Quick Summary
Table of Contents
The aneroid barometer is a compact, elegant instrument designed to measure atmospheric pressure without liquid. This modern device relies on a sealed, flexible metal chamber called an aneroid cell, which expands and contracts with pressure fluctuations. The word “aneroid” itself comes from Greek, meaning “without liquid.” This mechanical movement makes it a powerful and portable tool for forecasting weather and measuring altitude in fields from aviation to home use.

Barometric pressure, also known as atmospheric pressure, is the force or “weight” exerted by the atmosphere on the Earth’s surface. This pressure is not constant; it changes with weather conditions and altitude. Atmospheric pressure is measured by a barometer. A barometer is the instrument used to measure it, and “barometric ” refers to the interpretation of these pressure readings, especially for weather forecasting. High barometric pressure typically indicates calm, clear weather, while low pressure is associated with storms and precipitation.
A barometer is a scientific instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure- the weight of the air in the atmosphere pressing down on the Earth. Because this pressure changes with weather conditions and altitude, barometers are essential tools for two main purposes: forecasting weather and determining elevation. The word itself comes from the Greek báros (weight) and métron (measure). Changes in pressure can signal coming storms or clear skies, making the barometer a cornerstone of meteorology.
While there are several variations, barometers are generally classified into three main types:
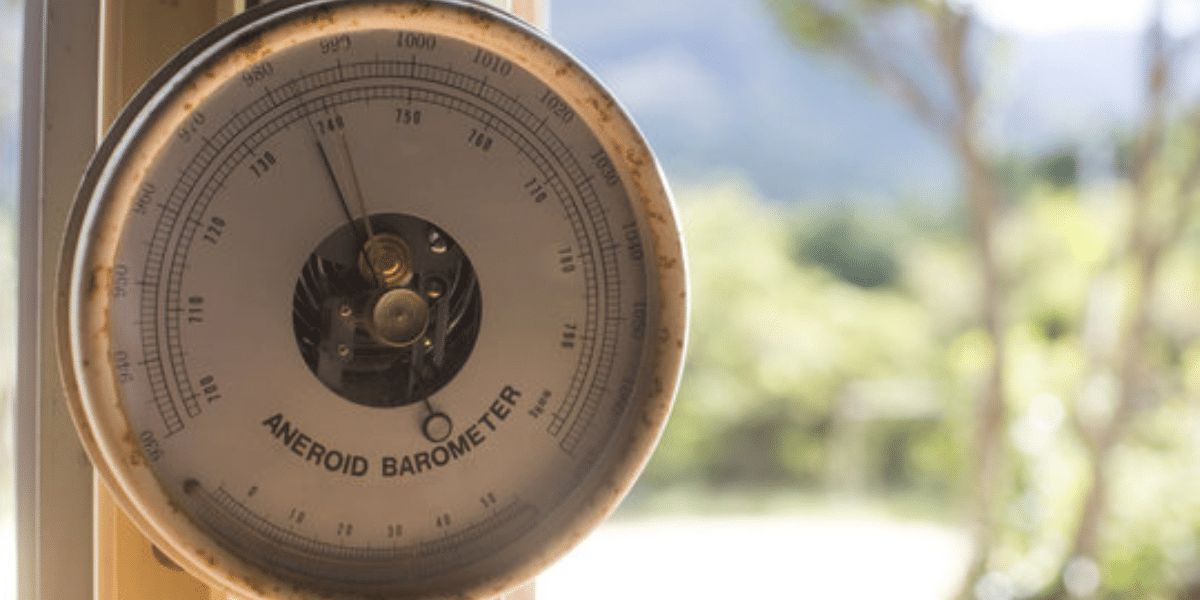
An aneroid barometer is a device used to measure atmospheric pressure without the use of any liquid, as its name, derived from the Greek for “without liquid”, suggests. Invented in 1844 by Lucien Vidi, it operates using a small, flexible, and sealed metal capsule that has been partially emptied of air. Changes in the external air pressure cause this capsule to expand or contract. This small movement is then magnified by an intricate system of levers and springs, which moves a pointer on a calibrated dial to indicate the current atmospheric pressure.

The genius of the aneroid barometer is its ability to translate imperceptible air pressure changes into a visible reading. At its core is the aneroid cell: a small, flexible metal chamber, typically made of a beryllium-copper alloy, which is partially evacuated to create a near-vacuum. Its corrugated faces act as a diaphragm, responding with high sensitivity to atmospheric pressure.
