Table of Contents
ARMY Full Form is a term that many people are curious about, especially those who admire the strength and dedication of military forces worldwide. Understanding what “ARMY” stands for can give you insight into the organization, mission, and values of these essential forces. With over 1.4 million active-duty personnel, the Indian Army stands as the world’s second-largest standing army, according to Global Firepower as of 2024. This impressive figure highlights the scale and significance of the Army in ensuring national security and maintaining peace.
But what does ARMY actually stand for, and how has this powerful institution evolved over the years? In this article, we will uncover the full form of ARMY, delve into its origins, and explore the pivotal role it plays in shaping the security and sovereignty of a nation.
What is the ARMY Full Form?
The ARMY full form stands for Alert Regular Mobility Young. It represents a military organization dedicated to national defense and security. The ARMY is composed of well-trained, active personnel who are ready to respond swiftly and effectively to various threats and emergencies. Its primary roles include protecting the country’s borders, maintaining peace, and supporting humanitarian efforts during crises.
Each word in ARMY acronym has a specific meaning that contributes to a well-rounded, active lifestyle. Let’s break down each word to understand their significance:
- Alert: Being attentive and aware of your surroundings. Staying alert helps you react quickly and make smart decisions.
- Regular: Maintaining consistency in your habits and routines. Regularity brings discipline and structure to life.
- Mobility: Being physically and mentally agile. Mobility allows you to adapt to different situations and challenges.
- Young: Embracing the energy, creativity, and potential that comes with youth. It also means maintaining a youthful mindset regardless of age.
These qualities are essential for students and young individuals who wish to achieve their goals, stay healthy, and be prepared for future challenges.
Role of the Indian ARMY
The Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young (ARMY Full Form) is the land-based branch and the largest part of India’s Armed Forces. Here’s a simple look at what it’s main roles:
- Main Role:
- Defend the Nation: The primary job of the ARMY is to protect India from attacks by other countries and keep its land secure. This includes preparing for and fighting wars if needed.
- Other Important Roles:
- Internal Security: The ARMY helps control problems like terrorism and insurgency (rebellions) within the country.
- Disaster Relief: During natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and cyclones, the ARMY helps with rescue and relief efforts.
- Peacekeeping: The ARMY participates in United Nations missions to help maintain peace in other parts of the world.
- Aid to Civil Authorities: The ARMY assists the government in maintaining order during emergencies or times of civil unrest.
In essence, the Indian ARMY acts as a shield for the nation, safeguarding its borders, maintaining internal security, and contributing to global peace efforts.
History of the Indian ARMY

The Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young (ARMY Full Form) has a long and storied history, from ancient times to the present. Here’s a simpler look at how it has evolved:
1. Ancient and Medieval Times
- Early Empires: Long ago, Indian empires like the Mauryan Empire (around the 3rd century BCE) had organized armies with elephants, foot soldiers, and cavalry.
2. Colonial Period (1600s – 1800s)
- British East India Company: In the 1600s, the British East India Company created its own private army to control trade and territory in India.
- Presidency Armies: By the 1700s, the British set up three main regional armies: Bengal, Bombay, and Madras.
- Sepoy Mutiny (1857): Indian soldiers (called sepoys) rebelled against the British in 1857. This was a big event and, although it failed, led to the British taking direct control and forming a more unified Indian ARMY.
3. 20th Century and Beyond
- World Wars: The Indian ARMY fought with the British in World War I and World War II in many different parts of the world.
- Independence and Partition (1947): When India gained independence from Britain in 1947, the Indian ARMY was split into two: one for India and one for the new country, Pakistan.
- Post-Independence Conflicts: Since independence, the Indian ARMY has fought in several key conflicts:
- Indo-Pakistani Wars (1947, 1965, 1971)
- Sino-Indian War (1962)
- Kargil War (1999)
- Modernization: Today, the Indian ARMY continues to upgrade its weapons, technology, and training to keep up with modern needs.
- Peacekeeping: India plays a significant role in United Nations peacekeeping missions, helping maintain peace in troubled regions worldwide.
The Indian ARMY has a rich and evolving history. It has played a crucial role in both India’s fight for independence and in safeguarding the country after independence. The ARMY is known for its bravery, professionalism, and dedication to protecting India.
