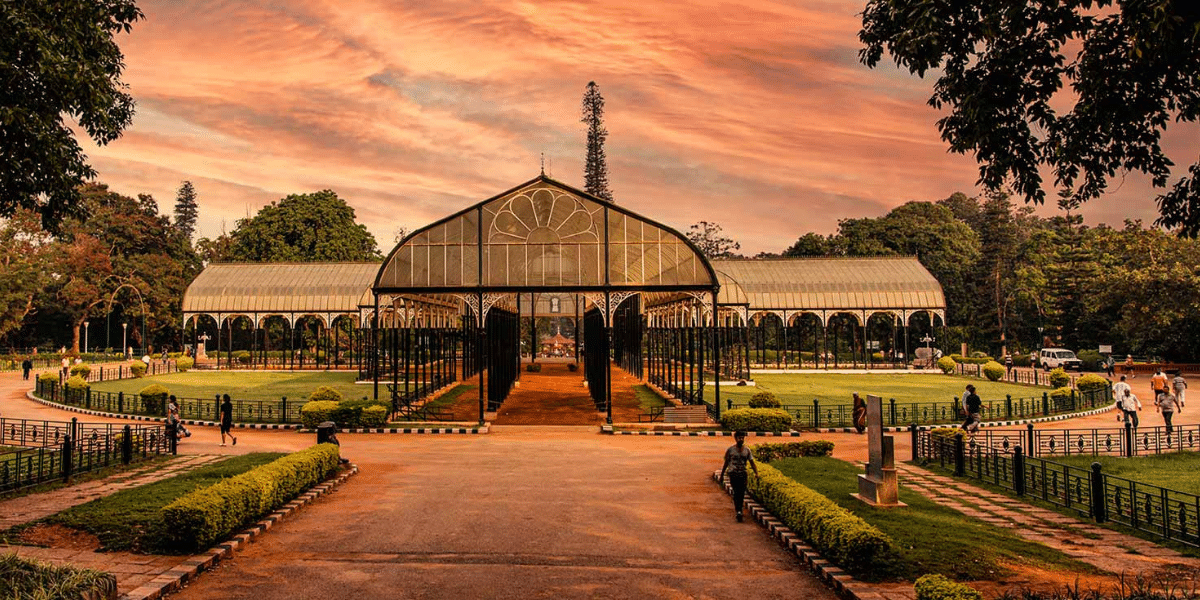

Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Did you know that the Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata is home to the world-famous Great Banyan Tree, spread over 3.5 acres, or that Asia’s largest Tulip Garden blooms every spring in Srinagar? These natural wonders highlight the rich diversity and charm of botanical gardens in India.
A botanical garden is a carefully designed space where plants of different varieties—from medicinal herbs to exotic flowers are grown, conserved, and studied. Unlike ordinary parks, botanical gardens in India act as living museums of biodiversity, supporting researchers, students, and nature enthusiasts in understanding plant life and ecological balance.
They also play a crucial role in preserving endangered plant species, offering safe habitats against deforestation and climate change threats. At the same time, botanical gardens in India serve as popular tourist attractions, blending scientific importance with cultural, educational, and recreational experiences across the country.
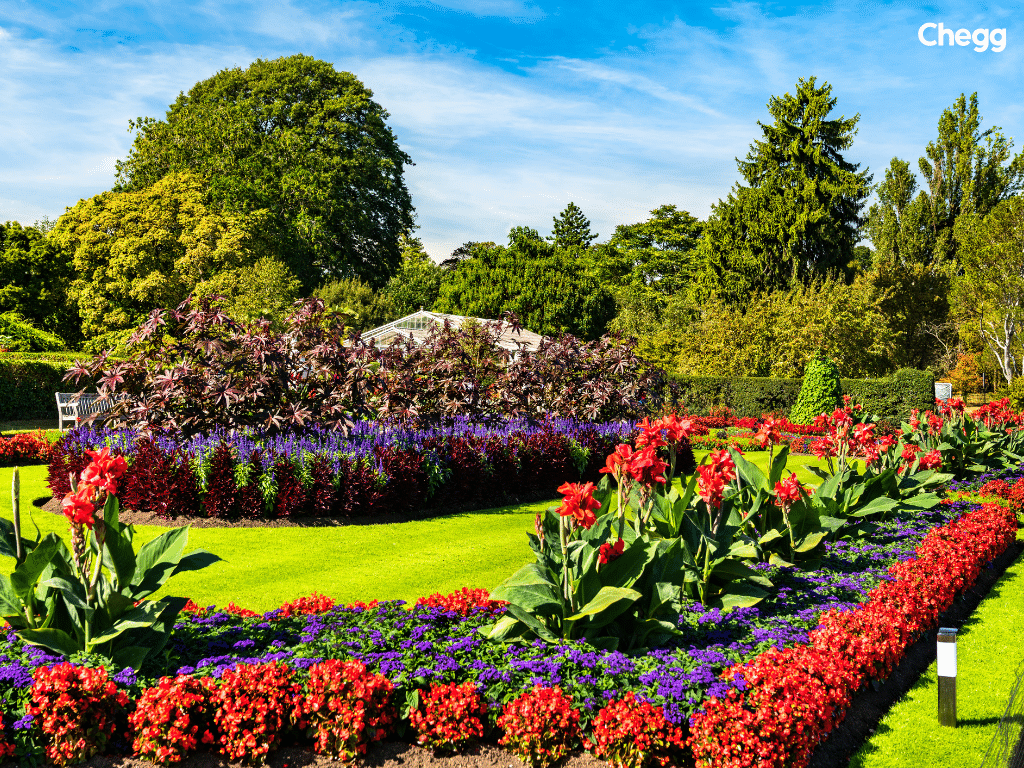
Botanical gardens in India are green spaces and vital centers of scientific, educational, cultural, and recreational importance. Each garden contributes uniquely to biodiversity conservation while enriching society in multiple ways.
These gardens act as living laboratories where scientists and researchers study plant species, their medicinal properties, and ecological relationships. For example, the National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in Lucknow conducts advanced research on plant taxonomy, genetics, and conservation, making it a hub for scientific innovation.
Botanical gardens in India provide immense learning opportunities for students, botanists, and environmentalists. They host workshops, guided tours, and exhibitions that spread awareness about plant conservation and sustainable practices. School and university visits often include trips to these gardens to encourage practical learning.
Beyond science, botanical gardens are also major tourist attractions. The Lalbagh Botanical Garden in Bengaluru, famous for its annual flower shows, attracts thousands of visitors who witness spectacular floral arrangements and rare plant species. Similarly, the Tulip Garden in Srinagar has become a cultural symbol, drawing tourists from across the globe.