Increased external pressure compresses the cell, while decreased pressure allows it to expand. These subtle movements are the key to the instrument’s function.
A mechanical linkage system of levers and a spring translates these tiny displacements into the visible movement of a pointer.
This amplification system transforms the cell’s microscopic movements into a clear, readable sweep of the pointer across a calibrated dial, allowing users to monitor pressure trends for weather forecasting.
| Aspect | Aneroid Barometer | Mercury Barometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Mechanism | Measures pressure through the expansion and contraction of a metal chamber. | Measures pressure by adjusting the height of mercury in a column. |
| Complexity | Utilizes a more complex mechanism involving mechanical components. | Operates with a simpler, straightforward mechanism. |
| Accuracy | Generally accurate but may require periodic calibration. | Known for high accuracy and stability over time. |
| Portability | More portable due to the absence of liquid. | Less portable because it contains liquid mercury. |
| Durability | Less fragile, more durable for outdoor use. | Fragile due to the glass components and liquid mercury. |
| Maintenance | Requires maintenance for mechanical parts. | Minimal maintenance but needs to be handled with care. |
| Safety | Safe to use, as it does not contain toxic materials. | Mercury is toxic and poses a safety risk if broken. |
A barometer is a versatile and essential instrument with a wide range of important applications across various fields:
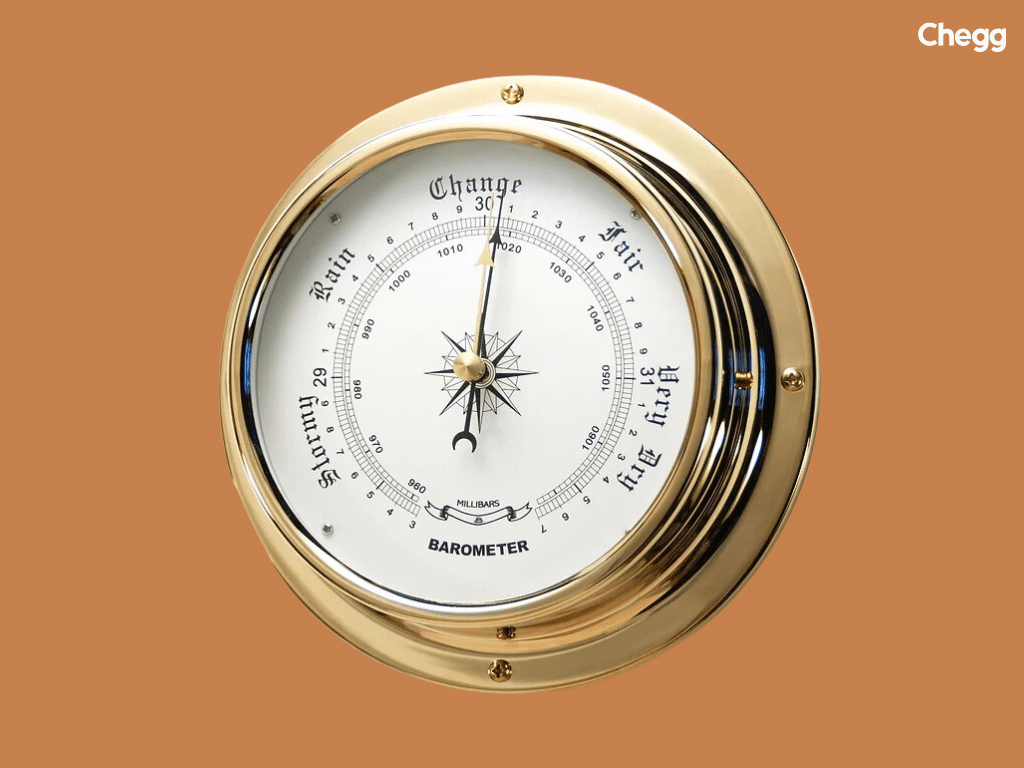

For accurate and scientific use, an aneroid barometer requires careful handling and an understanding of its potential for error.
The elegant principle of the aneroid barometer, a mechanical response to atmospheric pressure, has been adapted and evolved far beyond the simple wall-mounted dial. Engineers and scientists have built upon Lucien Vidi’s original design to create specialized instruments for specific, high-stakes applications, while modern technology has begun to merge the mechanical with the digital.
