Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Do you know how many district in India there are? Total district in India are approximately 800 as per the latest data of 2025, From language to food, there’s a wide range of diversity in the districts of India. Each district is an administrative unit of India because of the country’s large area and population.
A district is a specific area within a larger region, often defined for administrative, political, or organizational purposes. For example, a city might be divided into districts for managing services or elections. There are a total of 800 districts in India. Dist. is the short form of the district. Understanding the number of districts is essential for various administrative functions, resource allocation, and governance. Therefore, when asking “How Many District in India,” it is vital to note that this number can change due to administrative reorganization or the creation of new districts to serve the population better.
Below is a detailed map of India with Districts:

Before going any further on how many districts in India are there, let us know what is a district. The districts in India are territorial divisions. These divisions ensure the proper functioning of administrative and judicial features. The total number of districts in India as of 2025 is 800.
The most essential functions of districts are:
India is not the only country with districts. Countries like the US and China also have district-level governance.
Sources to data: Census.gov
With the creation of states based on the languages spoken in various areas, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 significantly changed India’s political landscape. India has 28 states and 8 Union Territories as a result of this division. There are present 400 cities in the entire nation. Eight major metropolises comprise these cities: Bangalore, Hyderabad, Chennai, Pune, Ahmedabad, New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Hyderabad. Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential for grasping the country’s administrative structure, as it reflects the organization of governance and resource distribution across these diverse regions.
There are 28 states and 8 union territories in India. Every place has unique aspects, such as cuisine, language, and tourist attractions. Kerala features serene waterways, while Maharashtra features busy cities. There are prominent forts in Rajasthan and beautiful valleys in Himachal Pradesh. These locations add diversity and interest to India. They have their leaders and are crucial to the development of India. Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential, as each state and Union Territory is further divided into districts, which are vital for local governance and administration, ensuring that the unique needs of each region are addressed effectively.
| STATES | DISTRICTS | District Names |
| ANDHRA PRADESH | 13 | Allurisitharamaraju, Ananthapuramu, Annamayya, Anakapalli, Baptla, Chittoor, East Godavari, Eluru, Guntur, Kakinada, Konaseema, Krishna, Kurnool, Nandyal, N.T.R, Palnadu, Parvathipurammanyam, Prakasam, Srisathyasai, SPS Nellore, Srikakulam, Tirupati, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, West Godavari, and YSR Kadapa |
| ARUNACHAL PRADESH | 26 | Anjaw, Changlang, Dibang Valley, East Kameng, East Siang, Itanagar, Kra Daadi, Kurung Kumey, Lohit, Longding, Lower Dibang Valley, Lower Subansiri, Namsai, Papumpare, Shiyomi, Siang, Tawang, Tirap, Upper Siang, Upper Subansiri, West Kameng, and West Siang. |