In essence, botanical gardens in India blend ecological conservation with education and tourism. They protect endangered plants, inspire curiosity about the natural world, and serve as spaces where people can connect with nature. Balancing science, culture, and leisure makes these gardens crucial in promoting sustainable development and preserving India’s botanical heritage.
| Botanical Garden | Location | Established Year | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Botanic Garden (Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose) | Kolkata, West Bengal | 1787 | Home to the Great Banyan Tree, over 12,000 plant species |
| Lalbagh Botanical Garden | Bengaluru, Karnataka | 1760s (Hyder Ali, Tipu Sultan) | Famous glasshouse, annual flower shows |
| National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) | Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh | 1953 (as NBRI) | Research hub, medicinal & ornamental plants |
| Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute | Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala | 1979 | Largest tropical garden in Asia, medicinal plants |
| Lloyd’s Botanical Garden | Darjeeling, West Bengal | 1878 | Orchids, rhododendrons, Himalayan flora |
| Government Botanical Garden | Ooty, Tamil Nadu | 1848 | Terraced garden, fossilized tree |
| Jawaharlal Nehru Botanical Garden | Gangtok, Sikkim | 1987 | Orchids, rhododendrons, Himalayan plants |
| Empress Garden | Pune, Maharashtra | 19th century | Managed by Agri-Horticultural Society, flower shows |
| Botanical Garden, Forest Research Institute | Dehradun, Uttarakhand | 1906 (FRI established) | Medicinal & Himalayan species, research + tourism |
| Assam State Zoo cum Botanical Garden | Guwahati, Assam | 1982 | Unique zoo + garden, orchids & NE flora |
| Government Botanical Garden | Shillong, Meghalaya | 20th century | Ornamental plants, orchids, near Ward’s Lake |
| TNAU Botanical Garden | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu | 1971 (TNAU) | Educational & research focus, experimental crops |
| Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden & Research Institute | Palode, Kerala | 1979 | Rare tropical plants, conservation hub |
| Nehru Park & Botanical Garden | Port Blair, Andaman Islands | Late 20th century | Coastal & island flora, mangroves |
| State Botanical Garden (Nandankanan Zoo) | Bhubaneswar, Odisha | 1963 | Orchid house, cactus collection, aquatic plants |
India is home to some of the world’s most diverse and historic botanical gardens. These green sanctuaries preserve rare plant species, promote ecological research, and attract millions of visitors annually. Below is a list of the most famous botanical gardens in India, each with its own unique history, attractions, and visitor appeal.

