
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Ancient Indian architecture is a remarkable fusion of art, spirituality, and engineering, reflecting the country’s rich cultural and historical heritage. Spanning from the urban sophistication of the Indus Valley Civilization to the grandeur of the Gupta and Chola dynasties, it encompasses diverse structures such as the Ajanta and Ellora caves, Sanchi Stupa, and Brihadeeswarar Temple.
Characterized by symbolic geometry, precise use of Vastu Shastra, intricate carvings, and masterful stone artistry, these architectural marvels demonstrate aesthetic brilliance and technical ingenuity. Beyond their religious and cultural significance, ancient Indian architectural principles have influenced modern design in India and worldwide, showcasing their builders’ timeless creativity, innovation, and enduring legacy.
The architectural heritage of ancient India is both vast and varied, showcasing a rich history that spans centuries. Ancient architecture in India includes a wide range of structures, from temples and palaces to rock-cut caves and urban planning in the Indus Valley Civilization. Each region boasts its unique style, influenced by local materials, climate, and cultural beliefs.
| Architecture | Ruler | Place | Medieval architecture is made of White Marble and had many precious stones like lapis lazuli. |
| Ajanta Caves | Various | Maharashtra | Rock-cut caves with Buddhist murals |
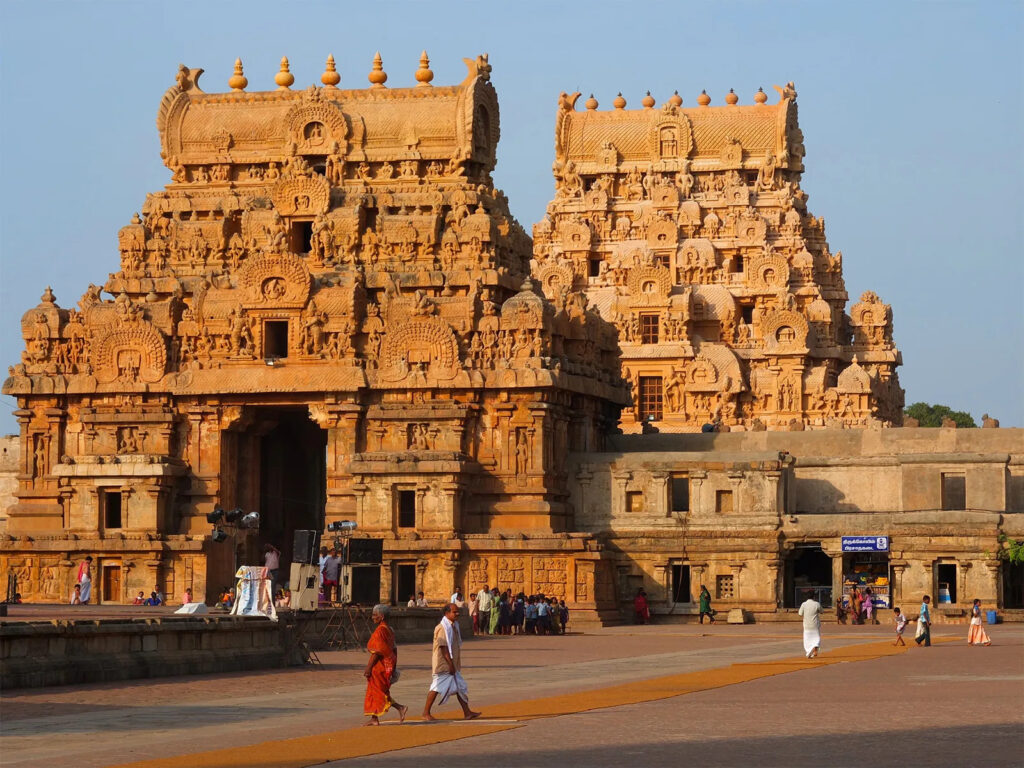
| Brihadeeswarar Temple | Raja Raja Chola | Tamil Nadu | Dravidian architecture masterpiece |
| Sanchi Stupa | Ashoka | Madhya Pradesh | Buddhist monument with intricate carvings |
