Table of Contents
What is RSA Full form?

RSA full form is Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, an algorithm commonly used in cryptography for secure communication, data protection, and digital signatures. MIT colleagues Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman founded RSA in 1977, deriving its name from the initials of their surnames. They were intrigued by the study of public-key cryptography (PKC), invented in 1976 by Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman, and Ralph Merkle. Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman created cryptographic algorithms and procedures to enable secure encoding and decoding of communications between communicating parties.
Establishment and Expansion of RSA
In RSA cryptography, communication may be encrypted using public and private keys. Use the opposite key that was used to encrypt the message to decode it. One of the reasons it has become the most widely used asymmetric algorithm is that it provides a means for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, reliability, and non-repudiation of electronic communication and information storage.
Overview of the Creation and Evolution of RSA
Over the years, the RSA algorithm in full form has undergone significant developments to better its security and efficiency. Key milestones include:
- Introducing larger key sizes.
- Advancements in encryption and decryption operations.
- Creating quicker methods for prime number production.
These improvements have helped increase the security of Rivest-Shamir-Adleman and assure its continuous relevance in the ever-evolving world of cryptography.
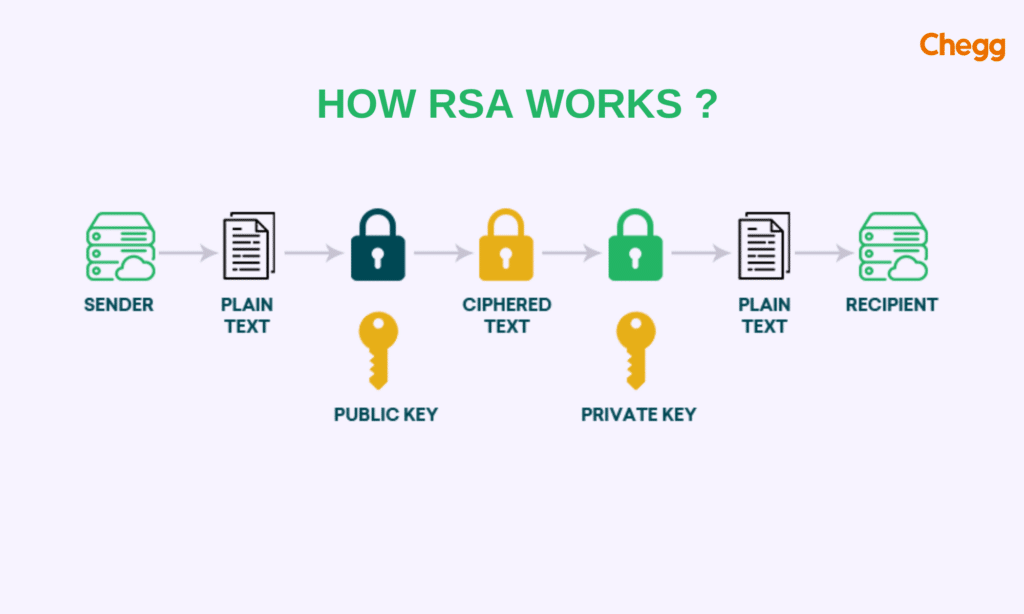
How RSA Works as a Cryptographic Algorithm
Understanding the Notion and Scope of RSA
RSA full form is Rivest-Shamir-Adleman. It is a public-key cryptography technique that employs two separate keys for encryption and decoding. Users widely circulate and use the public key for encryption, while they keep the private key secret and use it for decoding. The security relies on the mathematical difficulty of factoring huge prime integers.
Importance of RSA as a Frequently Used Cryptographic Algorithm
RSA stands for essential in the world of cryptography because of its adaptability and security. It offers a safe means for delivering sensitive information across unsecured networks, maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the data. It is utilized in several applications, including secure email communication, online banking, e-commerce transactions, and digital signatures.
Principles of RSA Cryptography
- RSA is based on three fundamental concepts: public-key encryption, private-key decryption, and digital signatures.
- Using public-key encryption, the sender utilizes the recipient’s public key to encrypt data.
- The receiver can decode the encrypted data solely with the corresponding private key, which they keep secret.
- Thanks to public-key encryption, only the intended receiver may decode and access the data.
- Digital signatures enable the authentication and integrity of digital documents.
- Encrypting a hash value of the document with the sender’s private key yields a digital signature.
Key Generation in RSA
Generation of public and private key pairs in RSA
The critical generation procedure in RSA means producing a pair of mathematically linked keys: public and private keys. Multiplying two large prime numbers creates the public key while deriving the private key from these prime numbers and distinct characteristics. The crucial generation process ensures the concealment of the private key while sharing the public key.