Located in Howrah near Kolkata, this is the oldest and most iconic of all botanical gardens in India, established in 1787 by Colonel Robert Kyd. Spread across 273 acres, it is home to more than 12,000 plant species, including rare tropical and aquatic plants. Its main attraction is the world-famous Great Banyan Tree, spread over 3.5 acres and considered one of the largest trees in the world. The garden is a must-visit for researchers, students, and tourists alike.
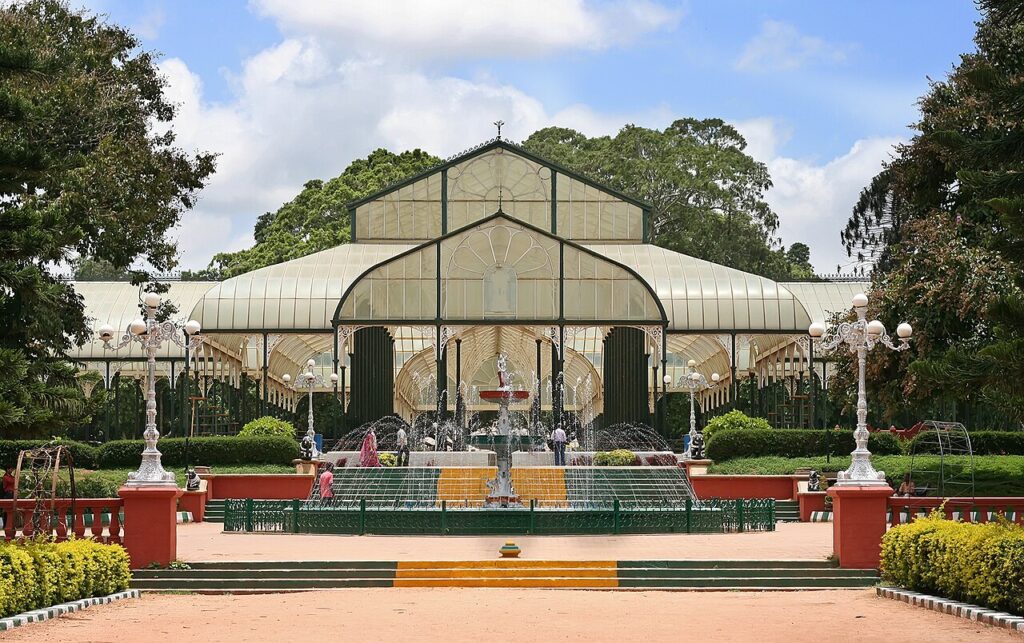

Hyder Ali started one of India’s most celebrated botanical gardens, Lalbagh, in the 18th century, and it was later developed by Tipu Sultan. Spanning over 240 acres, it is known for its glasshouse modeled after London’s Crystal Palace. The annual flower shows here attract thousands of visitors, showcasing exotic plants and artistic floral displays. Lalbagh is also home to centuries-old trees and a rich collection of tropical and subtropical plants, making it both a scientific treasure and a popular tourist attraction.

