
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
The year 1857 marked a significant chapter in India’s fight for freedom. It was the year of the First War of Indian Independence, also known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857 or the Sepoy Mutiny. This was one of the earliest large-scale revolts against British rule in India. The rebellion was fueled by widespread resentment towards British policies and acts of injustice, particularly among Indian soldiers, known as sepoys, in the British army.
In this article, we will explore the lives and contributions of the Freedom Fighters of 1857, who played pivotal roles in the 1857 revolt. We will also examine the causes, significant events, and the lasting legacy of this historic uprising.
The 1857 rebellion did not occur overnight. It resulted from decades of British exploitation, cultural interference, and events that eventually led to widespread anger and discontent. Here are the key causes that triggered the revolt:
These causes created a perfect storm of anger and rebellion against British rule.
Several brave individuals emerged as key leaders during the 1857 revolt. They came from different regions and backgrounds, but all had one goal: to free India from British rule.
Mangal Pandey is often considered the first hero of the 1857 rebellion. He started the Revolt as a sepoy in the British East India Company’s army, serving in the 34th Bengal Native Infantry.
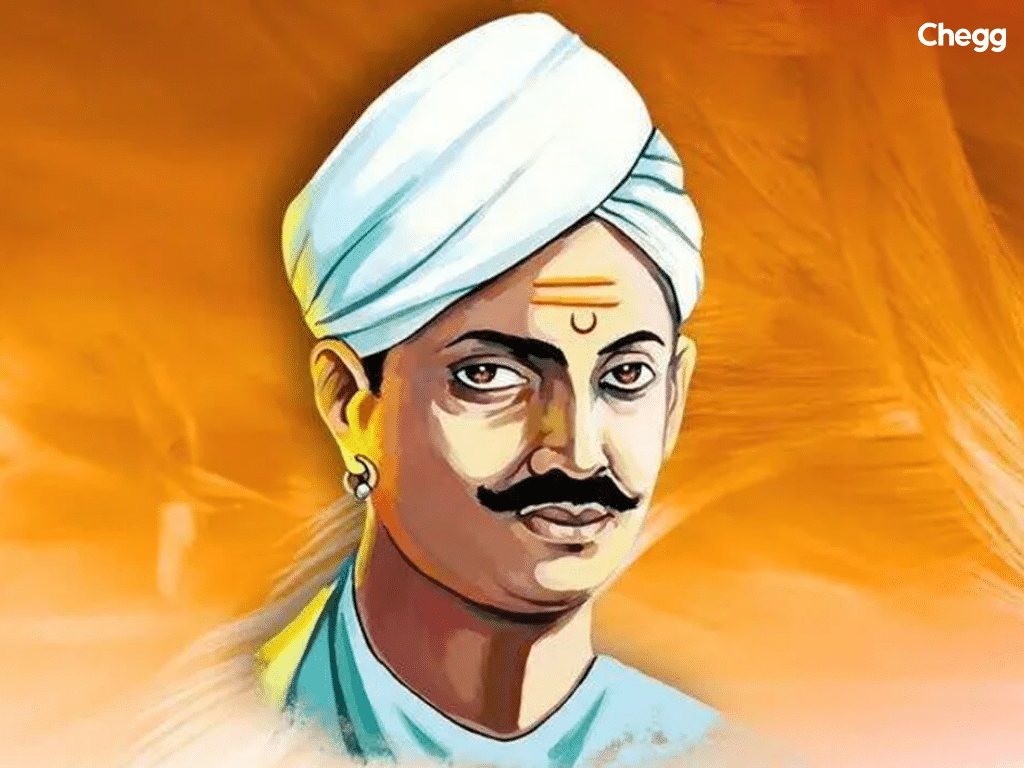

Mangal Pandey’s bravery inspired others to join the rebellion. He is remembered as one of the first freedom fighters who started the Revolt of 1857 and dared to stand up against British rule.
Rani Lakshmibai, also known as the Queen of Jhansi, is one of the most iconic figures of the 1857 rebellion. Her courage, leadership, and dedication to protecting her kingdom have made her a symbol of resistance and bravery.