Security Concerns and Key Length Recommendations
The security of RSA depends on the difficulty of factoring huge prime integers. As computational power grows over time, higher key lengths are recommended to retain the same degree of security. It is vital to employ appropriately long keys to guard against possible attacks and preserve the secrecy of encrypted data.
Encryption and Decryption in RSA
Process of Encryption Using the RSA Algorithm
The sender utilizes the recipient’s public key to encrypt a message using RSA to conduct the encryption procedure. The process involves transforming the message into numerical form and performing modular exponentiation on the numerical representation of the message using the recipient’s public key. The resulting ciphertext can only be decrypted with the recipient’s private key.
Process of Decryption Using the RSA Algorithm
The receiver of an encrypted communication uses their private key to decode the ciphertext and retrieve the original message. The receiver uses modular exponentiation with their private key to reverse the encryption process and get the plaintext message. To ensure that only the intended receiver can decode the communication, one keeps the private key secret.
RSA and Data Security
Applications of RSA in Secure Communication and Data Protection
Organizations deeply utilize it in applications that require secure communication and data security. It finds use in secure email protocols, virtual private networks (VPNs), secure socket layer (SSL) for safe online browsing, and secure file transfer protocols. Securing sensitive information during transmission is crucial for ensuring data security and privacy.
Strengths and Vulnerabilities of the RSA Algorithm
While RSA stands for a powerful and widely deployed cryptographic technique, it has weaknesses. One of the flaws of RSA meaning is the prospect of quantum computers, which might factor in big numbers effectively and jeopardize RSA’s security. However, continuing research and the development of post-quantum cryptography attempt to solve this weakness and offer alternative safe encryption techniques.
RSA in Digital Signatures and Authentication
RSA is crucial in maintaining the integrity and validity of digital communications via digital signatures.
- Through digital signatures, Rivest-Shamir-Adleman ensures message integrity and authenticity.
- RSA digital signatures confirm the integrity of a message during transport and verify its origin from the stated sender.
- Various applications deeply employ digital signatures based on this, including electronic transactions, software distribution, and identity verification.
- When producing a digital signature, the sender encrypts the message’s hash value with their private key, resulting in a unique signature.
- Using the sender’s public key, the recipient may verify the signature.
- Digital signatures based on Rivest-Shamir-Adleman provide a secure technique for certifying the sender’s identity and protecting the integrity of digital documents.
Advantages of RSA
- You can easily implement the RSA algorithm.
- Transmitting sensitive data is safe and secure when using the RSA algorithm.
- Because the RSA algorithm requires complicated mathematics, it is very difficult to crack.
- Public key distribution to users is simple.
Disadvantages of RSA
- It can sometimes fail because RSA only employs asymmetric encryption, whereas full encryption requires both symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
- The large number of participants causes the data transfer rate to be slow.
- Sometimes, Verifying the validity of public keys requires the involvement of a third party.
- The recipient’s end requires high processing power for decryption.
- RSA is not suitable for encrypting public data, such as election voting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the acronym RSA stands for Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, representing a widely used cryptographic algorithm that plays a critical role in providing secure communication, data security, and digital signatures. Developed by Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in 1977, the RSA algorithm in full form has experienced substantial development and advances. It offers a safe mechanism for encrypting and decrypting communications, developing digital signatures, and verifying the validity of digital documents. Despite possible weaknesses, It is a cornerstone of contemporary cryptography, and its contributions to data security and digital communication are essential. The Rivest-Shamir-Adleman algorithm continues to alter the landscape of secure communication and cryptography, protecting the secrecy and integrity of critical information in the digital era.
| LPG full form | |
| LIC full form | SDM full form |
| SUV full form | PPS full form |
| PFMS full form | IMDB full form |
| SC full form | PRO full form |
RSA Full Form: FAQs
Where are RSA keys used?
The RSA private key is used to create digital signatures, while the public key is used to validate them.
What kind of key is RSA?
The RSA key is a private key based on the RSA algorithm.
Is the RSA key fingerprint safe?
Yes, the fingerprint is just a hash of the public key used to confirm it.
How long does an RSA key signature last?
The signature consists of a 1024-bit integer. This signature size is equivalent to the RSA key size.
Is RSA a trustworthy cryptographic algorithm?
Yes, It is a trustworthy cryptographic algorithm. As explained in the complete form of RSA, it is a dependable but slow processing procedure that employs prime numbers, a factoring issue, and the computation of mod values.
Got a question on this topic?