| ASSAM | 33 | Baksa, Barpeta, Bongaigaon, Cachar, Charaideo, Chirang, Darrang, Dhemaji, Dhubri, Dibrugarh, Dima Hasao, Goalpara, Golaghat, Hailakandi, Jorhat, Kamrup Metropolitan, Kamrup, Karbi Anglong, Karimganj, Kokrajhar, Lakhimpur, Majuli, Morigaon, Nagaon, Sivasagar, Sonitpur, South Salmara- Mankachar, Tinsukia, Udalguri, and West Karbi Anglong. |
| BIHAR | 38 | Araria, Arwal, Aurangabad, Banka, Begusarai, Bhagalpur, Bhojpur, Buxar, Darbhanga, East Champaran, Gaya, Gopalganj, Jamui, Jehanabad, Kaimur, Katihar, Khagaria, Kishanganj, Lakhisarai, Madhepura, Madhubani, Munger, Muzaffarpur, Nalanda, Nawada, Patna, Purnea, Rohtas, Saharsa, Samastipur, Saran, Sheikhpura, Sheohar, Sitamarhi, Siwan, Supaul, Vaishali, and West Champaran. |
| CHATTISGARH | 27 | Balod, Balodabazar Bhatapara, Balrampur, Bastar, Bemetara, Bijapur, Bilaspur, Dantewada, Dhamtari, Durg, Gariaband, Gaurela Pendra Marwahi, Jangir Champa, Jashpur, Kanker, Kawardha, Kondagaon, Korba, Korea, Mahasamund, Mungeli, Narayanpur, Raigarh, Raipur, Rajnandgaon, Sukma, Surajpur, and Surguja. |
| GOA | 2 | North Goa and South Goa |
| GUJARAT | 33 | Ahmedabad, Amreli, Anand, Arvalli, Banaskantha, Bharuch, Bhavnagar, Botad, Chhotaudepur, Dahod, Devbhumi Dwarka, Gandhinagar, Gir Somnath, Jamnagar, Junagadh, Kutch, Kheda, Mahesana, Mahisagar, Morbi, Narmada, Navsari, Panchmahals, Patan, Porbandar, Rajkot, Sabarkantha, Surat, Surendranagar, Tapi, Dang, Vadodara, and Valsad. |
| HARYANA | 22 | Ambala, Bhiwani, Charkhi Dadri, Faridabad, Fathehabad, Gurugram, Hisar, Jhajjar, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal, Kurukshetra, Mahendragarh, Nuh, Palwal, Panchkula, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Sirsa, Sonipat, and Yamunanagar. |
| HIMACHAL PRADESH | 12 | Bilaspur, Chamba, Hamirpur, Kangra, Kinnaur, Kullu, Lahaul and Spiti, Mandi, Shimla, Sirmapur, Solan, and Una. |
| JHARKHAND | 24 | Bokaro, Chaibasa, Chatra, Deoghar, Dhanbad, Dumka, Garhwa, Giridih, Godda, Gumla, Hazaribagh, Jamshedpur, Jamtara, Khunti, Koderma, Latehar, Lohardaga, Pakur, Palamu, Ramgarh, Ranchi, Sahibganj, Seraikela, and Simdega. |
| KARNATAKA | 30 | Bidar, Kalaburagi, Vijaypura, Yadagiri, Belagavi, Bagalkot, Raichur, Uttar Kannada, Dharwad, Gadag, Koppal, Ballari, Vijayanagar, Haveri, Davangere, Shivamogga, Udupi, Chikkamagaluru, Chitradurga, Dakshin Kannada, Kodagu, Hassan, Tumakuru, Mysuru, Mandya, Chamrajnagar, Ramanagara, Bengluru, Bengaluru Rural, Kolar, and Chikkaballapura. |
| KERALA | 14 | Alappuzha, Ernakulam, Idukki, Kannur, Kasaragod, Kollam, Kottayam, Kozhikode, Mallapuram, Palakkad, Pathanamthitta, Thrissur, Trivandrum, and Wayanad. |
| MADHYA PRADESH | 52 | Agar Malwa, Alirajpur, Anuppur, Ashokanagar, Balaghat, Barwani, Betul, Bhind, Bhopal, Burhanpur, Chhatarpur, Chhindwara, Damoh, Datia, Dewas, Dhar, Dindori, Guna, Gwalior, Harda, Indore, Jabalpur, Jhabua, Katni, Khandwa, Khargone, Mandla, Mandsaur, Mauganj, Morena, Narmadapurm, Narsinghpur, Neemuch, Niwari, Panna, Raisen, Rajgarh, Ratlam, Rewa, Sagar, Satna, Shehore, Seoni, Shahdol, Shajapur, Sheopur, Shivpuri, Sidhi, Singrouli, Tikamgarh, Ujjain, Umaria, and Vidisha. |
| MAHARASHTRA | 36 | Ahmednagar, Akola, Amravati, Aurangabad, Need, Bhandara, Buldhana, Chandrapur, Dhule, Gadchiroli, Gondia, Hingoli, Jalgaon, Jalna, Kolhapur, Latur, Mumbai City, Mumbai Suburban, Nagpur, Nanded, Nandurbar, Nashik, Osmanabad, Palghar, Parbhani, Pune, Raigad, Ratnagiri, Sangli, Satara, Sindudurg, Solapur, Thane, Wardha, Washim, and Yavatmal. |