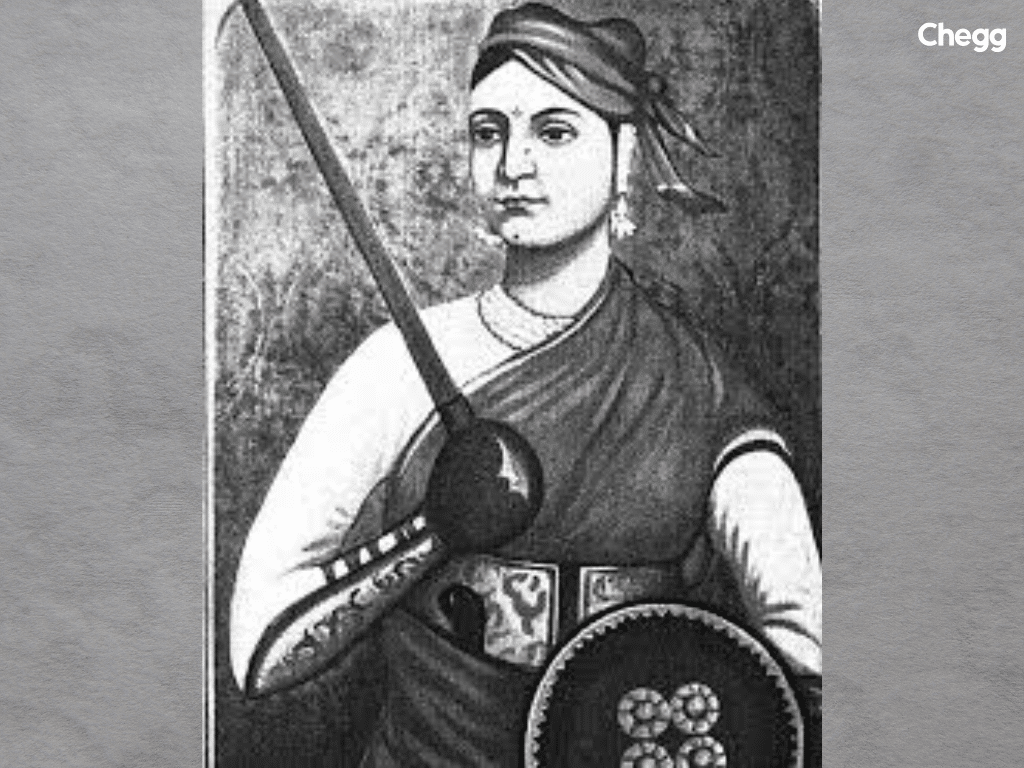

Rani Lakshmibai is remembered as a fearless leader who fought bravely until her last breath. She remains an inspiration for generations of Indians, symbolizing the spirit of resistance against oppression.
Bahadur Shah Zafar, the last Mughal emperor, was an unlikely leader in the 1857 rebellion. Though old and powerless, he became a symbolic figure for the rebels who rallied under his leadership.
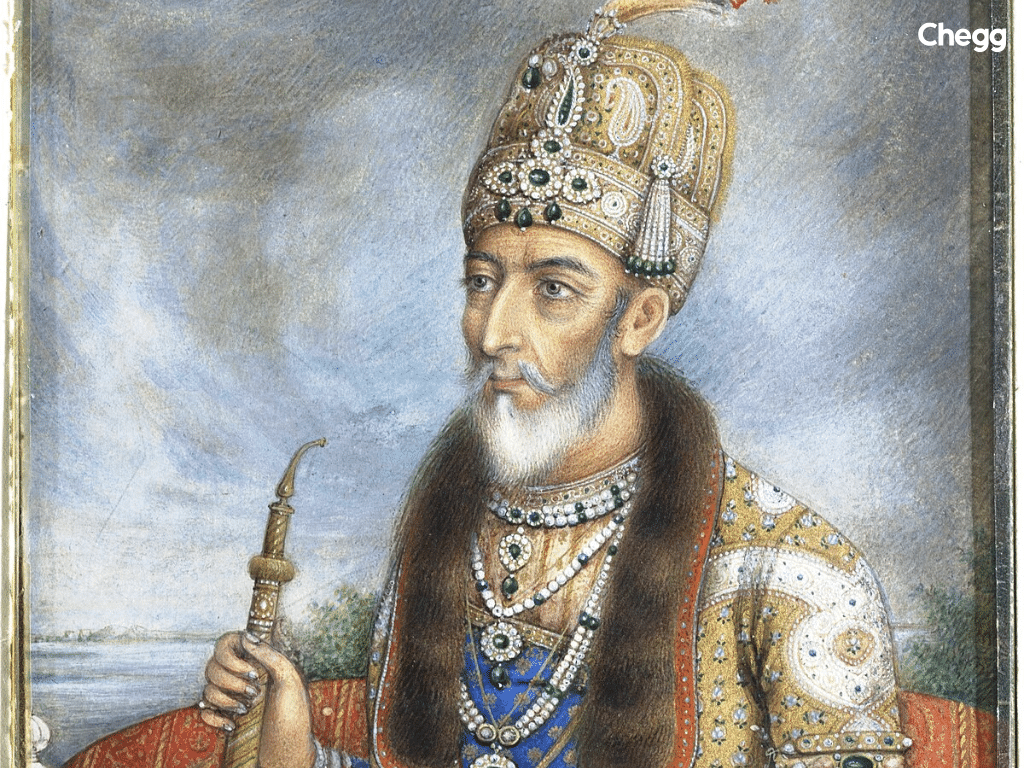