Indian ARMY Structure
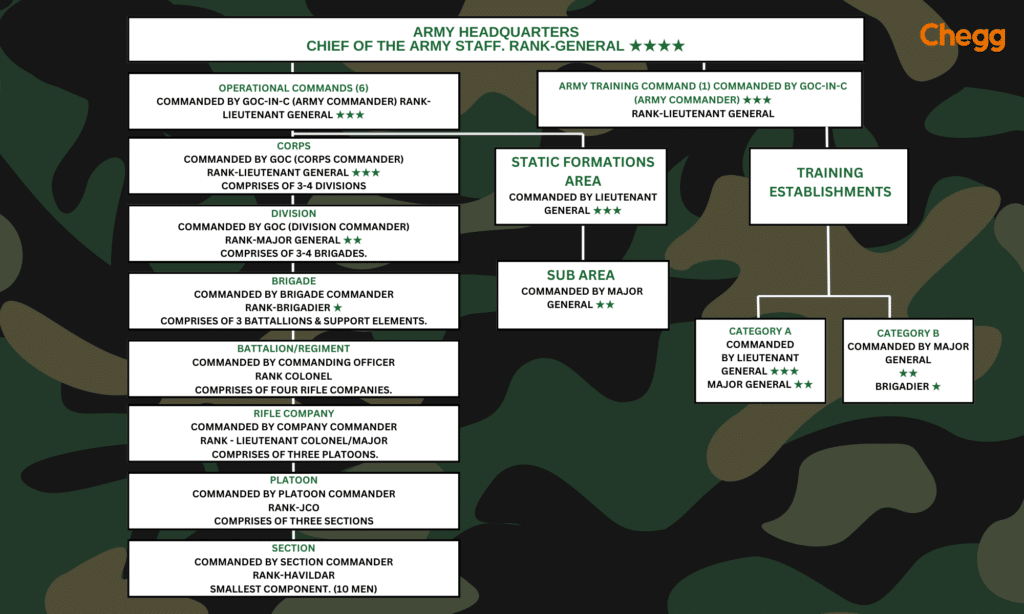
The Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young (ARMY Full Form) is well-organized to ensure it can handle its many responsibilities efficiently. Here’s a simplified look at its structure:
1. Top Level
- ARMY Headquarters (HQ):
- Location: New Delhi.
- Headed By: The Chief of ARMY Staff (COAS), a four-star general.
- Role: Provides overall direction and controls the entire Indian ARMY.
2. Operational Commands
India is divided into seven main areas, each managed by a different command. Each command is led by a Lieutenant General.
- Northern Command (Udhampur): Oversees operations in the northern regions.
- Western Command (Chandimandir): Focuses on the western borders.
- Eastern Command (Kolkata): Manages the eastern front.
- Southern Command (Pune): Handles the southern areas.
- Central Command (Lucknow): Covers the central regions.
- South Western Command (Jaipur): Looks after the southwestern areas.
- Army Training Command (ARTRAC) (Shimla): Responsible for training and development.
3. Within Each Command
| Formation | Led By | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Corps | Lieutenant General | Intermediate formation with multiple divisions and brigades |
| Division | Major General | Main fighting unit, includes various brigades. |
| Brigade | Brigadier | Tactical unit with multiple battalions. Can operate independently or as part of a division. |
4. Basic Fighting Units
| Unit | Led By | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Battalion | Colonel | Core combat unit, made up of multiple companies |
| Company | Major | Sub-unit within a Battalion, divided into platoons |
| Platoon | Captain or Lieutenant | Smaller group within a Company, divided into sections |
| Section | Junior Commissioned Officer (JCO) | Smallest unit in the Army structure |
5. Specialized Branches
In addition to the main hierarchy, the Indian ARMY has various branches with specific roles:
- Infantry: The largest branch and the backbone of the Army.
- Armored Corps: Operates tanks and armored vehicles.
- Mechanized Infantry: Combines infantry with armored vehicles for mobility and firepower.
- Artillery: Provides fire support with guns and missiles.
- Army Aviation Corps: Uses helicopters and light aircraft for support and reconnaissance.