| Mahabalipuram Temples | Narasimhavarman | Tamil Nadu | Pallava dynasty’s rock-cut temples |
| Qutub Minar | Qutub-Ud-Din Aibak | Delhi | Tallest brick minaret in the world |
| Red Fort | Shah Jahan | Delhi | Mughal-era fort with palatial structures |
| Konark Sun Temple | Narasimhavarman | Odisha | The chariot-shaped temple dedicated to the sun |
| Hampi | Various Vijayanagara rulers | Karnataka | Ruins of the last great Hindu kingdom |
| Khajuraho Group of Monuments | Chandela Dynasty | Madhya Pradesh | Erotic sculptures and Nagara-style temples |
| Fatehpur Sikri | Akbar | Uttar Pradesh | Mughal imperial city with unique ancient Indian buildings |
| Rani ki Vav | Bhima | Gujarat | Intricately constructed stepwell |
| Ellora Caves | Rashtrakuta Dynasty | Maharashtra | Monolithic rock-cut temples and monasteries |
| Meenakshi Temple | Various | Tamil Nadu | Twin temples with towering gopurams |
| Dilwara Temples | Various | Rajasthan | Jain temples are known for marble carvings |
| Taj Mahal | Shah Jahan | Uttar Pradesh | Jain temples are known for their marble carvings |
The characteristics of ancient architecture in India are deeply connected to symbolism and Vastu Shastra principles-
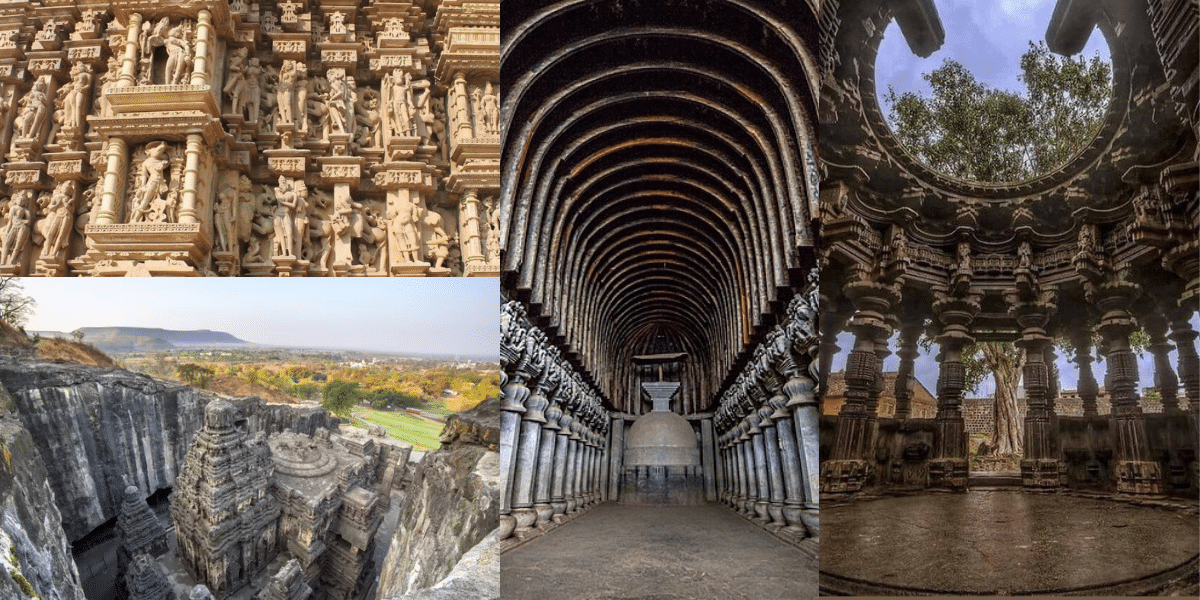
Ancient Indian architecture features three distinct temple styles: Nagara, dominant in the north; Dravida, which evolved in the south; and Vesara, a fusion of both. Each of these styles of ancient architecture in India reflects different historical periods and cultural influences, showcasing the rich diversity and depth of India’s architectural heritage.

