
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
India’s march towards independence was not a straight road but a long, winding journey filled with events that stirred national consciousness and united the masses. One such major turning point was the Simon Commission. Introduced at a critical time, the Simon Commission became a lightning rod for Indian political movements, protest marches, and a collective demand for self-governance. This article dives deep into the history, purpose, criticism, boycott, and long-term impact of the Simon Commission, while highlighting key events that reshaped the Indian freedom movement.
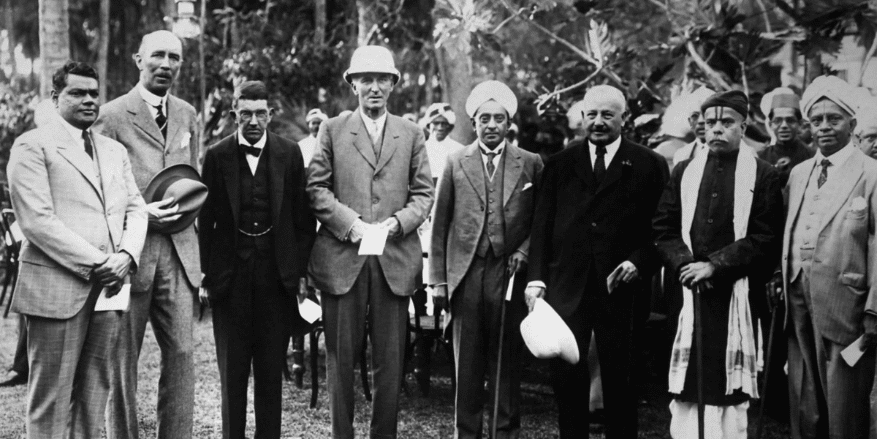
The Simon Commission, officially known as the Indian Statutory Commission, was a group of seven British Members of Parliament under Sir John Simon’s leadership. The British government formed it in 1927, thus often referred to as the Simon Commission 1927, to review the functioning of the Government of India Act 1919. The key objective was to evaluate the need for further constitutional reforms in British India.
However, the primary reason for the intense backlash was that no Indian was included in the commission. This ignited a national movement questioning, “Why was the Simon Commission sent to India if it excluded Indian representation?” The absence of Indian members made the commission’s legitimacy highly questionable in the eyes of the Indian public.
Key Highlights:
The Simon Commission arrived in India on February 3, 1928, sparking nationwide protests. Despite its official intent to recommend reforms, the commission’s lack of an Indian member led to its outright rejection by political parties.
When the Simon Commission arrived in India, it faced black flag processions and protests under the rallying cry, “Simon Go Back.” Major political groups such as the Indian National Congress, the Muslim League, and other regional parties openly condemned its formation and arrival.
Notable Incident: In Lahore, a peaceful protest led by Lala Lajpat Rai turned violent when police conducted a brutal lathi charge. Rai was critically injured and later died from his wounds, turning him into a national martyr.
Despite its controversial composition, the stated objective of the Simon Commission was to:
But many questioned, “Why was Simon Commission sent to India without Indian participation?” The British government’s exclusionary approach exposed its intent to retain control while giving the illusion of reform.
The official purpose of the Simon Commission was to:
While these may have seemed progressive on paper, the exclusion of Indian voices in shaping their own governance rendered the entire exercise deeply problematic. Most Indians viewed the Commission as a tool to delay genuine self-rule and continue colonial dominance under the guise of administrative review.
The criticism of the Simon Commission came from all corners of Indian political life. Even moderate leaders who had earlier worked with British institutions were disillusioned by the racial arrogance and lack of consultation.
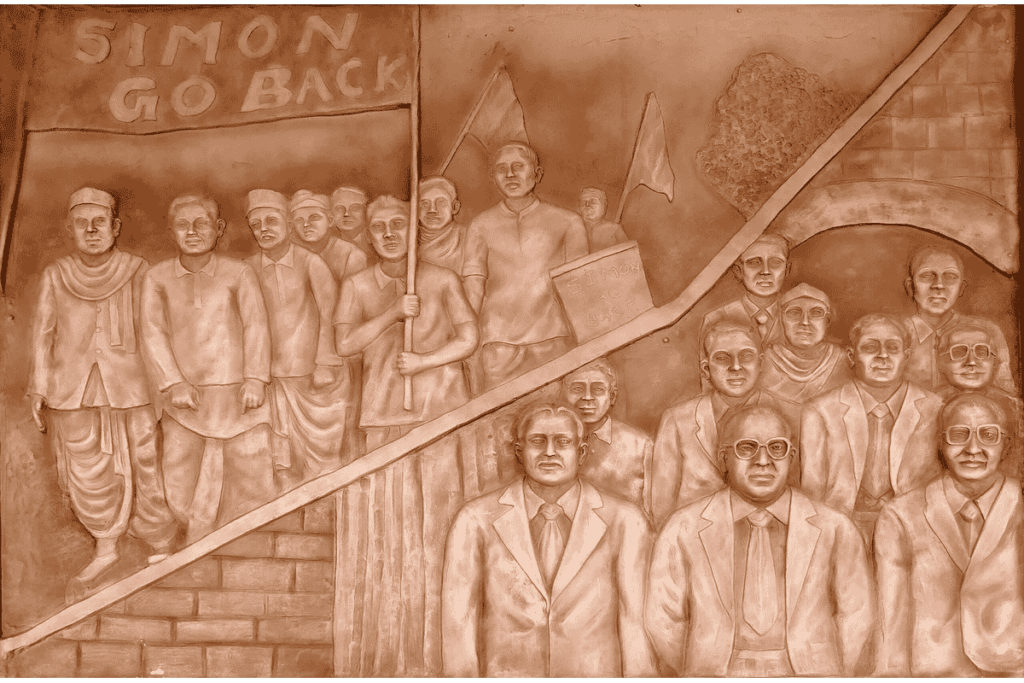
Key Indian leaders, including Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhas Chandra Bose, Sardar Patel, and others, rallied against the Commission, calling it a blatant betrayal of Indian aspirations.