Bahadur Shah Zafar’s exile marked the official end of the Mughal dynasty, but his role in the 1857 rebellion made him a martyr in India’s freedom struggle. He is also remembered for his poetry, which reflects the pain of his lost empire.
Nana Sahib was a prominent leader of the 1857 rebellion. Born Dhondu Pant, he was the adopted son of Baji Rao II, the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire.
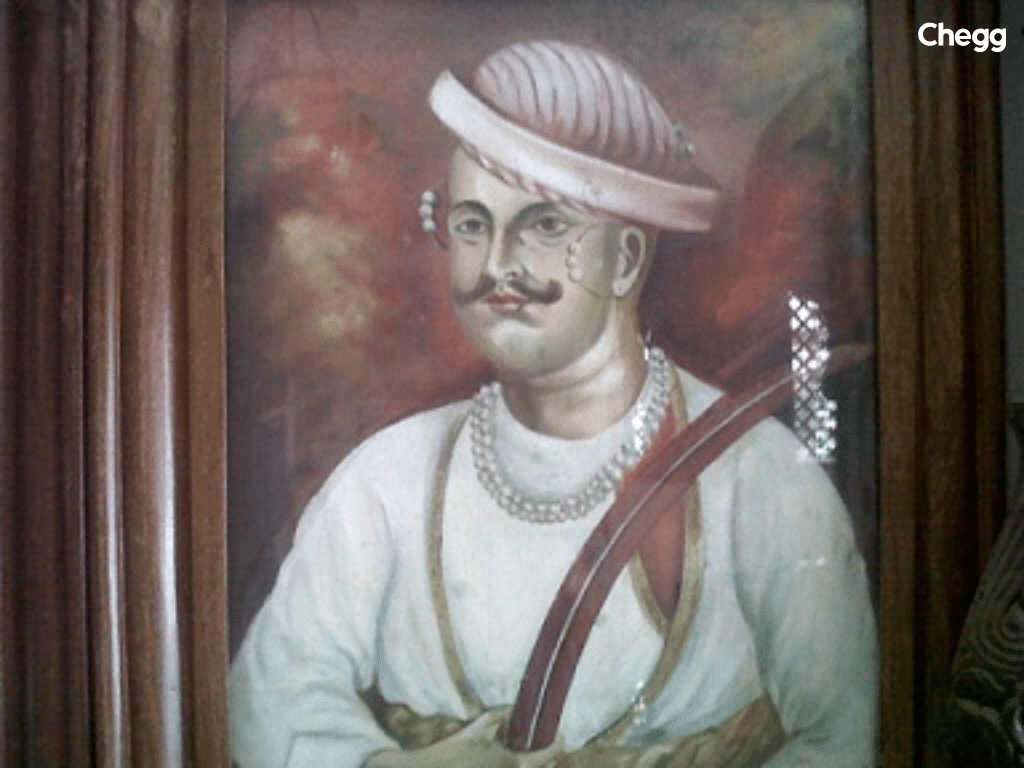

Nana Sahib’s role in the rebellion made him a key figure in the fight against British rule. His disappearance after the revolt remains a mystery to this day.