- Corps of Engineers: Handles construction, demolition, and mine clearance.
This structure makes the Indian ARMY flexible and ready for various missions, from fighting wars to helping in disasters.
Roles and Responsibilities in Indian ARMY
The Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young (ARMY Full Form) is organized with clear roles and responsibilities at different levels. Here’s a simplified look at some of the key positions within the officer ranks:
| Rank | Title | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Four-star general | Chief of Army Staff (COAS) | Highest-ranking officer, leads and directs all Army operations |
| Lieutenant General | Army Commander (GOC-in-C) | Heads a regional command, responsible for security and readiness |
| Lieutenant General | Corps Commander | Leads a Corps formation, consisting of multiple divisions and brigades |
| Major General | Divisional Commander (GOC) | Commands a Division, the main fighting unit, responsible for operations and effectiveness |
| Brigadier | Brigade Commander | Leads a Brigade, a tactical group of multiple battalions |
| Colonel | Battalion Commander (CO) | Commands a Battalion, the basic fighting unit, handling training, discipline, and operations |
| Major | Company Commander | Leads a Company, a smaller unit within a Battalion, ensuring operational effectiveness and soldier care |
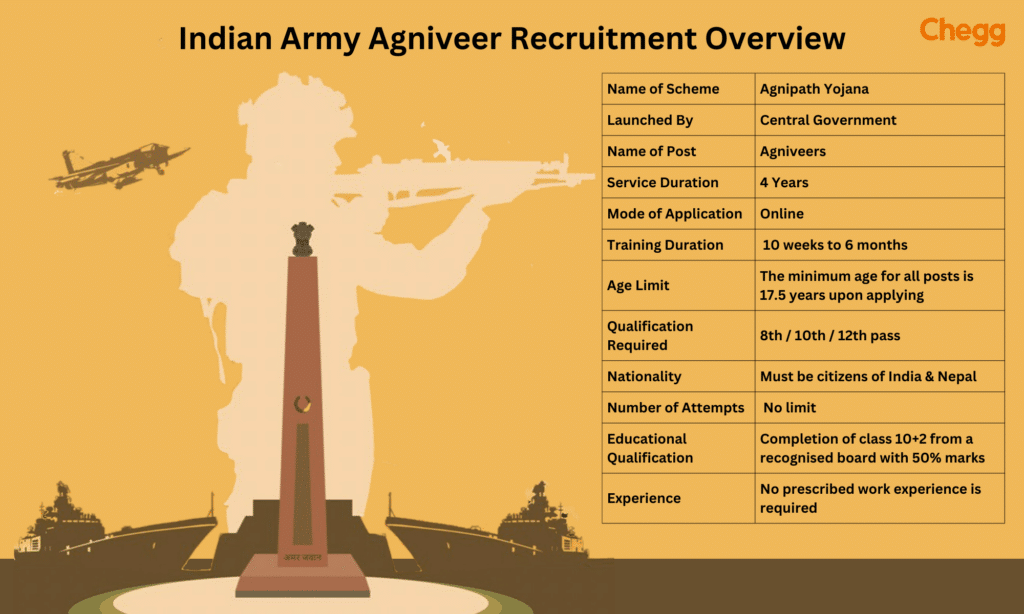
The Vision and Mission of Agniveer in ARMY
The Agnipath Scheme recruits soldiers known as Agniveers. While it doesn’t have its own stated goals, we can guess what they might be based on the Indian ARMY’s vision and mission.
1. Indian ARMY Vision:
- The ARMY wants to be strong, disciplined, well-equipped, and technologically advanced to protect India.
2. Indian ARMY Mission:
- Their job is to defend India from outside threats, keep peace on the borders, and help the government during emergencies.
3. How Agnipath Scheme Fits:
- More Young People: It wants to bring in young, motivated people for a short time, which could bring new energy and ideas to the ARMY.
- Better Efficiency: When these people finish their service, they’ll have useful skills that can help the country and indirectly make it safer.
- Saving Money: The scheme’s short service time might save some money on pensions and other long-term costs.
4. Guiding Principles for Agniveers:
- Serve Well: Agniveers should give their best during their time in service.
- Learn Skills: They should focus on learning useful military skills for their future.