| MANIPUR | 16 | Bishnupur, Chandel, Churachandpur, Pherzawl, Tengnoupal, Kakching, Noney, Imphal East and West, Jiribam, Kamjong, Kangpokpi, Senapati, Tamenglong, Thoubal, and Ukhrul. |
| MEGHALAYA | 11 | South West Garo Hills, West Garo Hills, North Garo Hills, East Garo Hills, South Garo Hills, West Khasi Hills, South West Khasi Hills, Easter West Khasi Hills, East Khasi Hills, Ri Bhoi, West Jaintia Hills, and East Jaintia Hills. |
| MIZORAM | 8 | Aizawl, Lunglei, Champhai, Mamit, Serchhip, Kolasib, Lawngtlai, Saiha, and Khawzawl. |
| NAGALAND | 11 | Dimapur, Kiphire, Kohima, Longleng, Mokokchung, Mon, Paren, Phek, Tuensang, Wokha, Zunheboto, Chumukedima, Niuland, Noklal, Shamator, and Tseminyu. |
| ORISSA | 30 | Angul, Balangir, Baleshwar, Bargarh, Bhadrak, Boudh, Cuttack, Deogarh, Dhenkanal, Gajapati, Ganjam, Jagatsinghpur, Jajpur, Jharsuguda, Kalahandi, Kandhamal, Kendrapara, Kendujhar, Khorda, Koraput, Malkangiri, Mayurbhanj, Nabarangpur, Nayagarh, Nuapada, Puri, Rayagada, Sambalpur, Subarnapur, and Sundargarh. |
| PUNJAB | 22 | Amritsar, Barnala, Bathinda, Faridkot, Fatehgarh Sahib, Fazilka, Ferozepur, Gurdaspur, Hoshiarpur, Jalandhar, Kapurthala, Ludhiana, Malerkotla, Mansa, Moga, Sas nagar, Sri Muktar Sahib, SBS Nagar, Pathankot, Patiala, Rupnagar, Sangrur, and Tarn Taran. |
| RAJASTHAN | 33 | Ajmer, Alwar, Banswara, Baran, Barmer, Bharatpur, Bhilwara, Bikaner, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Churu, Dausa, Dholpur, Dungarpur, Hanumangarh, Jaisalmer, Jaipur, Jalor, Jhalawar, Jhunjhunu, Jodhpur, Karauli, Kota, Nagaur, Pali, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Sawai Madhopur, Sikar, Sirohi, Sri Ganganagar, Tonk, Udaipur. |
| SIKKIM | 4 | Gangtok, Mangan, Gyalshinh, Namchi, Pakyong, and Soreng. |
| TAMIL NADU | 37 | Ariyalur, Chengalpattu, Chennai, Coimbatore, Cuddalore, Dharmapuri, Dindigul, Erode, Kallakurichi, Kancheepuram, Kanniyakumari, Karur, Krishnagiri, Madurai, Mayiladuthurai, Nagapattinam, Namakkal, Nilgiris, Perambalur, Pudukkottai, Ramanathapuram, Ranipet, Salem, Sivaganga, Tenkasi, Thanjavur, Theni, Thoothukudi, Tiruchirapalli, Tirunelveli, Tirupathur, Tiruvannamalai, Tiruvarur, Vellore, Viluppuram, and Virudhunagar. |
| TELANGANA | 33 | Adilabad, Hyderabad, Jagtial, Jangaon, Jayashankar Bhupalapally, Jogulamba Gadwal, Kamareddy, Karimnagar, Khammam, Bhadradri Kothagudem, Komaram Bheem Asifabad, Mahabubnagar, Mahabubabad, Mancherial, Medak, Medchal Malkajgiri, Mulugu, Nagarkurnool, Nalgonda, Narayanpet, Nirmal, Nizamabad, Pedapalli, Rajanna Sircilla, Rangareddy, Sangareddy, Siddipet, Suryapet, Vikarabad, Wanaparthy, Hanumakonda, Warangal, and Yadadri Bhuvanagari. |
| TRIPURA | 8 | Dhalai, Gomati, Khowai, North Tripura, Sepahijala, South Tripura, Unakoti, and West Tripura. |
| UTTAR PRADESH | 75 | Agra, Aligarh, Allahabad, Ahmednagar, Amroha, Auraiya, Azamgarh, Badaun, Bahraich, Ballia, Balrampur, Banda, Barabanki, Bareilly, and more. |
| UTTARAKHAND | 13 | Almora, Bageshwar, Chamoli, Champawat, Dehradun, Haridwar, Nainital, Pauri Garhwal, Pithoragarh, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, Udham Singh Nagar, and Uttarkashi. |
| WEST BENGAL | 23 | North 24 Parganas, South 24 Parganas, Bankura, Birbhum, CoochBihar, Dakshin Dinajpur, Darjeeling, Hooghly, Howrah, Jalpaiguri, jhargram, Kalimpong, Kolkata, Malda, Murshidabad, Nadia, Paschim Burdwan, Purba Burdwan, Paschim Medinipur, Purba Medinipur, Purulia, Uttar Dinajpur, and Alipurduar. |
Do you know how many district in India? There are 800 total district in India.
