Quick Summary
Table of Contents
This article has 10 points about Rani Laxmi Bai that will tell us about her bravery and patriotism. In the nineteenth century, Rani Laxmi Bai was born into a Maharashtrian family at Kashi, Varanasi. Later on, she was remembered for her bravery and courage. 10 points about Rani Laxmi Bai are insufficient to describe her contribution to the Indian freedom struggle, so read carefully in detail.
Shubhdra Kumari Chauhan beautifully describes her contribution in one of her poems. The lines are “Khoob ladi mardaani woh toh Jhanshi wali rani Thi”. So, who is ‘Rani Lakshmi Bai’? She is an example of bravery and women’s empowerment, too. She is still an inspiration for many women fighting against discrimination in society. All of Rani Lakshmi Bai’s information in this article is well-researched.
Here is a list of 10 lines on Rani Lakshmi Bai in English that kids and Students can easily include in their essays:
Rani Lakshmi Bai, also known as the Queen of Jhansi, is one of the most iconic figures in Indian history, renowned for her courage, leadership, and determination during the Indian Rebellion 1857. Born as Manikarnika Tambe on November 19, 1828, in Varanasi, she married Maharaja Gangadhar Rao of Jhansi at a young age. After her husband died in 1853, Lakshmi bai was left to govern the princely state of Jhansi, which faced political and social upheaval during the British colonial rule.
1857, when the First War of Indian Independence broke out, Lakshmi Bai became a symbol of resistance against British oppression. The British attempted to annex Jhansi under the Doctrine of Lapse, claiming that her adopted son was not a legitimate heir. Rani Lakshmi Bai, refusing to surrender, led her troops to defend her kingdom. She fought valiantly, displaying exceptional military strategies and leadership on the battlefield. Despite her brave efforts, Jhansi fell to the British after a prolonged siege.
However, her resistance did not end there. After the fall of Jhansi, she continued to lead the rebels and participated in several battles, becoming a symbol of India’s fight for independence. Rani Lakshmi Bai’s bravery and resolve during the revolt made her a hero and a martyr. She died on June 18, 1858, in the battle of Gwalior, fighting for her country’s freedom.
Rani Lakshmi Bai’s legacy is remembered as a beacon of strength, resilience, and patriotism. She inspired countless individuals, especially women, to fight for justice and equality. Her life is a testament to the indomitable spirit of resistance against tyranny and oppression. Today, she is remembered as a national heroine, and her contributions to India’s struggle for independence continue to inspire generations.
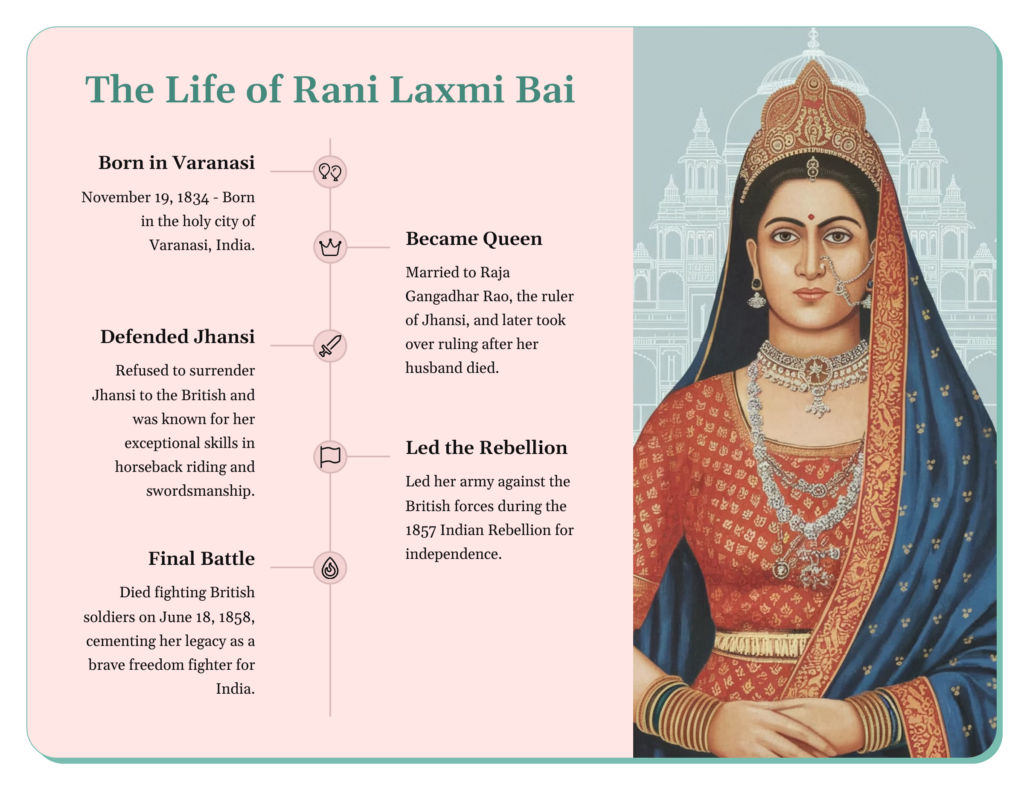
Rani Lakshmi Bai, the Queen of Jhansi, is remembered as a symbol of courage, leadership, and patriotism in Indian history. Born on November 19, 1828, in Varanasi as Manikarnika Tambe, she was trained in martial arts, archery, and horse riding, preparing her for a remarkable role in Indian history. At 14, she married Maharaja Gangadhar Rao of Jhansi and became Lakshmi bai. The couple adopted a son, Damodar Rao, as their heir.