Nagara style is emblematic of northern India’s temple architecture. These temples have a beehive-shaped shikhara (tower), typically curvilinear. The Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum) sits beneath the shikhara, often surrounded by more miniature replicas called Urushringas. Notable examples include the Khajuraho temples in Madhya Pradesh and the Jagannath Temple in Odisha. Their regional presence spans Central and North India, with variations like the Orissan Khajuraho and Solanki styles.
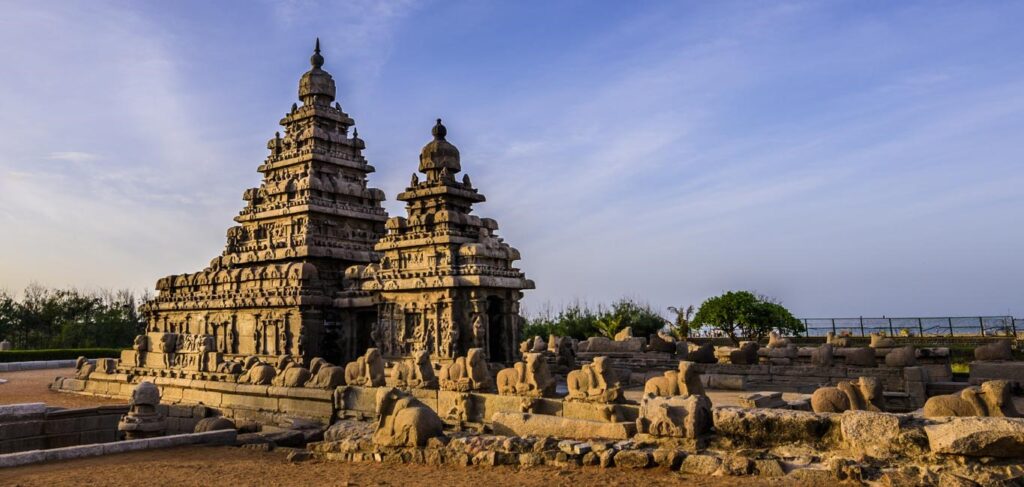

The Dravidian style is predominant in southern India, characterized by its towering gopurams (gateway towers) and sprawling complexes. These temples are enclosed within high walls and the vimana. The structure over the garbhagriha is stepped and rises as a pyramid. The intricacies of Dravidian architecture are evident in magnificent temples like the Brihadeeswarar Temple at Thanjavur and the Meenakshi Temple at Madurai. The architecture is structural and narrative, with walls and pillars depicting stories from Hindu texts.
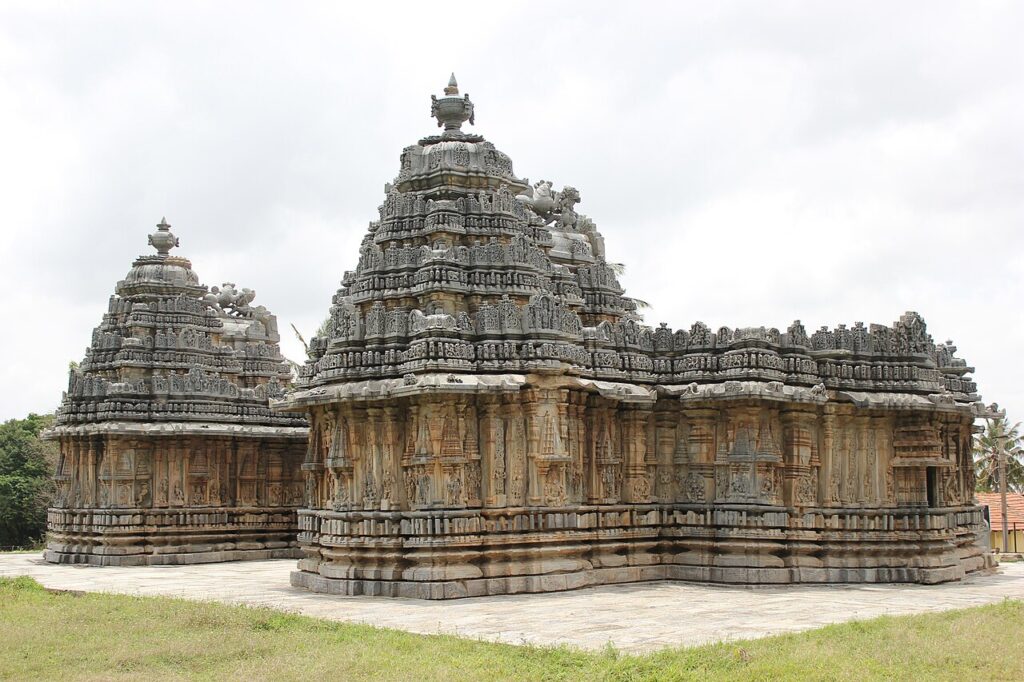