Tantia Tope was one of the most brilliant military commanders of the 1857 rebellion. He was a close associate of Nana Sahib and played a crucial role in several battles.

Tantia Tope’s military strategies and bravery made him legendary in India’s freedom struggle. He is remembered as one of the most skilled leaders of the rebellion.
Begum Hazrat Mahal was one of the few women leaders who played a key role in the 1857 rebellion. She was the wife of Nawab Wajid Ali Shah of Awadh (now Uttar Pradesh).
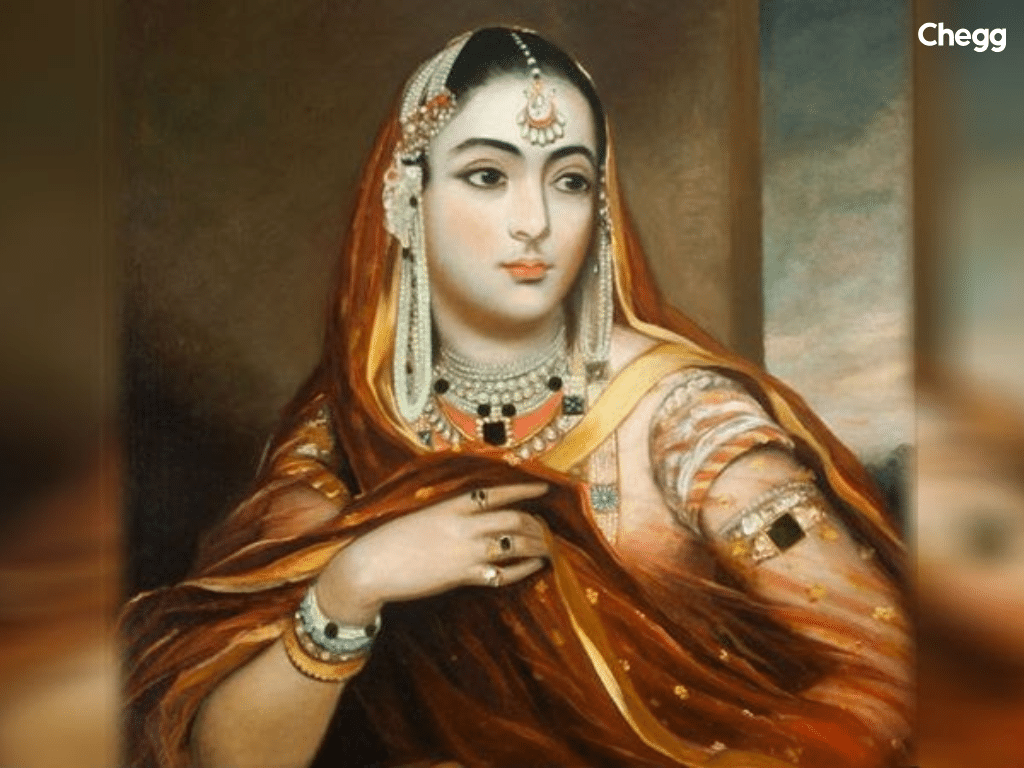
Begum Hazrat Mahal is remembered for her courage and leadership in defending her kingdom. She is a symbol of women’s empowerment in India’s freedom movement.
General Bakht Khan was a prominent leader during the 1857 rebellion and served as the commander of rebel forces in Delhi. He brought organizational skills and military expertise to the revolt.

General Bakht Khan is remembered for his leadership and as a symbol of the collective efforts to resist British oppression.
Kunwar Singh, the “Lion of Bihar,” was a landlord who emerged as a key leader of the rebellion at the age of 80.