1853, after the Maharaja’s death, the British East India Company invoked the Doctrine of Lapse, which threatened to annex Jhansi. Rani Lakshmibai refused to surrender her kingdom, and during the Indian Rebellion 1857, she became one of the central figures in the fight for independence. Her leadership and military strategies were crucial in organizing her forces, including men and women soldiers, to defend Jhansi against the British forces. She displayed exceptional courage, even leading her troops in battle and inspiring her soldiers with her resolve to protect her kingdom.
Despite fierce resistance, the British captured Jhansi after a prolonged siege in March 1858. However, Lakshmi Bai managed to escape and continued her resistance. She joined forces with other freedom fighters, including Tantia Tope, and moved to Gwalior, where she fought valiantly to reclaim the city from the British. Her determination and leadership remained unmatched, and she became a beacon of hope for the Indian rebels.
On June 18, 1858, during a battle near Gwalior, Rani Lakshmi bai was mortally wounded while riding her horse, fighting alongside her troops. She died while holding her adopted son, symbolizing her dedication as both a mother and a warrior. Her death marked the end of her direct involvement in the rebellion, but her legacy symbolized India’s resistance to British colonial rule.
Rani Lakshmi Bai’s bravery, unwavering commitment to her people, and leadership during the rebellion earned her a place as one of India’s most iconic national heroines. Today, she is remembered through statues, memorials, and her portrayal in literature and films. Her life inspires generations, particularly women, as a symbol of courage, resilience, and the fight for freedom.
खूब लड़ी मर्दानी वह तो झाँसी वाली रानी थी॥ खूब लड़ी मर्दानी वह तो झाँसी वाली रानी थी॥ हो मदमाती विजय, मिटा दे गोलों से चाहे झाँसी। खूब लड़ी मर्दानी वह तो झाँसी वाली रानी थी॥
Rani Lakshmi Bai, or Manikarnika Tambe, also known as the Rani of Jhansi, was a prominent figure in Indian history. She is mainly known for her resistance against the British East India Company during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Here’s a summarized biography of Rani Lakshmi Bai and her legacy. There are many important events in Rani Lakshmi Bai’s history and struggle for freedom.
Her journey was remarkable, with ups and downs in her life. Her father worked under Peshwa Baji Rao II. When she was four years old, her mother died. She learned to read and write at home. Along with this, she also learned shooting, horsemanship, fencing, and Mallakhamb. Her childhood was different from the other children of her age. She has lived an independent life since her childhood. She was an intelligent, simply-dressed woman determined to protect Jhansi from the Britishers.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Jhansi, located in modern-day Uttar Pradesh, India |
| Leadership | Led by Rani Laxmi Bai, the Queen of Jhansi |
| Role in the Uprising | Spearheaded the resistance against British rule in Jhansi |
| Symbol of Courage | Represents bravery and the spirit of India’s fight for freedom |
| Defense Strategy | Fortified Jhansi and prepared an army to protect it from British invasion |
| Major Confrontation | Engaged in fierce battles, including the Battle of Jhansi |
| Alliance | Formed strategic alliances with other rebel leaders |
| Martyrdom | Fell in battle, becoming a martyr for Indian independence |
| Legacy | Inspired future freedom fighters and became a symbol of women’s empowerment |
19 November 1828 was when she was born in a Karhade Brahmin family in Varanasi. Although named Manikarnika Tambe, she was nicknamed Manu. Moropant Tambe was her father, and her mother was Bhagirathi Sapre. She was fond of horsemanship and had three horses. They were Sarangi, Pavan and Badal. She was free from fear since her childhood. Laxmi Bai’s history is very inspiring.
Manikarnika Tambe completed her education at home. Her education included reading, writing, martial arts, and sword fighting. She learned many things while growing up with boys in the Peshwa family. Nana Sahib and Tantya Tope were her childhood pals. Now, all of you are aware of who Rani Laxmi Bai is.
In May 1842, Manu married the Maharaja of Jhansi, Gangadhar Rao Newalkar. Her name was later changed to Lakshmi Bai. Her son died four months after his birth in 1851. They adopted his cousin’s kid and named him Damodar Rao. But the Maharaja passed away in 1853. Governor General Dalhousie introduced a policy called the ‘Doctrine of lapse’. The Governor General refused to accept the adopted son as heir to the throne, which made Rani of Jhansi furious.
