
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Did you know that some of the world’s earliest universities were in India? Before institutions like Oxford or Cambridge came into existence, India was home to incredible centers of learning that attracted scholars from all corners of the globe. These were not mere schools; they were thriving hubs of knowledge that shaped the foundation of education as we know it today.
Universities like Nalanda, Takshashila, Vikramshila, and Valabhi stood out as prominent centers for advanced learning, offering philosophy, mathematics, medicine, law, and more studies. While Nalanda and Vikramshila were famed for their Buddhist teachings, Takshashila and Valabhi embraced a broader spectrum of intellectual and religious pursuits. Scholars worldwide flocked to these institutions, creating networks of knowledge that influenced global learning. Unfortunately, many great universities were destroyed during medieval invasions, leaving only memories of their brilliance.
In this article, we’ll explore India’s top 10 ancient universities, diving into what made them extraordinary, the minds that studied there, and why their legacy still matters today. Get ready to journey back in time and uncover the roots of higher education in India!

| University | Time Period / Founding Period | Location | Main Focus | Special Feature | Founder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Takshashila University | 5th century BCE – 5th century CE | Modern-day Pakistan | Various subjects | Oldest known university | Bharata dynasty (Exact founder unknown) |
| Nalanda University | 5th – 12th century CE | Bihar, India | Buddhist studies | Largest ancient university | Kumaragupta I (Gupta Empire) |
| Vallabhi University | 6th – 12th century CE | Gujarat, India | Buddhist and Jain studies | Focus on secular subjects | Bhattarka (Maitraka dynasty) |
| Vikramashila University | 8th – 12th century CE | Bihar, India | Tantric Buddhism | 108 temples within campus | Dharmapala (Pala dynasty) |
| Odantapuri University | 8th – 12th century CE | Bihar, India | Vajrayana Buddhism | Model for Tibetan monasteries | Gopala I (Pala dynasty) |
| Somapura Mahavihara | 8th – 12th century CE | Bangladesh | Buddhist studies | UNESCO World Heritage site | Dharmapala (Pala dynasty) |
| Jagaddala Mahavihara | 11th – 12th century CE | Bangladesh | Tantric Buddhism | Important for Tibetan Buddhism | Ramapala (Pala dynasty) |
| Nagarjuna University | 2nd – 3rd century CE | Andhra Pradesh, India | Mahayana Buddhism | Named after famous philosopher | Nagarjuna (Philosopher) |
| Pushpagiri University | 3rd – 11th century CE | Odisha, India | Buddhist studies | Important in eastern India | Ancient Kalinga rulers (Exact founder unknown) |
| Mithila University | 12th century CE – present | Bihar, India | Hindu philosophy | Non-monastic, continuing tradition | Scholars of Mithila region (Self-established tradition) |
Before we explore each ancient university of India, let’s consider how education worked in ancient India. Long ago, India had a system called the Gurukul. In this system, students lived with their teacher, a Guru. They learned from books, helped with daily chores, and watched how their Guru lived. It was like going to school and living with your favorite teacher simultaneously!
As time went on, India needed bigger places to teach more people. That’s when these large universities started to appear. Kings and rich people gave money to build and run these universities. They believed that supporting education was a good and essential thing to do.

Takshashila University is like the great-grandparent of all ancient universities in India. It existed from about 500 BCE to 500 CE, over 1,000 years!
Takshashila was in what is now Pakistan, near Rawalpindi. It was part of ancient India. Students at Takshashila learned all sorts of cool things:
Some of the most famous people in ancient Indian history studied here:
Sadly, Takshashila, the oldest university in India, no longer exists. It declined after multiple invasions, notably by the Huns in the 5th century CE.