The barograph is perhaps the most well-known adaptation. Instead of a simple pointer, the mechanism moves a pen arm across a paper chart wrapped around a slowly revolving drum. This drum, typically driven by clockwork, completes a full rotation over a set period (often seven days). The result is a continuous, visual record of pressure changes called a barogram. For meteorologists and sailors, a barograph is invaluable. It doesn’t just show the current pressure; it tells the story of the pressure trend, revealing at a glance the speed and intensity of an approaching weather system. Oil-damping mechanisms are often used in marine barographs to prevent the ship’s vibrations and movements from creating a shaky, unreadable trace.
For applications where extreme accuracy is non-negotiable, such as in aviation control towers or meteorological research labs, the precision aneroid barometer is used. This instrument features a more sensitive aneroid cell or a stack of multiple cells to increase the mechanical response. Its key innovation is a micrometer dial that is manually turned to make a reading. Instead of just looking at a pointer, the operator turns the micrometer until a tiny indicator light turns on or off, signaling the exact point of contact within the mechanism. This eliminates parallax error (the error from viewing the needle at an angle) and allows for readings of much higher precision.
In recent years, a new class of hybrid instruments has emerged. These devices retain the reliable, self-powered mechanical aneroid cell as their core sensor. However, instead of just moving a physical pointer, the mechanism also actuates a digital sensor. This allows the instrument to display the pressure on an LCD screen, log data internally, and even transmit readings wirelessly. These hybrids offer the resilience of a mechanical barometer with the convenience and data-rich features of modern electronics, making them ideal for remote, automated weather stations.
In an age dominated by digital technology, the aneroid barometer continues to hold its own as a reliable, elegant, and indispensable instrument. Its clever mechanical design, which masterfully translates the invisible force of the atmosphere into a visible, understandable format, remains a marvel of 19th-century ingenuity. Free from the need for power and the inherent dangers of mercury, it offers a unique combination of safety, portability, and durability that modern devices often struggle to match. Whether it is used by a meteorologist tracking a developing storm, a pilot navigating the skies, or a homeowner simply curious about tomorrow’s weather, the aneroid barometer provides a direct and tangible connection to the dynamic and ever-changing world of our atmosphere.
Read More :-
An aneroid barometer has a flexible metal chamber. It measures atmospheric pressure. When the pressure outside rises or falls, it swells or shrinks accordingly. This advanced architecture provides accurate pressure readings. Barometers measure pressure. This motion generates a calibrated scale reading.
Handheld aneroid barometers are reliable and safe. Because of these qualities, they are often the best option available. They are often the best. Mercury harms ecosystems and human health, so doing so eliminates it.
Aneroid barometers are highly effective for short-term weather forecasting. By observing pressure trends—rising, falling, or steady—users can predict approaching storms, fair weather, or stable conditions. Rapid drops often signal storms, while rising pressure means clearer skies. Though not as precise as digital systems for complex analysis, aneroid barometers remain reliable tools in homes, ships, and fieldwork for everyday weather prediction.
An aneroid barometer operates using a sealed, flexible metal cell that expands and contracts in response to changes in atmospheric pressure. This movement is transferred by a system of levers and springs to a pointer on a calibrated dial. Without liquid, the device provides quick and accurate readings of air pressure, making it portable and safe for diverse applications in weather monitoring and altitude measurement.
An aneroid barometer is a device that measures atmospheric pressure without using any liquid. It features a sealed, flexible metal capsule that expands or contracts with pressure changes. This mechanical movement is amplified by levers and displayed by a needle on a calibrated dial, making it a portable and safe alternative to mercury barometers.
Aneroid barometers have diverse applications, including:
Weather forecasting for homes and meteorology stations
Aviation as altimeters to determine altitude
Maritime navigation to predict storms
Mountaineering and hiking for altitude tracking
Scientific research in field studies
Educational tools in classrooms
Industrial processes
Agriculture
Scuba diving (as depth gauges)
And even in some fishing and hunting activities.
“Barometer” is the general name for any instrument that measures atmospheric pressure. An “aneroid barometer” is a specific type of barometer that operates without liquid (“aneroid” means “without fluid”). The key difference is the mechanism: a traditional mercury barometer uses a liquid column, while an aneroid barometer uses a mechanical, flexible metal cell.
Imagine a sealed, empty metal can with a flexible lid. When outside air pressure increases, it squeezes the can and pushes the lid down. When air pressure decreases, the lid springs back up. In an aneroid barometer, this tiny movement is magnified by a system of levers connected to a pointer, which moves across a dial to show the pressure reading.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.