Vesara-style temples blend the Nagara and Dravidian architectural elements often seen in the Deccan region. This style emerged as a hybrid incorporating the north’s square-based structures and the south’s circular motifs. The Chalukya dynasty’s temples, like the Virupaksha Temple at Pattadakal, are prime examples. Vesara temples often feature richly decorated pillars and intricate ceiling panels showcasing a confluence of artistic traditions.
Ancient Indian architecture perfectly blends strength, artistry, and spirituality. Palaces and forts like the Red Fort and Agra Fort combined strong defensive features with opulent designs, showcasing the wealth and power of their builders. Early Buddhist architecture, including stupas and monasteries such as the Sanchi Stupa, served as spiritual and communal centers, with domes symbolizing the universe.
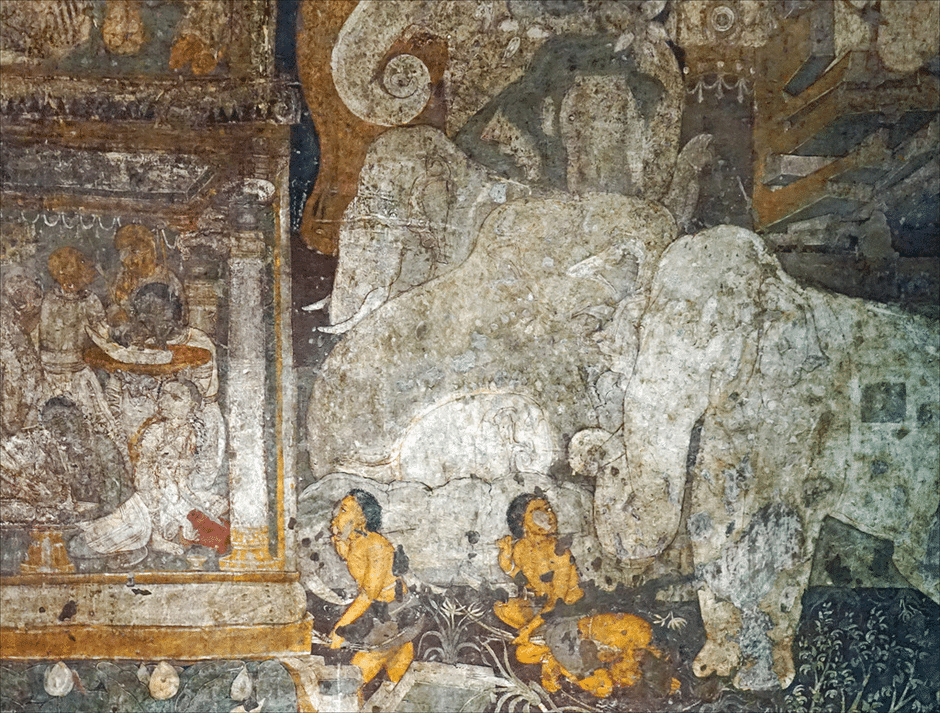
Rock-cut caves like Ajanta and Ellora display exceptional craftsmanship. They offer serene monastic retreats adorned with intricate frescoes and sculptures narrating Jataka tales. Together, these structures highlight India’s rich heritage, illustrating its ancient architecture’s sophistication, creativity, and cultural depth.