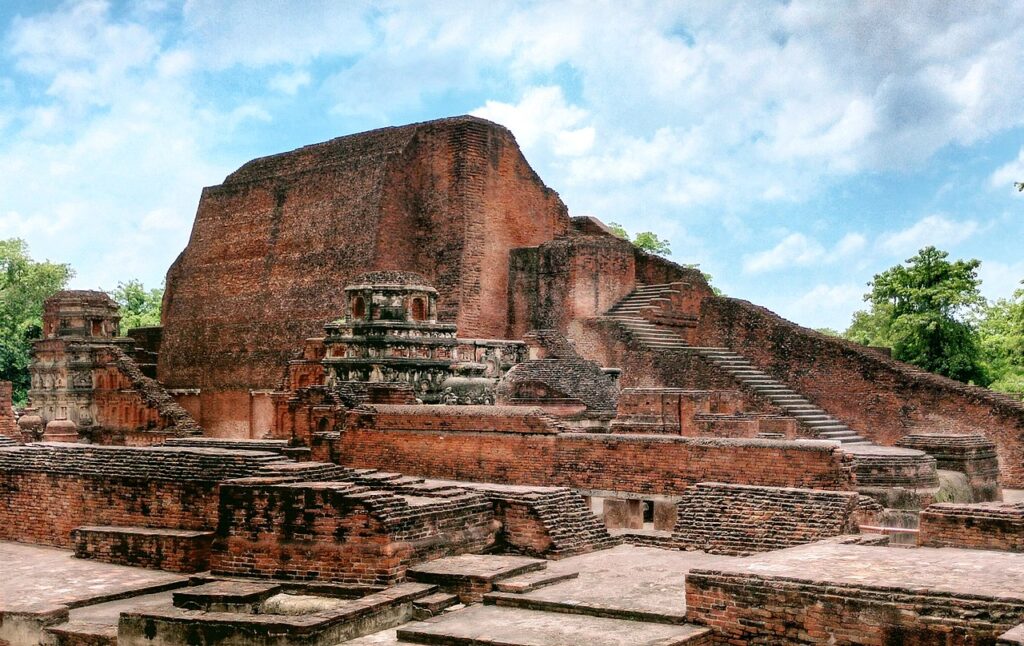

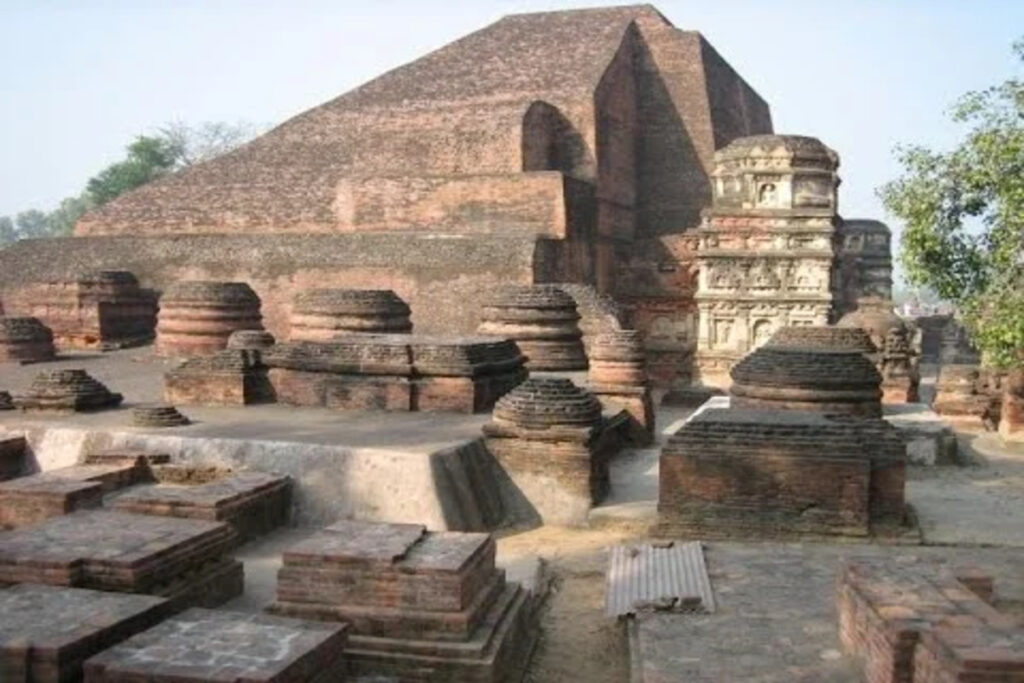
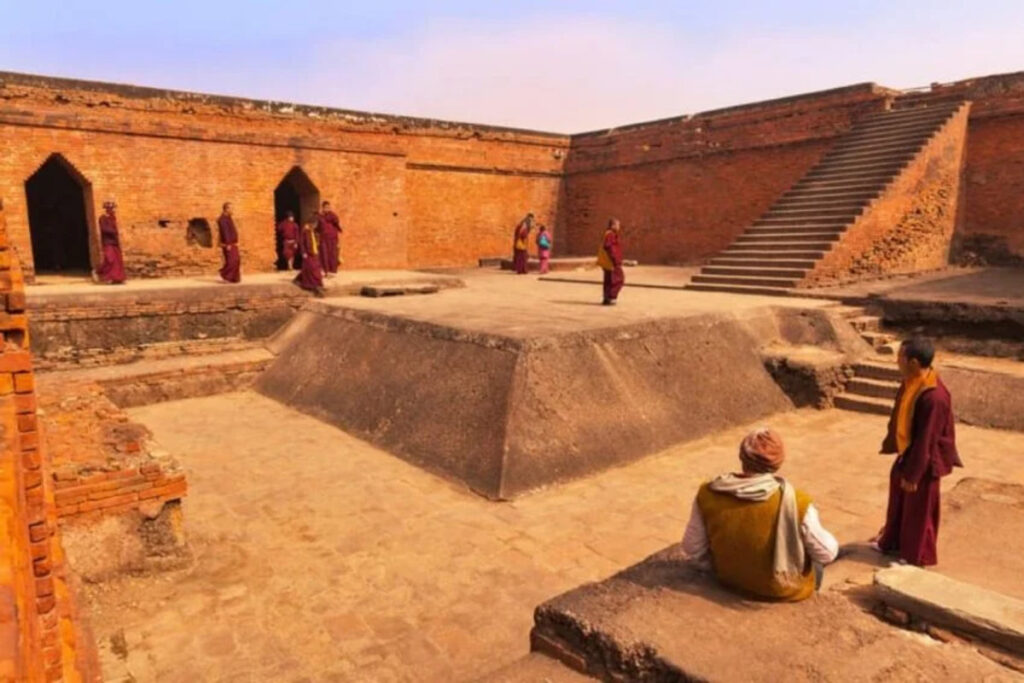
Nalanda University was another superstar of ancient Indian education. It was around 400 CE to 1200 CE.
Nalanda was in Bihar, a state in eastern India. You can still visit its ruins today!
At its peak, Nalanda had over 10,000 students, 2,000 teachers, and the Dharmaganja library with hundreds of thousands of books.
What did they study?
Nalanda was destroyed in the 12th century by the Turkish invader Bakhtiyar Khilji, marking the end of its illustrious existence. But guess what? In 2014, a new Nalanda University opened near the ancient site to continue its legacy of learning!