NBRI in Lucknow is not just a garden but a premier research institute dedicated to plant science. It houses a vast collection of medicinal plants, ornamental species, and rare herbs. Scientists here focus on conservation, taxonomy, and genetic improvement of plants. With its combination of lush landscapes and advanced laboratories, it stands out among botanical gardens in India for its contribution to modern research and being a peaceful destination for visitors.

Spread across 300 acres in Kerala, this is one of the largest tropical botanical gardens in Asia. Known for its vast collection of medicinal plants, orchids, and endangered tropical species, it serves as a conservation hub and a center for ethnobotanical studies. Visitors can explore themed plant sections and rare collections that highlight the immense biodiversity of the Western Ghats. Its focus on research and preservation makes it one of India’s most significant botanical gardens.

In the Himalayan hill station of Darjeeling, Lloyd’s Botanical Garden is famous for its high-altitude flora. Established in 1878, it covers over 40 acres and features rhododendrons, conifers, and hundreds of orchid varieties native to the Eastern Himalayas. The garden also houses medicinal plants and a conservatory for exotic species. Nestled amidst mountains and mist, it is one of India’s most scenic botanical gardens, attracting tourists who love nature and botany.

The Government Botanical Garden in Ooty is a colonial-era heritage site, established in 1848 by the Marquis of Tweedale. Spread across 55 acres on the slopes of the Nilgiri Hills, it features terraced gardens, rare orchids, and a 20-million-year-old fossilized tree. The beautifully maintained lawns and diverse plant species make it one of the most popular tourist spots in South India. This garden is a classic example of how botanical gardens in India blend science, history, and tourism.

Located near the famous Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, this botanical garden is home to an extraordinary collection of Himalayan flora. Known for its vibrant orchids, rhododendrons, and alpine plants, it highlights the biodiversity of the Eastern Himalayas. Visitors can enjoy serene walks through landscaped lawns and themed plant sections. Being one of the few botanical gardens in India in the Northeast, it offers a unique glimpse into mountain ecosystems and rare plant conservation.

Managed by the Agri-Horticultural Society of Western India, the Empress Garden spans 39 acres and is among the most prominent botanical gardens in India. It features sprawling lawns, a variety of flowering trees, and specialized plant nurseries. The garden is especially popular for its seasonal flower shows and exhibitions that attract thousands of visitors annually. Besides being a place for recreation, it plays a role in educating the public about plant diversity and horticulture.

The Forest Research Institute in Dehradun is well-known for its colonial architecture, but its botanical garden is equally fascinating. Spread over lush landscapes, it includes medicinal plants, ornamental species, and trees from the Himalayan and tropical regions. As one of the research-focused botanical gardens in India, it serves as an educational hub for forestry students and scientists. It is also a popular tourist destination for its scenic beauty and biodiversity.

This unique garden in Guwahati combines a zoo with a botanical garden, making it one of the most diverse attractions in Northeast India. Established in the 1980s, it showcases rare orchids, medicinal herbs, and plant species native to Assam and neighboring states. Visitors can explore both animal and plant life in a single location. Its distinctive blend of conservation and recreation sets it apart from other botanical gardens in India, drawing families and tourists year-round.

Located near the famous Ward’s Lake, the Shillong Botanical Garden is one of the most charming botanical gardens in India. It is home to a wide variety of orchids, ornamental plants, and native species of Meghalaya. The garden also features small ponds with aquatic plants and fish, adding to its beauty. It is a favorite spot for locals and tourists, offering a peaceful retreat amidst the natural splendor of Shillong.