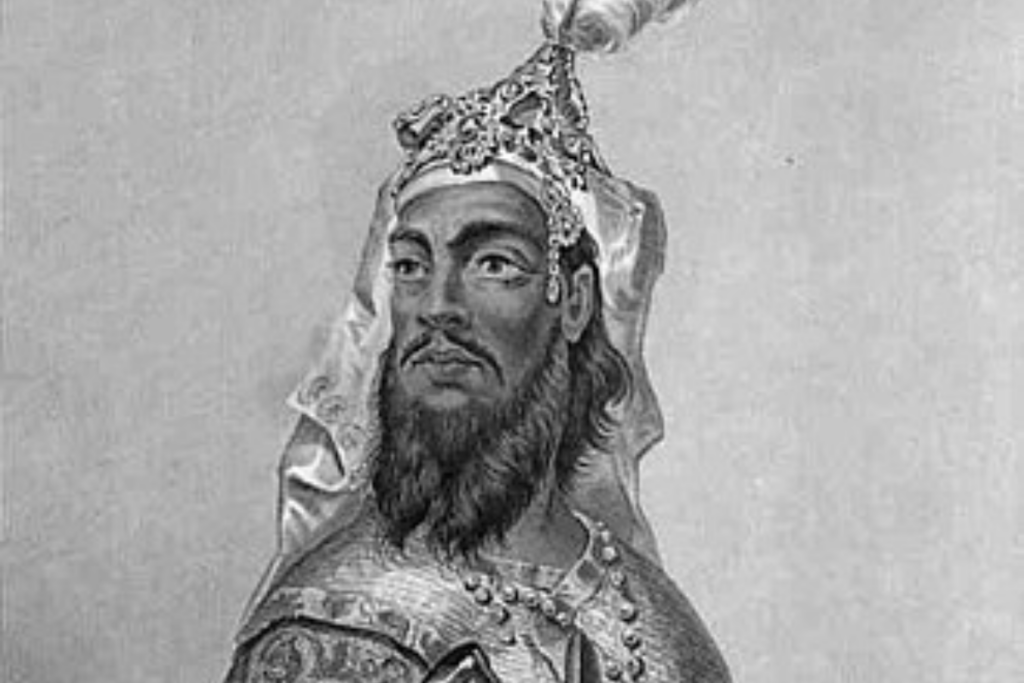

Kunwar Singh is a celebrated hero in Bihar and is honored for his indomitable spirit and courage in adversity.
Maulvi Ahmadullah was a key figure in the revolt and was known for his charisma and ability to mobilize the masses in Faizabad and Awadh.

Maulvi Ahmadullah remains a symbol of resistance and religious unity, inspiring people to fight for freedom.
Udmi Ram was a grassroots leader from the village of Libaspur near Delhi who rose to prominence during the revolt.
He is remembered as an unsung hero who embodied the spirit of the typical Indian fighting for freedom.
Seth Ramjidas was a wealthy merchant who supported the rebellion through financial contributions.

Seth Ramjidas Gurwala is honored as a martyr who sacrificed his life and wealth for the cause of India’s freedom.
The 1857 rebellion was marked by several key events and battles that shaped the course of the revolt. Below is a timeline of some of the most important events:
| Date | Event/Battle | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| May 1857 | Mutiny at Meerut | The rebellion began when Indian soldiers mutinied. |
| June 1857 | Siege of Cawnpore (Kanpur) | Nana Sahib led the rebels to capture Kanpur. |
| June 1857 | Battle of Delhi | The rebels captured Delhi and declared Bahadur Shah Zafar as their emperor. |
| March 1858 | Fall of Jhansi | Rani Lakshmibai’s forces were defeated by the British. |
| April 1859 | Execution of Tantia Tope | One of the last major leaders of the rebellion was executed. |
These events marked both the rise and fall of the rebellion, with the British eventually regaining control by 1859.
Although the 1857 rebellion was ultimately unsuccessful in overthrowing British rule, it laid the groundwork for India’s future independence movements.