Ancient Indian architecture spans diverse eras and features temples, palaces, forts, and intricate sculptures. Each period introduced unique styles and techniques, reflecting cultural, spiritual, and practical needs. This rich heritage blends artistry with functionality, leaving a timeless legacy that inspires and showcases India’s architectural brilliance.
The Harappan civilization is known for its urban planning. It boasted advanced architectural features like fortified cities, grid layouts, drainage systems, and standardized fired brick sizes. The Great Bath of Mohenjo-Daro exemplifies their civil engineering and urban planning skills.
The Mauryan period saw the emergence of stone architecture, with Emperor Ashoka pioneering the construction of stupas and pillars. The Ashokan Pillar at Sarnath and the Stupas at Sanchi are monumental examples. These showcase the use of polished sandstone and intricate carvings.

Post-Mauryan architecture spanning the Sunga, Kushan, and Satavahana periods witnessed the evolution of Buddhist architecture. This era saw the embellishment of stupas and the construction of rock-cut caves, like those at Ajanta, which were adorned with elaborate sculptures and paintings.
The Gupta era, often called the Golden Age of India, saw the refinement of temple architecture. The Dashavatara Temple at Deogarh and the temples at Sanchi illustrate the nascent stages of temple construction. This period later influenced Indian architectural styles.
South Indian architecture is distinguished by its towering gopurams and expansive temple complexes. The Dravidian style began in the Pallava period and flourished under the Cholas and Pandyas. It is epitomized by the Brihadeeswarar temple in Thanjavur, which has elaborate sculptures and a towering vimana.

The Harappan civilization showcased advanced urban planning, with a layout that featured grid patterns and sophisticated civic amenities. Cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were characterized by their systematic streets and standardized urban structures, which reflected a high level of social organization and understanding of urban dynamics.
Harappan architects employed revolutionary techniques utilizing materials like baked bricks, which were uniform in size and quality. This uniformity is a testament to their advanced knowledge of kiln technology and production standardization. It contributed significantly to the durability and resilience of their constructions.
Among the ancient architecture in India, the architectural remains of the Harappan civilization include the Great Bath of Mohenjo-Daro, granaries, dockyards, and warehouses. These remnants provide insight into a society that values architectural precision, urban planning, and innovative construction methods.
Emperor Ashoka’s reign marked a transformative era in ancient architecture in India. His patronage led to the widespread construction of pillars and stupas. These were not only architectural feats but also media for disseminating his edicts.
The Mauryan pillars are renowned for their structural elegance and polished stone finish. The most famous of these, the Ashokan Pillar at Sarnath, bears the four-lion capital and has become an enduring symbol of India.
The builders constructed solid domed structures, like the grand Sanchi Stupa, over relics of the Buddha. These served as focal points for the Buddhist community. They were architectural representations of the universe, embodying the ancient Indian architectural ethos of combining form with spirituality.
Stupas, pillars, and palaces are key elements of court art, reflecting architectural and artistic grandeur. Let’s explore their significance briefly.
The Sunga and Satavahana dynasties enriched ancient Indian architecture, building on Mauryan foundations with more intricate stupas and religious structures. Stupas like Bharhut and Amaravathi featured elaborate railings and sculptural decorations, depicting Buddhist narratives. The Western Kshatrapa and Saka periods introduced foreign influences, fostering an eclectic style and pioneering rock-cut architecture.
Cave sites such as Bhaja and Karla showcased monasteries and chaityas with detailed facades and interior carvings, reflecting both architectural skill and deep religious devotion, marking a significant evolution in India’s ancient architectural heritage.
During the Gupta Period, India experienced a golden age of art and architecture, marked by the construction of iconic Vishnu and Shiva temples. The Dashavatara Temple in Deoghar exemplifies this era, showcasing perfect harmony in design, proportion, and ornamentation, reflecting aesthetic beauty and spiritual significance.