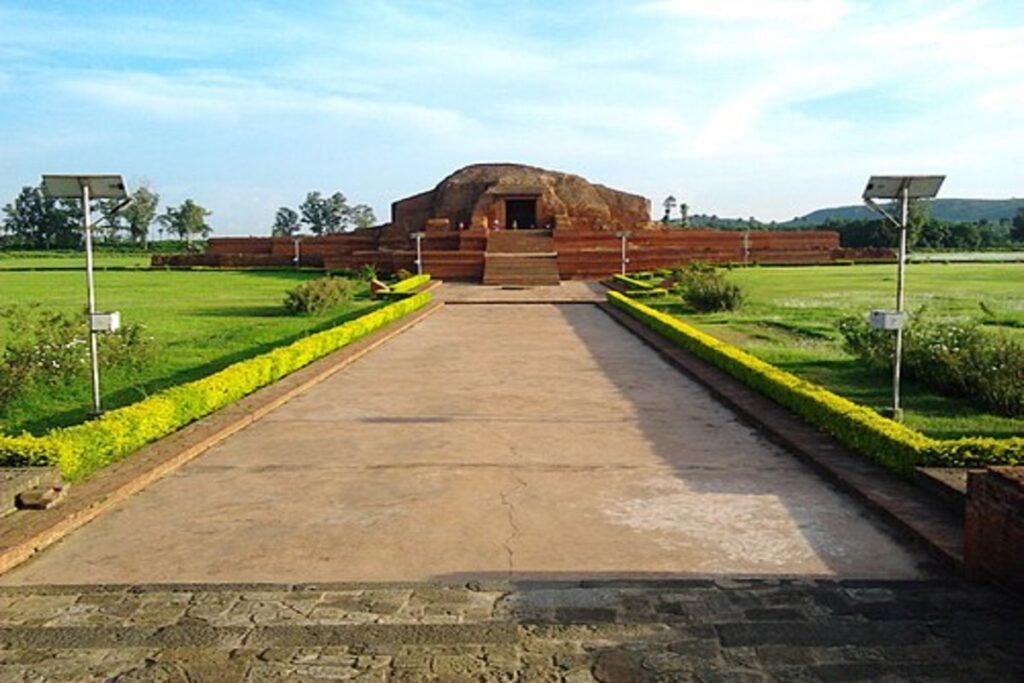
Vallabhi University was another important center of learning in ancient India. It existed from the 6th to the 12th century CE and was founded by Bhattarka, the king of the Maitraka empire.
Vallabhi was located in what is now Gujarat, in western India.
Vallabhi was almost as famous as Nalanda! It was known for:
Vallabhi didn’t leave behind big ruins like Nalanda did. Also, fewer travelers wrote about it. But it was still super important in spreading knowledge across ancient India.

Vikramashila University was a major ancient university in India that served as a prominent Buddhist learning center from the 8th to the 12th century CE.
It was founded by King Dharmapala, who also supported Nalanda. He wanted to create more places for people to learn about Buddhism.
Vikramashila had:
Vikramashila was known for teaching Tantric Buddhism, which involved special meditation practices. It also:
Many critical Buddhist teachers studied or taught here, like Atisha, who helped spread Buddhism to Tibet. This makes it one of the most ancient universities in India.
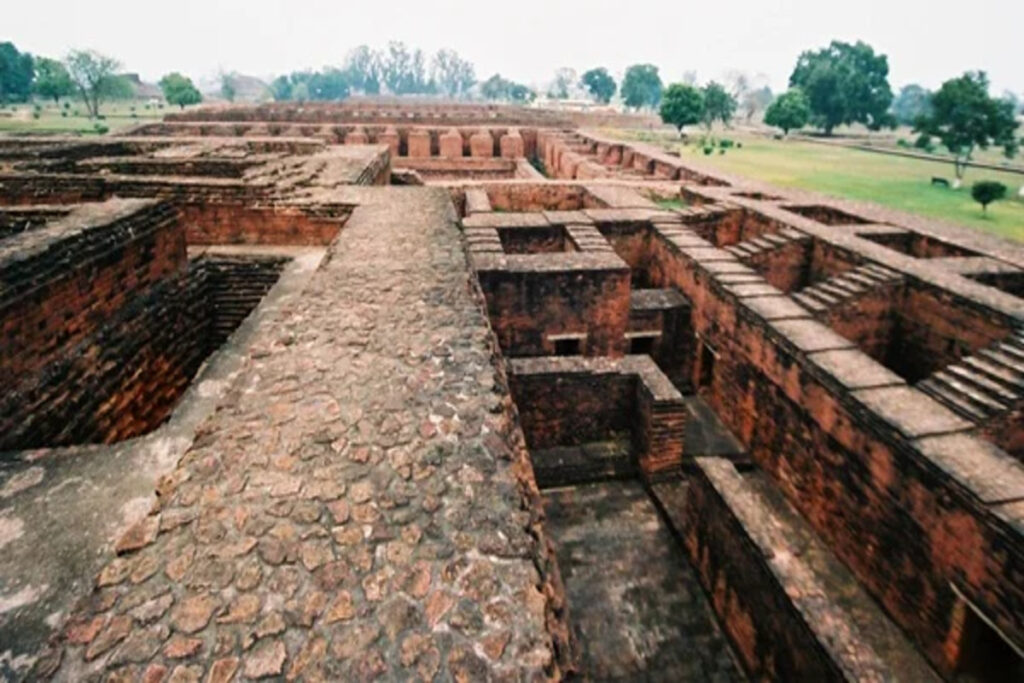

Odantapuri University was another important center of learning in ancient Bihar. It was around from the 8th to the 12th century CE.