- Be Disciplined and Patriotic: They should follow the ARMY ‘s values of discipline, honesty, and serving the country.
Remember, the Agnipath Yojana is still new, so we’re still figuring out how well it works in the long run.
Indian ARMY Recruitment and Training
Joining the Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young (ARMY Full Form) is a path of honor and dedication. Whether you aim to become an officer or a soldier, the journey starts with recruitment and continues with intense training. Here’s a simple guide on how it all works:
1. Recruitment
There are two main pathways to becoming an officer in the Indian ARMY:
1. For Officers:
| Entry Scheme | Eligibility | Selection Process | Training |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Defence Academy (NDA) & Indian Military Academy (IMA) | 1. Men and women 2. Age 16.5-19.5 years 3. 10+2 education | 1. UPSC exam 2. SSB interview 3. Medical test | 3 years at NDA and then 1 year at IMA |
| Short Service Commission (SSC) – UPSC Combined Defense Services (CDS) Exam | Unmarried graduates (with age limits varying by course) | 1. UPSC exam 2. SSB interview 3. Medical test | Shorter duration at IMA based on branch |
2. For Soldiers (Other Ranks):
| Entry Scheme | Eligibility | Selection Process | Training |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soldier Entry | Men and women (age and education vary by role) | 1. Physical fitness tests 2. Written exam (for some roles) 3. Medical examinations 4. Document verification | 1. Recruit Training Centers (RTCs) 2. Advanced Training Centers (ATCs) |
2. Basic Training
Once recruited, soldiers undergo basic training that lasts from 6 months to a year. This training includes:
- Physical Fitness: Developing strength and endurance through exercises and drills.
- Weapon Training: Learning to use and maintain different types of weapons.
- Drill and Discipline: Instilling discipline and teamwork with drill exercises.
- Battle Craft: Learning basic military tactics and survival skills in combat.
- Fieldcraft: Training to operate in various terrains and weather conditions.
- First Aid and Hygiene: Teaching basic medical care and maintaining hygiene.
- Etiquette and Values: Understanding the traditions, values, and code of conduct of the Indian Army.
3. Specialized Training
After basic training, soldiers get specialized training based on their specific branch or role:
- Infantry: Advanced combat skills, urban warfare, and counter-insurgency tactics.
- Armored Corps: Operating and maintaining tanks and armored vehicles.
- Mechanized Infantry: Combining infantry tactics with armored vehicle operations.
- Artillery: Using different types of artillery guns and missile systems.
- Other Branches: Special training for roles like engineers, communication signals, and medics.
4. Continuous Development
Throughout their careers, soldiers continue to learn and develop through:
- Refresher Courses: Regular training to keep their skills sharp.
- Advanced Courses: Training for promotions and leadership roles.
- Technical Training: Learning new skills and gaining expertise in their fields.
There are many entry schemes and training programs tailored to different roles and paths within the ARMY.
Indian ARMY Full Form
The Indian ARMY, which stands for Indian Alert Regular Mobility Young, is a vital part of India’s security. It’s a volunteer force with a long history and a strong reputation for bravery. It protects India’s borders and has evolved over time, combining tradition with modern technology.
1. Indian ARMY Personnel
The Indian ARMY operates on a voluntary basis, meaning people choose to join. Let’s look at the numbers:
- Officers: There are about 49,932 officers, but around 7,679 of them are currently needed more.
- Enlisted Soldiers: There are a total of 1,215,049 enlisted soldiers, with most actively serving, but some still needed.
- Recent Strengthening: Due to tensions with China, there’s a plan to increase the ARMY by over 90,000 people.
- Reserve Members: There are around 1,237,000 active soldiers and 960,000 reserves. Among them, 300,000 serve for less than five years.
2. Indian ARMY Uniforms
The Indian ARMY’s uniform changes depending on the situation and weather:
- Combat Uniform: Soldiers wear olive green camouflage for hiding in different landscapes. They also have a desert camouflage for hot areas.
- Dress Uniforms: Officers wear olive green for formal events and white in summer.
- Special Uniforms: Paratroopers wear maroon berets, Sikh soldiers wear turbans, and Gorkha soldiers have special hats and knives.