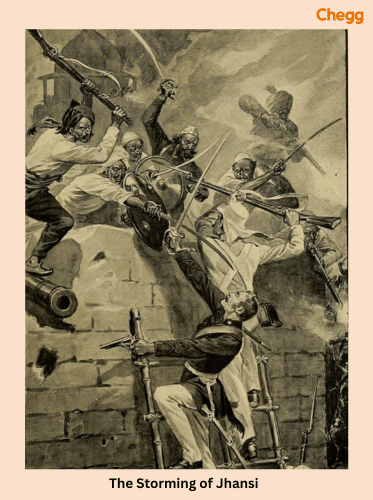
The ‘Doctrine of Lapse’ was initiated to capture Jhansi by the Britishers. But Rani Laxmi Bai decided not to give up control over Jhansi. The revolt of 1857 was raising the fuel of rebellion in many places against the British government. Lakshmi Bai emerged as a freedom fighter from Jhansi and resolved to resist British conspiracies. Engaging in combat with the British troops, she faced Commander Sir Hugh Rose, who defeated her.
Rani Lakshmi Bai has an enduring impact on generations of people. Many institutions bear her name in honor. A few are Rani Lakshmi Bai Central Agricultural University in Jhansi, the Maharani Laxmi Bai Medical College in Jhansi, and the Lakshmi Bai National University of Physical Education in Gwalior. Even Subhash Chandra Bose established a unit in his Indian National Army, the Rani of Jhansi Regiment, for women.
It was the first organized revolt against the British government. The Britishers were trying to expand their territories through the Doctrine of Lapse policy. This doctrine annexed Satara, Jhansi, and Nagpur. Interference of the British government in the religious practices of Indians was also one primary reason for revolt.
The incident of greased cartridges was the immediate reason for the mutiny of 1857. The circulation of a rumor claiming that the new Enfield rifle cartridges greased with the fats of cows and pigs hurt the sentiments of both religious groups. Lord Canning finally established peace on July 8, 1858.

Read More:
Top Women Freedom Fighters Of India – Name, List and their Roles
Freedom Fighters of India List, Names and their Contributions
Bhagat Singh Biography: A Glimpse into Education, and Facts
Indian National Movement – 4 Powerful Moments
Rani Jhansi Lakshmi Bai took control of Jhansi after the death of his husband. She had taken specific welfare policies like the abolition of Sati and training women for self-defense. Never left her Jhansi and its people alone and surrendered her whole life with a dedication to protect it. She tried to bring reforms in agriculture, infrastructure, and administration. Her leadership on the battlefield was magnificent.

Rani Laxmi Bai broke the stereotype of the patriarchal society and stood against the oppressive norms against women. The Jhansi ki Rani Laxmi Bai not only challenged the norms but also worked to uplift marginalized society. She still inspires generations of women. She proved that women are not only for nurturing the child but can also fight with a sword. Her fight was not only for the nation’s freedom but also for women’s freedom from societal stereotypes. She is rightly a symbol of women’s empowerment.
Rani Lakshmi bai remains a timeless symbol of bravery, resilience, and patriotism in Indian history. Her courage in the face of overwhelming odds during the Indian Rebellion 1857 and her unyielding determination to defend her kingdom of Jhansi against British colonial forces have made her an iconic figure. From her early martial arts training to her battlefield leadership, Rani Lakshmi Bai displayed remarkable strength and strategy. Her role as a warrior queen, a mother, and a freedom fighter continues to inspire generations worldwide.
Rani Lakshmibai was an influential leader and a symbol of resistance against oppression. She led an army of men and women, showcasing her progressive and inclusive approach to warfare and leadership. Her exceptional strategic acumen and valor during the siege of Jhansi earned her a respected place in Indian and global history. Even after the British captured Jhansi, she did not surrender; instead, she escaped and joined other leaders like Tantia Tope to continue the fight for independence.
Although she died young, at the age of 29, during a battle near Gwalior, her legacy continues to inspire millions. Her name is etched in history through numerous memorials, statues, and her portrayal in literature and films. Rani Lakshmi Bai’s courage, resolve, and dedication to the freedom of her people make her one of the most revered national heroes in India’s history. She is remembered for her military prowess and undying commitment to her people, making her a role model for future generations. Her life is a testament to the strength of the human spirit in the face of adversity.
1. Rani Laxmi Bai was a freedom fighter.
2. Born on November 19, 1834.
3. Known as “Jhansi Ki Rani”.
4. She married Gangadhar Rao.
5. Known for her courage.
6. She fought valiantly.
7. She is a national hero.
8. She fought bravely and valorously.
9. She died in 1858.
10. She is an inspiration for all.
Rani Lakshmi Bai, also known as the Rani of Jhansi, was a fearless Indian queen who became a symbol of bravery against British colonial rule during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. She is remembered for her courage, leadership, and sacrifice in the fight for Indian independence.
The childhood names of Rani Laxmi Bai were ‘Chhabili’, ‘Manikarnika’, and ‘Manu’.
The 4 qualities of Rani Lakshmi Bai were Courage, Leadership, Patriotism, and Selflessness.
Rani Laxmi Bai was born in Varanasi on November 19, 1834, to a Karhade Brahmin family.
Rani Lakshmi Bai played a crucial role in the 1857 Revolt, leading Jhansi’s defense against British forces. Her bravery and sacrifice made her a symbol of resistance in India’s freedom struggle.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.