Like Nalanda and Vikramashila, the Pala kings who ruled that area supported Odantapuri. They believed that supporting education would strengthen and wiser their kingdom.
Odantapuri was known for:
Students and teachers often moved between Odantapuri, Nalanda, and Vikramashila, which helped spread ideas and knowledge between these places.
Even though we know less about Odantapuri than Nalanda, it significantly educates people in ancient Bihar and keeps Buddhist learning alive.

Somapura Mahavihara was a spectacular Buddhist monastery and learning center. It existed from the 8th to the 12th century CE.
Somapura was located in what is now Bangladesh. Its ruins are so impressive that UNESCO has named it a World Heritage Site!
At Somapura, students learned:
Somapura extensively spread Buddhism to Southeast Asian countries like Myanmar, Thailand, and Indonesia. Its beautiful design influenced Buddhist architecture in many places.

Jagaddala Mahavihara was one of the last great Buddhist universities from the ancient universities of India. It was active from the 11th to the 12th century CE.
Jagaddala was located in what is now Bangladesh, not far from Somapura.
Jagaddala was famous for:
Jagaddala was built relatively late compared to the other universities. Soon after it was built, many parts of India faced invasions that disrupted Buddhist institutions. This is why it only lasted for about a century.
Even though it existed briefly, Jagaddala produced some critical Buddhist scholars and texts that are still studied today, especially in Tibet.
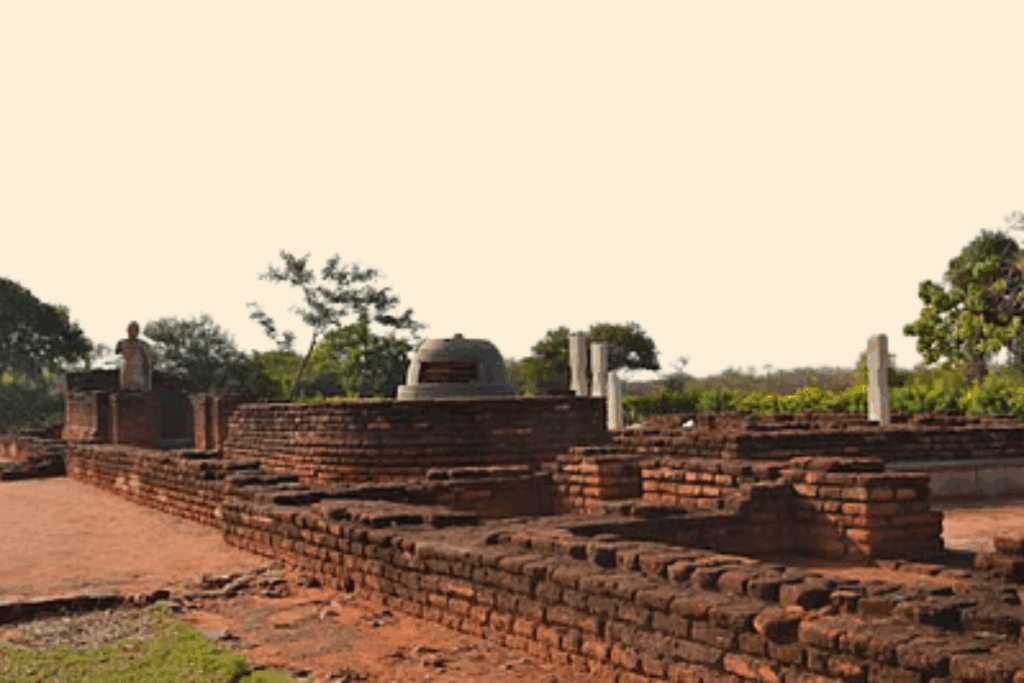

Nagarjuna University, named after the famous Buddhist philosopher Nagarjuna, was an important learning center from the 2nd to the 3rd century CE.