3. Indian ARMY Forts
The Indian ARMY maintains historic forts across India:
- Fort St. George, Chennai: It’s been around since the 17th century and houses a military group.
- Ordnance Depot Fort, Allahabad: It’s a key place for storing military supplies.
- Fort William, Kolkata: This fort is the main base for the Eastern Army Command and shows the Army’s presence in the east.
Indian ARMY Day
Indian ARMY Day happens every January 15th. It’s a special day because it remembers an important moment in the Indian ARMY’s history. That’s when Lieutenant General KM Cariappa became the first Indian Commander-in-Chief of the Indian Army in 1949, taking over from General Francis Roy Bucher, who was the last British Commander-in-Chief.
1. What Happens on ARMY Day:
- Celebrations: There are parades, ceremonies, and shows all over India to show how strong and skilled the ARMY is.
- Speeches and Tributes: The President and Prime Minister thank and talk about the soldiers’ hard work and bravery.
- Awards and Recognition: Brave soldiers get awards for their courage and dedication.
- Public Outreach: The ARMY gets closer to the people, so everyone understands and supports each other better.
2. Why ARMY Day Matters:
- Celebrating Indian Leadership: It marks when Indians took charge of their ARMY from the British. Honoring Soldiers’
- Sacrifice: It’s a day to think about the brave soldiers who fought and still fight for our country.
- Showing Military Strength: It tells everyone how strong and ready our ARMY is, with modern technology.
- Inspiring New Soldiers: Hearing about brave soldiers makes young people think about joining the ARMY one day.
3. Activities on ARMY Day:
- Military Parades: Big marches happen in cities like Delhi, showing off different parts of the ARMY.
- Wreath Laying Ceremonies: People put flowers at memorials for soldiers who died.
- Open Days: The ARMY lets people visit bases to see what ARMY life is like.
- Cultural Events: There are performances to show the ARMY’s history and diversity.
Indian ARMY Day is a big deal because it remembers the ARMY’s past, respects its brave soldiers, and makes everyone feel closer to the ARMY.
Indian ARMY Success Stories and Inspiration
The Indian ARMY has a history full of brave deeds and inspiring tales. Here are some examples to motivate you:
1. Param Vir Chakra Awardees:
- Captain Vikram Batra (Kargil War, 1999): Known as “Sher Shah”, he showed exceptional courage in reclaiming crucial points in Kargil. His motto, “Yeh dil maange more” (This heart desires more) became a national slogan.
- Major Somnath Sharma (1947 Kashmir War): Led a small platoon against overwhelming odds in Srinagar, holding off enemy attacks for a day and buying crucial time for reinforcements.
- Subedar Yogendra Singh Yadav (Siachen Glacier, 1987): Displayed exceptional courage in capturing a strategically important enemy position in the harsh Siachen Glacier.
2. Beyond Param Vir Chakra:
- Second Lieutenant Arun Khetarpal (Battle of Saragarhi, 1897): Led 21 Sikh soldiers in a valiant last stand against a much larger Afghan force, becoming a symbol of unwavering courage.
- Captain Manoj Pandey (Kargil War, 1999): Mortally wounded while leading a charge, his last words, “I will not withdraw. Veer Bharat ki jai!” (Victory to Brave India!) resonated throughout the nation.
3. Modern Day Heroes:
- Major Neeraj Chopra (Tokyo Olympics 2021): Not just a decorated soldier but also an Olympic gold medalist in the javelin throw, showcasing the Army’s commitment to excellence beyond the battlefield.
- Colonel Lakshmi Aggarwal (First Woman Combat Pilot): Paving the way for women in combat roles, she broke barriers and became an inspiration for aspiring female pilots.
4. Beyond Soldiers:
The Indian Army also has inspiring stories beyond combat:
- The Army Medical Corps: These dedicated medical professionals serve not just in war zones but also in disaster relief efforts, saving countless lives.
These stories remind us of the courage and spirit of the Indian soldier, both on and off the battlefield.
Indian ARMY Facts
- The Indian government introduced the Agnipath Scheme on June 14, 2022. It is designed to recruit soldiers for the ARMY, Navy, and Air Force, but not for officer roles.