End of the Mughal Empire
Direct British Rule
Military Reforms
Inspiration for Future Leaders
Symbol of Unity
Shift in Indian Nationalism
Some of the reasons of the Failure of the Revolt of 1857 were:
The freedom fighters of 1857 are remembered as heroes who laid the foundation for India’s eventual independence in 1947. They are honored in history books, statues, and memorials nationwide. Their courage, sacrifice, and resistance stories inspire millions of Indians today.
| Place | Important Leaders |
|---|---|
| Delhi | Bahadur Shah II, General Bakht Khan |
| Lucknow | Begum Hazrat Mahal, Birjis Qadir, Ahmadullah |
| Kanpur | Nana Sahib, Rao Sahib, Tantia Tope, Azimullah Khan |
| Jhansi | Rani Laxmibai |
| Bihar | Kunwar Singh, Amar Singh |
| Rajasthan | Jaidayal Singh, Hardayal Singh |
| Farrukhabad | Tufzal Hasan Khan |
| Assam | Kandapareshwar Singh, Maniram Dutta Baruah |
| Orissa | Surendra Shahi, Ujjwal Shahi |
This table showcases the key places and the prominent 1857 Revolt Leaders and Places, reflecting the widespread resistance against British rule across India.
The Freedom Fighters of 1857 left a lasting legacy in India’s history. Their bravery, sacrifice, and determination to fight against British rule laid the groundwork for future generations to continue the struggle for independence. While the rebellion was ultimately crushed, the spirit of resistance it ignited continued to burn brightly in the hearts of Indians, leading to the eventual victory of freedom in 1947.
These heroes of 1857 are not just names in history books; they are symbols of the courage and resilience that shaped the nation we know today.
Explore more about India’s rich history and the heroes who shaped the nation. Share this article to spread awareness about the contributions of the freedom fighters of 1857, or read more about India’s journey to independence.
Recommended Read:-
The key leaders of the Revolt of 1857 included Rani Laxmi Bai, Bahadur Shah Zafar, and Mangal Pandey. Several other prominent figures, such as Nana Saheb, Tantia Tope, Kunwar Singh, and Man Singh, significantly contributed to the uprising.
The top 10 freedom fighters of 1857 include Mangal Pandey, Rani Lakshmibai, Bahadur Shah Zafar, Nana Saheb, Tantia Tope, Begum Hazrat Mahal, Kuwar Singh, Bakht Khan, Azimullah Khan, and Firoz Shah.
The First War of Independence began in 1857. It was fought by leaders like Mangal Pandey, Rani Lakshmibai, Nana Saheb, and Tantia Tope, along with Indian soldiers and civilians who rebelled against British rule.
Key leaders of the Revolt of 1857 were Rani Lakshmibai, Nana Saheb, Bahadur Shah Zafar, Tantia Tope, and Kuwar Singh, who united to challenge British dominance.
Mangal Pandey was the first freedom fighter of 1857. He is considered one of the first freedom fighters of the Revolt of 1857. On March 29, 1857, he attacked and injured two British officers with his bayonet after refusing to sign a new order that demanded the use of greased cartridges.
Rani Lakshmibai, the Queen of Jhansi, was a pivotal figure in the Indian Revolt of 1857. Known for her bravery and leadership, she fiercely resisted British forces and became a symbol of resistance during the rebellion.
The 1857 revolt occurred due to a combination of economic exploitation, religious and cultural insensitivity, and military discontent among Indian soldiers (sepoys) serving in the British army.
Rani Lakshmibai led the defense of Jhansi against British forces, fighting bravely on the battlefield. Her leadership and courage made her a symbol of resistance against British rule.
Bahadur Shah Zafar, the last Mughal emperor, was declared the symbolic leader of the rebellion by the rebels. Although he did not actively participate in battles, his leadership gave legitimacy to the revolt.
1857 के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में कई प्रमुख सेनानियों ने महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई। यहां 10 प्रसिद्ध स्वतंत्रता सेनानियों के नाम दिए गए हैं: मंगल पांडे, रानी लक्ष्मी बाई, नाना साहेब, बाहादुर शाह जफर, तात्या टोपे, सर्गेण्ट मेजर जमीश (कर्नल जिमी), बेगम हज़रत महल, कुँवर सिंह, हजारी प्रसाद द्विवेदी।
इन सेनानियों ने भारतीय स्वतंत्रता के लिए संघर्ष में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया और ब्रिटिश शासन के खिलाफ विद्रोह में शामिल हुए।
The revolt began on May 10, 1857, at Meerut as a sepoy mutiny. It was initiated by sepoys in the Bengal Presidency against the British officers.
Mangal Pandey fired the first shot of the Indian Rebellion of 1857 at a British officer in Barrackpore in late March 1857.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.