Quick Summary
Turtles and tortoises have distinct physical features and different habitats.
Turtles typically live in water, while tortoises are land-dwelling creatures.
Understanding the difference between a turtle and a tortoise helps you identify them based on diet, movement, and lifespan.
Table of Contents
When it comes to reptiles, turtles and tortoises often get confused. Though they belong to the same animal family and share similar features, they are distinct creatures with very different traits, habits, and lifestyles. Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise, in this detailed guide, we’ll explore the difference between turtles and tortoises, helping you easily identify them and understand their unique characteristics.
The main difference between turtle and tortoise lies in their habitats and physical characteristics.
Here is a table showing the difference between Turtle and Tortoise difference:
| Turtle vs Tortoise | |
| Their shell texture is normally smooth or slightly serrated, helping them to withstand less water. | Tortoise shells have a rough, scaly structure that protects them from potential attacks. |
| Tortoiseshells have a rough, scaly structure that protects them from potential attacks. | Tortoises bask extensively, using the warmth of the sun to maintain their body temperature. |
| Turtles lay their eggs in nests on beaches or sandy coasts, and they frequently return to the same nesting sites. | Tortoises have a distinct nesting and reproductive strategy, digging nests in the earth to lay their eggs. |

Before moving further, let us learn what a turtle is. Turtles, ancient reptiles with a million-year evolutionary history, continue to fascinate us with their various qualities and behaviors. These mysterious creatures are distinguished by their extraordinary characteristics, beginning with their distinctive shell, which distinguishes them from other reptiles. Turtles, being cold-blooded by nature, rely on external sources to control their body temperature. Another notable feature is their longevity, with some species surviving for decades. Here’s a quick guide to these shelled wonders:

Tortoises display a variety of unique behavioral behaviors in addition to their morphological characteristics. Their slow and methodical motions, frequently characterized by a sluggish and leisurely tempo, represent patience and perseverance. Tortoises are strictly herbivores, preferring to eat plants and vegetation. They have evolved to flourish in dry areas, demonstrating their tolerance to harsh conditions. Let’s move forward now that we know what a tortoise is. Here’s what sets them apart:
Here is a table showing the 5 difference between turtle and tortoise
| Difference between Turtle and Tortoise | ||
| Characteristics | Turtle | Tortoise |
| Habitat | Aquatic or semi-aquatic in nature, they may survive in both water and on land. | Terrestrial in nature, located on land. |
| Limbs | Swimmers with webbed feet or flippers. | Walking legs that are strong and column-like. |
| Shell Shape | Shell that is more streamlined and hydrodynamic. | A thick, dome-shaped shell for protection. |
| Ability to retract | They have the ability to withdraw their heads and limbs within their shells. | They are usually unable to withdraw their heads and limbs within their shells. |
| Diet | Consumes aquatic vegetation, tiny fish, and invertebrates. | Herbivores consume mostly plants and plant debris. |
Understanding the differences between turtles and tortoises is not only intriguing, but it is also necessary for the correct care and maintenance of these amazing reptile species in their unique ecosystems.
When discussing the difference between turtle and tortoise, one of the most significant aspects to consider is their habitat. While both belong to the order Testudines, their living environments are quite distinct, reflecting their adaptations to different lifestyles. This article will explore the habitat variations difference between turtle and tortoise, highlighting how these differences influence their behavior, diet, and overall survival.
The physical differences between turtle and tortoise are unique and necessary for distinguishing these animals. Differences between Turtles and tortoises, both members of the order Testudines, exhibit distinct physical characteristics that reflect their adaptations to different environments. Here’s a brief overview of their key differences:
Good eyesight for spotting movement on land, but limited hearing compared to turtles.
The Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise is evident in their shell structures. Tortoises have dome-shaped, heavy shells that provide protection and support for their land-dwelling lifestyle. In contrast, turtles possess lighter, flatter shells that are streamlined for swimming, aiding their aquatic movement. This adaptation highlights their distinct habitats and evolutionary traits.
The Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise extends to their reproductive habits. Tortoises generally lay eggs in burrows on land, where the hatchlings emerge and adapt to a terrestrial life. Turtles, being aquatic or semi-aquatic, lay eggs on sandy beaches or soft soil near water bodies, with hatchlings heading toward water after birth. This variation reflects their distinct habitats and life cycles.
The Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise is evident in their lifespans. Tortoises are known for their remarkable longevity, often exceeding 100 years, with some living up to 150 years. In contrast, turtles, as per studies on turtle vs tortoise lifespan, generally live shorter lives, ranging between 20 and 50 years. This distinction underscores their diverse biological and environmental adaptations.
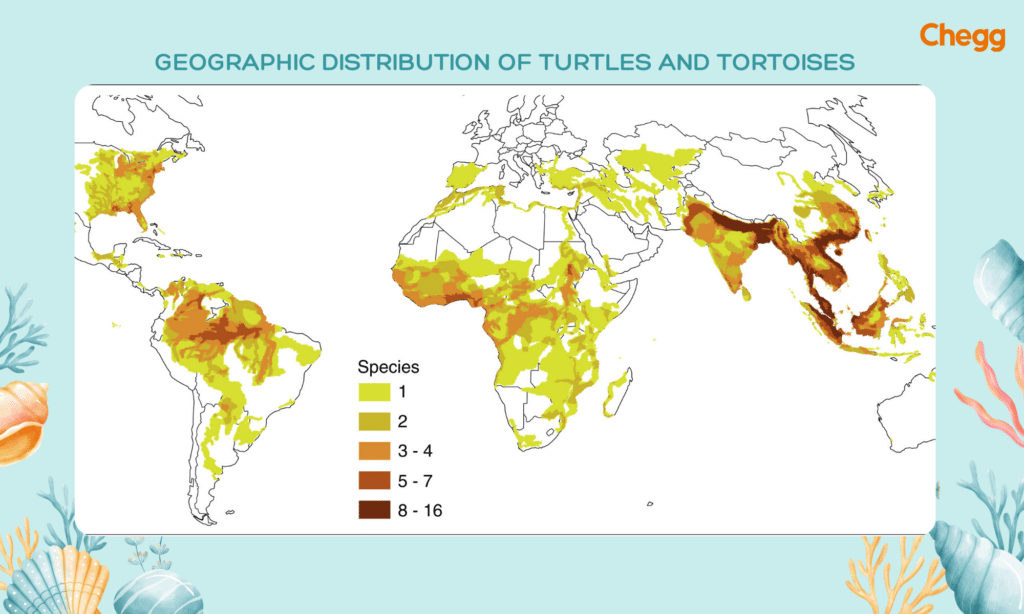
Exploring where turtles and tortoises live is like creating a map of their favorite spots. Turtles often thrive in places with water, like ponds and rivers, while tortoises prefer drier areas with lots of land. By figuring out these preferred regions, scientists can understand more about their habitats and plan how to protect them.
It’s like putting together puzzle pieces to see the bigger picture of their homes. This knowledge helps us make informed decisions to safeguard these incredible creatures and the places they call home.
Turtles and sea turtles are both fascinating creatures that belong to the order Testudines, a group of reptiles characterized by their hard shells. However, there are some key differences between these two types of turtles that are worth exploring.
Here are the main differences between a turtle and a sea turtle:
While turtles and sea turtles share many similarities as members of the Testudines order, they also have distinct differences that make each unique. Whether it’s their habitat, physical characteristics, or diet, these differences are a testament to the incredible diversity of life on our planet.