Salem, located in Tamil Nadu, holds a unique place in India’s history as the first district established on April 4, 1792. (As of 2025, India has a total of 806 districts.) Originally, Salem covered a vast area of 7,530 square kilometers, which included regions now known as Namakkal, Dharmapuri, and Krishnagar districts. Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential for grasping the administrative evolution of the country, as the creation of districts like Salem reflects the historical and geographical changes that have shaped India’s governance structure over the years.
In its early years, Alexander Reed served as the district’s collector from 1792 to 1799, pivotal in shaping its administrative framework. This historical milestone highlights Salem’s significant contribution to India’s early governance and enduring legacy as a key administrative unit. Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential, as it not only reflects the current administrative structure, with a total of 806 districts as of 2025 but also underscores the historical significance of districts like Salem in the evolution of governance in the country. Each district, including Salem, has played a vital role in the development and administration of India over the years.

Read More:
Do you know the smallest district in India? Mahe, located in the Union Territory of Puducherry, is the smallest district, with an area of just 9 sq. km and a total population of 41,934.
The largest district in India is Kutch, Gujrat. Factors that define the District size are:
Kutch is India’s biggest district. Let us know a bit about its economy.
The most populated district in India is North 24 Parganas, West Bengal, with a population of 10,082,852. Below is the complete district list with all details.
| State | District Names | Population |
| Maharashtra | Thane | 180.50 |
| West Bengal | North 24 Parangas | 160.9 |
| Karnataka | Bangalore | 126.7 |
| Delhi | Delhi East | 120.12 |
| Delhi | Delhi North | 118.34 |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai Suburban | 115.06 |
| West Bengal | Kolkata | 112.09 |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | 95.7 |
| Maharashtra | Pune | 94.27 |
| Gujarat | Ahmedabad | 87.79 |
The least populated district in India is Dibang Valley, Arunachal Pradesh, with a population of 8,004. Below is the complete district list with all details.
| State | District Names | Population |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Dibang Valley | 7,948 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Anjaw | 21,089 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Lahul and Spiti | 31,528 |
| Andaman & Nicobar | Nicobar | 36,842 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Upper Siang | 35,320 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Dibang Valley | 42,855 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Kinnaur | 84,298 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Kurung Kumey | 89,717 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Longding | 56,953 |
| Nagaland | Kiphire | 74,004 |
The district list of the Top 10 biggest District in India is given below:
| District Name | States | Size in sq. km. (Approximate) |
| Kutch | Gujarat | 45,652 |
| Ladakh | Ladakh Union Territory | 59,146 |
| Leh | Ladakh Union Territory | 45,110 |
| Bikaner | Rajasthan | 30,247 |
| Jaisalmer | Rajasthan | 38,401 |
| Rajasthan | Rajasthan | 31,139 |
| Sikar | Rajasthan | 10,813 |
| Barmer | Rajasthan | 28,387 |
| Pali | Rajasthan | 12,456 |
| Ganganagar | Rajasthan | 11,171 |
Uttar Pradesh, founded on January 24, 1950, has 75 districts and an area of 240,928 square kilometers. It is India’s largest state and also has the most districts. Every district is governed by a district magistrate employed by the Indian Administrative Service.