Part of the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, the TNAU Botanical Garden is a vital center for education and research in plant sciences. Spread across several acres, it showcases medicinal herbs, ornamental flowers, and experimental crop varieties. It is regularly visited by students, researchers, and horticulturists, making it a unique example of academically focused botanical gardens in India. For tourists, its landscaped sections and plant diversity offer a refreshing experience.

Located near Thiruvananthapuram, this tropical botanical garden is spread over 300 acres and is dedicated to conserving rare and endangered plants. It houses an impressive collection of orchids, bamboos, and tropical trees. With its active role in research and preservation of indigenous flora, it is considered one of the most important botanical gardens in India. Visitors can explore themed zones, medicinal plant collections, and lush greenhouses.

This garden uniquely showcases coastal and island biodiversity in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It features palms, mangroves, and other species native to tropical islands. As one of the most distinctive botanical gardens in India, it highlights how plant life adapts to maritime ecosystems. For tourists, it offers a relaxing retreat with scenic views and rare flora not commonly seen on the mainland.

Part of the Nandankanan Zoo, this botanical garden covers over 75 hectares and is famous for its orchid house and cactus collection. It also has aquatic plant species and themed gardens that appeal to visitors of all ages. As one of the largest state-run botanical gardens in India, it balances conservation, education, and recreation. Its integration with the zoo makes it an ideal destination for family outings.
Among all botanical gardens in India, two stand out for their sheer history and scale: the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata and the Botanic Garden of the Indian Republic in Noida.
The AJC Bose Botanic Garden, established in 1787 by Colonel Robert Kyd, is the oldest botanical garden in India. Spread across 273 acres, it is home to more than 12,000 species of plants. Its star attraction is the legendary Great Banyan Tree, which covers nearly 3.5 acres with over 3,600 aerial roots so massive that it looks like a mini forest. The garden has introduced economically valuable plants like tea, teak, and rubber into India.
On the other hand, the Botanic Garden of Indian Republic in Noida is recognized as the largest botanical garden in India, covering over 200 acres. Managed by the Botanical Survey of India, it focuses on ex-situ conservation and is home to various medicinal, endangered, and ornamental plants. With its sprawling landscapes, themed plant sections, and emphasis on eco-tourism, it has quickly become a hub for both research and recreation.
Together, these two gardens represent India’s legacy and future of plant conservation.
The diversity of botanical gardens in India can also be seen through their regional spread, each reflecting unique climates and plant life.
North India hosts renowned gardens like the Botanic Garden of Indian Republic, Noida, the Forest Research Institute Botanical Garden, Dehradun, and the Jawaharlal Nehru Botanical Garden in Sikkim, all of which showcase Himalayan and subtropical flora.
South India is famous for the Lalbagh Botanical Garden, Bengaluru, the Government Botanical Garden, Ooty, and Kerala’s Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute, which are rich in tropical and ornamental species.
East India treasures the historic Indian Botanic Garden, Kolkata, and Lloyd’s Botanical Garden, Darjeeling, which is known for orchids and rhododendrons.
West India highlights include Pune’s Empress Garden, the TNAU Botanical Garden in Coimbatore, and the State Botanical Garden at Nandankanan, Bhubaneswar (often linked with eastern geography but accessible from central India).
One of the most crucial functions of botanical gardens in India is their role in conservation. These gardens act as safe havens for endangered and rare plants that face deforestation, urbanization, and climate change threats. Cultivating such species in controlled environments ensures their survival beyond natural habitats. For instance, the Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata and the Botanic Garden of the Indian Republic in Noida are known for housing threatened tropical and medicinal plants.
Medicinal plant research is another significant contribution. Gardens like the National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in Lucknow actively study and conserve medicinal herbs with significant pharmaceutical value. This supports traditional knowledge systems like Ayurveda and contributes to modern healthcare discoveries.