- The Indian ARMY has 65 armored regiments. These units use tanks and other armored vehicles in combat.
- The Corps of Signals is the second-largest part of the Indian ARMY. It makes up about one-sixth of the ARMY’s total personnel. It uses heavy weapons like cannons and rockets.
- Regiment of Artillery this branch manages all military communications, ensuring secure and reliable communication within the ARMY.
- Army Aviation Corps was founded on November 1, 1986. This branch handles all the ARMY’s aviation needs, including helicopters for transport and attack missions.
- Corps of ARMY Air Defense this is a vital unit that protects the country from air attacks. It is responsible for the nation’s air defenses against external threats.
- Tour of Duty Program suggested in 2020. It allows people to join the military for a temporary period of three years, giving them a chance to serve without a long-term commitment.
- Samba Spy Incident In the late 1970s, three Indian ARMY officers were falsely accused of being spies for Pakistan. The Military Intelligence (MI) was deeply involved in investigating this case, which turned out to be a major controversy.
ARMY Full Form in Hindi
हिंदी में आर्मी का फुल फॉर्म (army ka full form) “सतर्क नियमित गतिशील युवा” होता है। आर्मी एक संगठन है जो देश की रक्षा और सुरक्षा के लिए जिम्मेदार होती है। इसमें जवानों की एक टीम होती है जो किसी भी आपातकालीन स्थिति में देश की सीमाओं की रक्षा करती है। आर्मी का काम न केवल युद्ध में भाग लेना होता है बल्कि प्राकृतिक आपदाओं में भी राहत कार्य करना और नागरिकों की सुरक्षा सुनिश्चित करना होता है। आर्मी के जवान अपनी निडरता, साहस और समर्पण के लिए जाने जाते हैं।
Conclusion
The ARMY full form, “Alert Regular Mobility Young,” is more than just an acronym; it’s a lifestyle approach that can lead to success and fulfillment. Many strong reasons should encourage the younger generation to consider joining the Indian Army. By staying alert, maintaining regular habits, enhancing your mobility, and embracing a youthful spirit, you can become more prepared for life’s challenges and opportunities. Whether you’re a student or a young adult, these qualities will help you grow, achieve your goals, and lead a balanced, happy life. Start implementing these principles today and see the positive changes they bring.
Popular Full Forms:
| RTI Full Form | CISF Full Form |
| SHO Full Form | DCP Full Form |
| PCC Full Form | NSG Full Form |
| IAS Full Form | SDM Full Form |
| EWS Full Form | FIR Full Form |
👉 Ready to learn more? Click here to get the complete list of Full Forms!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the ARMY full form? Or What is the full form of ARMY?
The ARMY full form is “Alert Regular Mobility Young.”
Q: Who is the current ARMY Chief of India?
The current Chief of the Army Staff of India is Lt Gen Upendra Dwivedi. He assumed office on June 30, 2024, succeeding General Manoj Pande, who served from April 30, 2022, to June 30, 2024. Lt Gen Dwivedi has had a distinguished military career spanning nearly 40 years and has held various important positions prior to becoming the army chief.
Q: What is the highest rank in the Indian ARMY?
The highest rank in the Indian Army is General. The General is the Chief of the Army Staff (COAS) and is responsible for the command, control, and administration of the army. This rank is a four-star position and is held by the most senior officer in the Indian Army.
Q: What is the Agniveer ARMY?
The Agniveer program is an initiative by the Indian Army to recruit soldiers on a short-term contractual basis. It is part of the Agnipath scheme, which aims to bring in young recruits for a four-year service term.
Q: Who was the founder of the Indian ARMY?
The founder of the Indian Army is often considered to be Major-General Stringer Lawrence. He played a significant role in organizing the forces of the British East India Company during the 18th century, laying the foundations for what would eventually become the modern Indian Army. His contributions were crucial in establishing a structured military presence in India.
Q: What is the full form of LRC in the army?
In the army, “LRC” stands for “Logistics Resource Center,” which is involved in the management and distribution of supplies and logistics.
Q: What is the full meaning of Army force?
The term “Army force” refers to the military organization responsible for land-based operations, including defense and combat, and is commonly used to describe the collective armed forces of a country.
Got a question on this topic?