Ancient architecture in India during this period combined intricate artistry with religious devotion, leaving a lasting cultural legacy. Rock-cut architecture flourished, with the Ajanta and Ellora caves standing out for their breathtaking murals and sculptures. These caves served as monastic retreats and artistic canvases, blending sanctity with visual splendor. Together, Gupta temples and rock-cut sites highlight India’s advanced architectural skill and enduring influence on world heritage.
Read More:
South Indian architecture is characterized by the grand Dravidian style, featuring towering gopurams and expansive temple complexes. The Chola dynasty’s architectural marvels, such as the Brihadeeswarar Temple, are a testament to their engineering prowess and artistic vision.
These temples’ elaborate sculptures and towering vimanas embody the divine. The Vijayanagara Empire furthered this legacy. The Hampi ruins reflect a blend of innovation and sacred geometry, marking the zenith of South Indian architecture.
| Aspect | Relationship between Ancient Indian Architecture and Modern Design |
|---|---|
| Symmetry and Geometry | Ancient Indian architecture’s emphasis on symmetry and geometric patterns influences modern design. |
| Spiritual Symbolism | Spiritual elements from ancient Indian designs are incorporated into contemporary architecture. |
| Decorative Elements | Modern architects use decorative brackets and rich carvings inspired by ancient Indian techniques. |
| Structural Features | Courtyards and other structural features from ancient architecture in India are integrated into modern buildings. |
Ancient architecture in India stands as a timeless legacy, blending art, engineering, and cultural expression. India’s architectural history showcases innovation, symbolism, and spiritual depth, from the planned cities of the Harappan civilization to the intricately carved temples of the Gupta and Chola periods. Modern Indian architects continue to draw inspiration from ancient principles like Vastu Shastra, incorporating age-old wisdom into contemporary designs.
Far beyond historical study, ancient architecture in India actively shapes today’s built environment and remains central to the nation’s cultural identity. It reflects past generations’ beliefs, values, and creativity, offering lessons that still influence how we design and inhabit spaces. Preserving this rich architectural heritage honors our past and inspires future generations to carry forward its beauty, purpose, and relevance.
The diversity of ancient Indian architecture is reflected by distinct regional styles but united in spiritual and artistic expressions. The Indus Valley civilization had rock-cut caves, grand temples, and urban planning marked with advanced engineering and symbolism. It also had the application of Vastu Shastra principles.
Indian temple architecture is classified into three main styles: Nagara (North Indian style), Dravida (South Indian style), and Vesara (a blend of both). Each style reflects distinct regional influences, cultural traditions, and architectural lineages, showcasing the diversity and richness of temple design across India.
Caves such as Ajanta and Ellora are the deeper aspects of ancient Indian architectural art. They served as a monastery with elaborate frescoes and sculptures. These structures chronicled histories and other religious stories, reflecting those times’ architectural and artistic prowess.
The oldest building in India is the Sanchi Stupa in Madhya Pradesh. Built in the 3rd century BCE by Emperor Ashoka, it is one of the earliest and most important examples of Buddhist architecture. The stupa reflects India’s ancient cultural and historical heritage and features a large dome and intricately carved gateways.
Balkrishna Doshi is considered the first formally recognized architect in modern India. He was the first Indian to receive the Pritzker Architecture Prize, often called the “Nobel of Architecture.” His work bridges traditional Indian principles with contemporary design. However, in historical terms, many anonymous artisans and temple architects in the Gupta and Chola periods were pioneers in ancient Indian architecture.
The Great Bath of Mohenjo-Daro and city plans from the Indus Valley Civilization (2600 BCE) are the oldest examples of ancient Indian architecture. These structures exhibit advanced urban planning, drainage systems, and baked-brick construction, predating even the earliest temples or stupas.
Ancient Indian architecture refers to structures built before the medieval period, including temples, caves, stupas, stepwells, forts, and palaces. It integrates religion, art, science, and cosmic symbolism, influenced by Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Styles include Dravidian, Nagara, Vesara, and rock-cut traditions from the Mauryan, Gupta, and Chola periods.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.