a question on this topic?