Nagarjuna was one of the most critical thinkers in Buddhism. He developed ideas that changed how people understood Buddhism and influenced philosophy in India and beyond.
At Nagarjuna University, students focused on:
The ideas developed at Nagarjuna University had a significant impact on:
While we don’t have big ruins like Nalanda, archaeologists have found evidence of the university in Andhra Pradesh. These findings help us understand what life was like at this ancient place of learning.
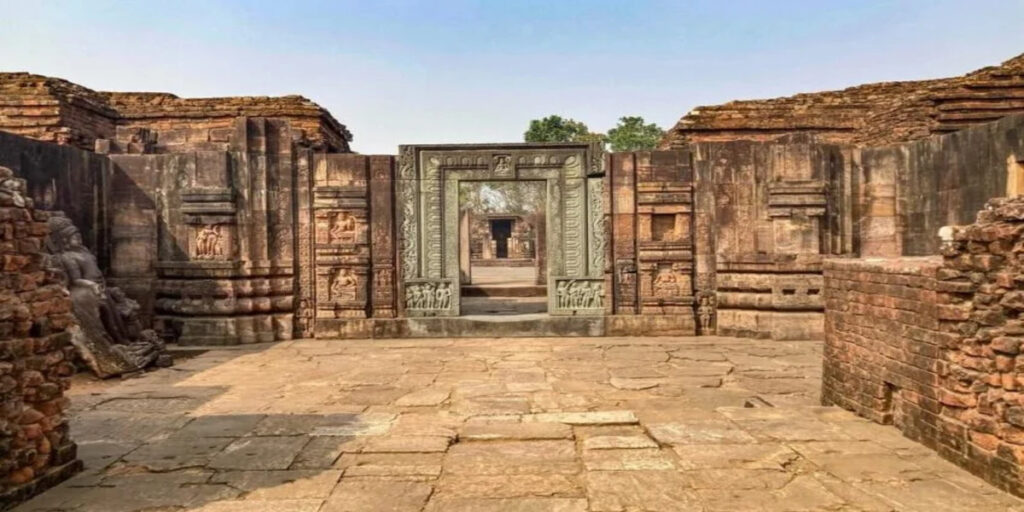

Pushpagiri University was a crucial ancient university in India and a renowned Buddhist center of learning from about the 3rd to the 11th century CE.
Pushpagiri was located in what is now Odisha, in eastern India.
At Pushpagiri, students studied:
Pushpagiri was super crucial for the kingdom of Kalinga (ancient Odisha). It helped make Kalinga a center of Buddhist learning and culture in eastern India.