Here are some fun and interesting facts about tortoises and turtles:
Difference between Turtle and Tortoise and Terrapin, ever looked at a shelled reptile and wondered, “Is that a turtle, a tortoise, or a terrapin?” Don’t worry, it’s a common question! These fascinating creatures, all belonging to the chelonian family, share a similar body plan but have distinct adaptations for their preferred habitats. Understanding these differences is a valuable lesson, especially in Class 5, as it showcases how animals evolve for their environment.
| Feature | Turtle | Tortoise | Terrapin |
| Habitat | Aquatic or semi-aquatic | Terrestrial | Semi-aquatic |
| Shell | Flatter, streamlined for swimming | High-domed, sturdy | Varies, flatter than tortoise but higher than turtle |
| Limbs | Modified into flippers | Sturdy legs for walking | Similar to turtles, but may be stockier |
| Diet | Omnivorous (varies by species) | Herbivorous | Omnivorous (leans towards aquatic prey) |
| Lifespan | Up to 40 years (varies by species) | Over 150 years (some species) | 40-80 years (varies by species) |
Ever looked at a turtle and a tortoise and wondered, “Aren’t they basically the same?” Well, that’s a common question, even for grown-ups! But look a little closer, and you’ll see these shelled superstars have some key differences. Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise, earning about these differences is a great fit for Class 5 because it helps you appreciate the diversity of life on Earth. Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise, it shows us how different species adapt to their environments in unique ways. Plus, it’s just really cool to know about these amazing creatures!
So, the next time you see a turtle or a tortoise, remember these cool differences! They’re both amazing animals with unique adaptations that help them thrive in their own special worlds.
Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise, in Class 5, we learned about vertebrates and how their bodies are adapted for different environments. Now, in Class 6, we’re diving deeper into the fascinating world of reptiles! Let’s crack the code on two shelled superstars – turtles and tortoises. They might seem similar, but look closer, and you’ll discover a world of fascinating differences!
So, there you have it! Turtles and tortoises, though both sporting impressive shells, have distinct adaptations that allow them to thrive in their unique environments. By understanding these differences, we gain a deeper appreciation for the amazing diversity of life on our planet!
Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise, both turtles and tortoises face significant conservation challenges. Habitat destruction, poaching, climate change, and the pet trade have led to declines in many species populations. Notably, freshwater turtles and tortoises are among the most endangered vertebrates, with nearly half of the 300 known species threatened with extinction.
A turtle is a cold-blooded reptile belonging to the order Testudines. It is characterized by its bony or cartilaginous shell, which serves as protection. Turtles are known for their adaptability to diverse environments, ranging from terrestrial to aquatic habitats, depending on the species.
Yes, tortoises are exclusively land-dwelling reptiles. Unlike turtles, which can be aquatic or semi-aquatic, tortoises are adapted to terrestrial environments, with strong, sturdy legs and dome-shaped shells that suit their life on land.
No, tortoises do not swim. They are land-dwelling reptiles with adaptations like strong legs and dome-shaped shells, which are suited for terrestrial habitats. Unlike turtles, they lack the webbed feet or streamlined body needed for swimming and spend their lives on land.
Whether tortoises are bigger than turtles depends on the species. Some tortoises, like the Galápagos tortoise, can grow exceptionally large, surpassing most turtle species. However, certain sea turtles, such as the leatherback turtle, can be even larger, with lengths exceeding 2 meters. So, it’s not a simple rule—size varies greatly among species!
Here are a few turtle species: Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas), known for tropical habitats; Leatherback Turtle (Dermochelys coriacea), the largest sea turtle; Box Turtle (Terrapene), terrestrial with hinged shells; and Snapping Turtle (Chelydra serpentina), with strong jaws.
All turtles are not tortoises! Turtles are a broader category, including both aquatic and semi-aquatic species, while tortoises are exclusively land-dwelling reptiles. For example, a Green Sea Turtle is not a tortoise; it lives in the ocean, unlike tortoises which thrive on land. Their distinct habitats and adaptations set them apart!
For Class 4: The difference between turtle and tortoise lies in their habitats. Tortoises live on land with dome-shaped shells and strong legs. Turtles are aquatic or semi-aquatic, with flatter, lighter shells and webbed feet for swimming. Their lifestyles vary greatly!
Also Read :-
Difference Between Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
Difference Between Meteors and Meteorites : Brief Overview
What is the Difference Between Prism and Pyramid Geometry? Two Key Shapes

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.