Beyond conservation, botanical gardens also enhance urban greenery and help mitigate climate change effects. Large spaces like Lalbagh Botanical Garden in Bengaluru and Government Botanical Garden in Ooty serve as the “green lungs” of their cities, improving air quality, regulating temperatures, and providing sustainable recreational spaces.
By combining plant preservation, scientific research, and urban ecology, botanical gardens in India play a pivotal role in protecting biodiversity while enriching human life.
Beyond their ecological role, botanical gardens in India are also thriving centers of tourism and education. Gardens like Lalbagh in Bengaluru and the Tulip Garden in Srinagar attract lakhs of visitors annually, offering scenic landscapes, seasonal flower shows, and cultural festivals that boost eco-tourism. Similarly, the Government Botanical Garden in Ooty is a favorite hill-station attraction, blending natural beauty with rare plant collections.
On the educational front, botanical gardens act as living classrooms. They organize workshops, guided tours, and exhibitions to teach students, researchers, and the public about plant diversity, conservation, and sustainability. Institutes like the NBRI in Lucknow combine research with awareness programs, inspiring future botanists and environmentalists.
By promoting recreation and learning, botanical gardens in India connect people with nature while spreading ecological awareness, making them vital spaces for cultural enrichment and scientific education.
Exploring the rich diversity of botanical gardens in India becomes more enjoyable when planned well. Most gardens have a nominal entry fee ranging from ₹20 to ₹100, with separate charges for cameras or special exhibitions. Timings are generally 8:00 AM to 6:00 PM, though some research-focused gardens may have restricted hours. The best seasons to visit are spring and early winter, when flowers are in full bloom and the weather is pleasant.
Visitors can enjoy activities like annual flower shows at Lalbagh in Bengaluru or Ooty’s rose festival, which display exotic floral arrangements. Some gardens, like the one at Ooty and Nandankanan, also offer boating facilities. Photography is a major attraction, with opportunities to capture rare orchids, landscaped lawns, and heritage trees.
For a smooth experience, wear comfortable walking shoes, carry drinking water, and plan visits during weekdays to avoid heavy crowds. Checking local schedules for special exhibitions ensures you don’t miss seasonal highlights. With these tips, a trip to botanical gardens in India becomes both memorable and enriching.
From preserving rare species to hosting vibrant flower shows, botanical gardens in India represent a perfect blend of ecological significance and cultural heritage. They safeguard endangered plants, support medicinal research, and act as the green lungs of cities while offering serene spaces for leisure and recreation. Gardens like the Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata, Lalbagh in Bengaluru, and the Botanic Garden of Indian Republic in Noida are biodiversity museums, reminding us of India’s rich natural wealth.
These gardens provide valuable lessons in sustainability and conservation for students, researchers, and nature lovers. For tourists and families, they are refreshing escapes filled with beauty, history, and education. By visiting and supporting these spaces, we enjoy their charm and contribute to protecting biodiversity for future generations. Truly, botanical gardens in India are treasures where science, culture, and leisure come together in harmony.
Read More :-
There are about 122 botanical gardens recorded in India. Below is the list of the famous botanical gardens in India: Assam State Zoo-cum-Botanical Garden– Guwahati, Assam.
Top Botanical Gardens in India
1. Lalbagh Botanical Garden, Bangalore.
2. Lloyd’s Botanical Garden, Darjeeling.
3. Assam State Zoo Cum Botanical Garden, Guwahati.
4. Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Botanical Garden, Srinagar.
5. National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow.
6. Empress Garden, Pune.
7. TNAU Botanical Garden, Coimbatore.
The Indian Botanic Garden is situated in Shibpur, Howrah, near Kolkata. It boasts various rare plants, including over 12,000 unique specimens.
The Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden (AJCBIBG) in Howrah, West Bengal, is India’s most extensive botanical garden.
William Roxburgh (3/29 June 1751 – 18 February 1815) made significant contributions to Indian botany, earning him the title of the founding father.
The first botanical garden in India is the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanical Garden, formerly known as the Indian Botanical Garden or Calcutta Botanical Garden.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.