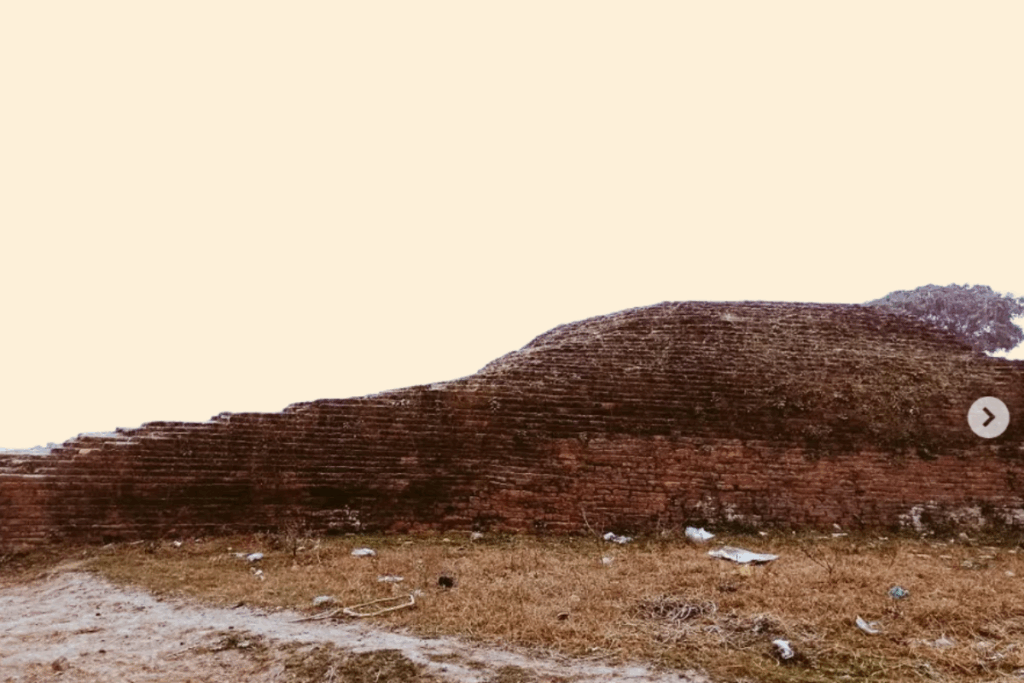

Mithila University was unique among ancient Indian universities because it wasn’t connected to a Buddhist monastery. Starting around the 12th century CE, it became part of a continuous tradition of learning that, in many ways, continues to this day, earning it a place among the oldest universities in India.
Unlike the other universities we’ve talked about, Mithila:
Mithila was famous for teaching:
While the ancient university in India doesn’t exist in the same form, the tradition of learning in Mithila continues. There’s even a modern university named after this ancient center of learning!
These ancient universities left a significant mark on the world, and their impact can still be felt today. Let’s look at how:
Today, people are working hard to preserve what’s left of these ancient universities of India and to continue their tradition of learning:

While much has been written about renowned institutions like Nalanda and Takshashila, there are still many surprising details about the ancient universities of India that remain lesser known. Here are some fascinating facts that highlight their uniqueness and legacy.
The ancient universities of India—like Takshashila, Nalanda, Vallabhi, and Mithila—were more than centers of education; they were thriving hubs of knowledge, welcoming scholars from across the world. These institutions taught various subjects and used advanced teaching methods that still inspire modern education. Though these universities no longer exist in their original form, their legacy remains, reminding us that India’s tradition of learning is thousands of years old. From timeless wisdom to global impact, the story of ancient Indian universities celebrates the power of knowledge and the enduring value of education.
Recommended Read:
Takshashila is considered the oldest university in India, dating to around the 5th century BCE.
Ancient Indian universities offered various subjects, including philosophy, astronomy, medicine, logic, grammar, metaphysics, mathematics, and different schools of Hindu and Buddhist thought. Some, like Takshashila, were also known for military science and statecraft.
The top three oldest universities in India are Takshashila, Nalanda, and Vikramshila, all significant learning centers in ancient times.
India’s oldest university is Nalanda University, established in the 5th century CE in present-day Bihar. Renowned globally, it attracted scholars from China, Korea, Tibet, and beyond. Nalanda was a major center for learning, especially in Buddhist studies, science, and philosophy.
India’s four most renowned ancient universities are Takshashila, Nalanda, Vikramashila, and Vallabhi. These major learning centers attracted scholars worldwide and offered studies in philosophy, mathematics, medicine, law, and religious teachings.
Before Oxford, India hosted remarkable universities. Nalanda University, established around 427 AD by Kumaragupta I, was a leading center for Buddhist studies, accommodating over 10,000 students, and thrived academically until its decline in the 12th century.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.