The Simon Commission boycott became a powerful act of civil resistance. The Indian National Congress, under the leadership of figures like Jawaharlal Nehru, declared that no constitution would be accepted unless drafted with Indian input.
The boycott of the Simon Commission became a nationwide movement. The Indian National Congress formally decided to boycott the commission in 1927, declaring that any constitution made without Indian participation was unacceptable.
Interestingly, even sections of the Muslim League, which had previously cooperated with the British, joined the boycott—showing the growing unity among Indian political forces.
The only exception came from the Justice Party in Madras, which chose not to boycott, primarily due to their opposition to the Congress and caste-based concerns. The chant “Simon Go Back” echoed through every Indian city. Except for the Justice Party in Madras, all major political groups participated in the boycott, showing rare unity in India’s fractured political landscape.
1. Lala Lajpat Rai’s Death: A turning point came on October 30, 1928, in Lahore. During a peaceful protest against the Commission, Lala Lajpat Rai was severely injured by police and died soon after. His death became a rallying cry against British repression.
2. Bhagat Singh’s Revolutionary Response: Bhagat Singh, along with Rajguru and Sukhdev, assassinated British officer John Saunders in December 1928 as an act of revenge for Rai’s death. This bold act drew attention to the growing revolutionary fervor inspired by the Commission.
3. Civil Disobedience Movement: The Commission’s rejection laid the foundation for the 1930 Civil Disobedience Movement, signaling a shift from cooperation to confrontation.
The Simon Commission, officially known as the Indian Statutory Commission, marked a defining moment in India’s fight for independence. Despite being widely rejected across the country, it played a crucial role in reshaping the trajectory of India’s freedom movement. From constitutional reforms to the rise of revolutionary nationalism, the Simon Commission 1927 had far-reaching implications that accelerated the demand for complete self-rule.
One of the most lasting effects of the Simon Commission was the Indian counter-response, The Nehru Report (1928), led by Motilal Nehru and supported by key leaders including Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhas Chandra Bose, and M.R. Jayakar.
The Simon Commission’s arrival in India united Indians across political and religious divides:
The protests marked the resurgence of mass civil agitation not seen since the Non-Cooperation Movement and brought a renewed sense of national unity.
The official Simon Commission recommendations, submitted in 1930, included:
These suggestions were seen as inadequate and failed to address India’s demand for self-governance. However, the British were forced to acknowledge the strength of Indian resistance:
Although the Simon Commission year was 1927, its delayed report directly influenced the drafting of the Government of India Act 1935, the most significant constitutional reform before independence.
Key elements from the Commission’s influence included:
The Simon Commission also had unintended yet profound consequences on India’s revolutionary landscape:
This act sparked a wave of youth-led movements and gave rise to the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA), reshaping the revolutionary agenda against British rule.
The global response to the events surrounding the Simon Commission in India added international momentum to India’s independence movement:
This helped shape global public opinion in favor of Indian independence in the future.
Though the Simon Commission 1927 failed in its original mission to propose inclusive reforms, it ended up being a watershed moment in India’s freedom struggle. The exclusion of Indians, the violent suppression of protests, and the unity of political voices against it set in motion critical events:
Most importantly, it sharpened India’s resolve for independence and exposed the colonial government’s unwillingness to share power. The Nehru Report, Simon Go Back movement, and Round Table Conferences emerged directly due to the Commission. The death of Lala Lajpat Rai and subsequent revolutionary activities created national heroes who inspired generations.
The Simon Commission’s failure was not just about policy; it was about representation, dignity, and national pride. It brought diverse political forces together, led to martyrdom and revolutionary awakening, and accelerated India’s demand for freedom.
Understanding the Simon Commission is crucial for students preparing for UPSC, SSC, and other government exams. It helps them grasp the transformational phase of India’s independence movement.
Read More:
Hindustan Socialist Republican Association
Hindustan Socialist Republican Association
The British created Simon Commission to check the governments administration abilities running at that time in India. It was aimed to examine the Government of India act of 1919.
The Simon Commission of 1919 was created to check the effectiveness of the administrative provisions outlined in the Government of India Act of 1919. Under the Stanley Baldwin’s guidance the efficacy of the
The Commission was led by Sir John Simon, a British statesman and lawyer. He served as the chairman of the seven-member all-British commission formed in 192
The slogan raised against the Commission was “Simon Go Back”. It became a unifying cry of protest across India during its arrival in 1928.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.