For better administration, the districts of Uttar Pradesh have been split up into eighteen administrative divisions, each with its headquarters. India’s most populous state has always been Uttar Pradesh. In 2011, the state’s Chief Minister, Mayawati, declared the establishment of three new UP districts: Prabuddhanagar, Panchsheel Nagar, and Bhimnagar. With a population exceeding 12 lakh people, Uttar Pradesh plays a significant role in the overall demographic landscape of India.
Understanding “How Many District in India” is crucial, as it highlights the administrative divisions within states like Uttar Pradesh, which contribute to effective governance and resource management in one of the country’s most populous regions. As of 2025, India has 806 districts, reflecting the ongoing evolution of its administrative framework.
India will have 800 districts in total in 2025. This number can fluctuate as the government creates new districts for administrative reasons.
The India district map can be used to explore towns, villages, rivers, tourist spots, and cultural locations.
Some of the most popular online resources for India district maps are Google Maps, Maps of India, and Open Street Map. These can give you a detailed view of the district structure.
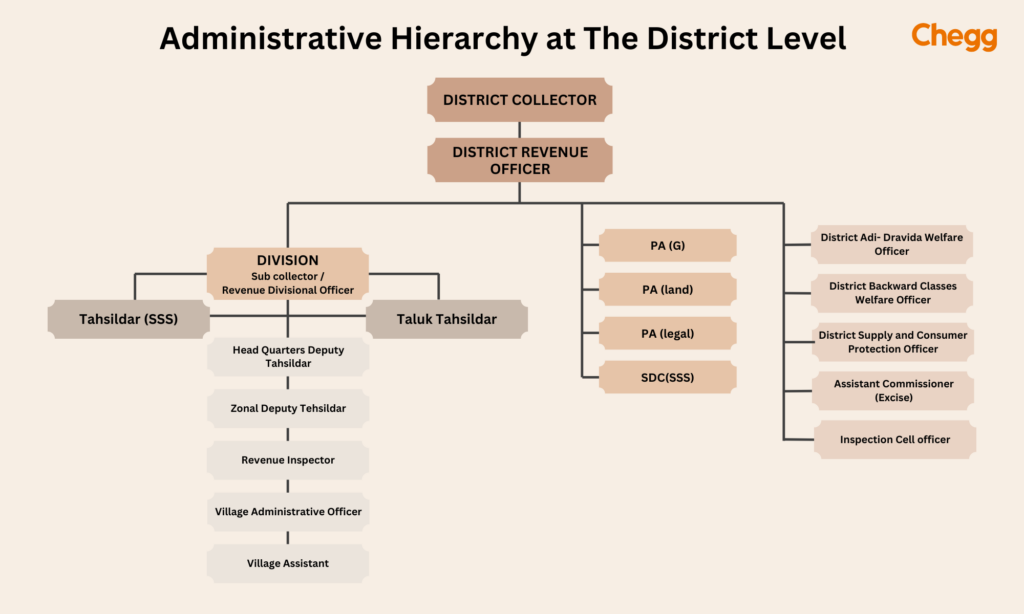
The district administration in India is handled by key officials, including:
These officials receive support from state government officers. While most districts have unique headquarters, some operate without district collectors, like Mumbai City in Maharashtra, Kolkata in West Bengal, Hyderabad in Telangana, and Chennai in Tamil Nadu.
Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential, as it provides insight into the country’s administrative structure, which currently consists of 806 districts as of 2025. Each district plays a vital role in governance, and the unique operational frameworks of certain districts highlight the diversity in administrative practices across India. This complexity is crucial for effective governance and resource allocation in various regions.
The Union Territory of Ladakh witnessed a significant administrative change in 2023 with the announcement of five new districts. This expansion from two to seven districts marks a significant milestone for the region, fulfilling a long-standing demand of residents.
The five newly created districts in Ladakh are:

The creation of these new districts is expected to bring several benefits to Ladakh:
In India, each district is unique, with its languages, food, and clothing styles. For instance, in places like Bengal and Bihar, women often wear sarees, while in Punjab, they prefer suits. Because of these differences, it’s vital to help all districts grow and develop equally. Understanding “How Many District in India” is crucial, as it highlights the current total of 806 districts as of 2025, each contributing to the rich tapestry of India’s cultural diversity.
The government is working on many programs to support districts. Programs like Make in India and Digital India aim to bring more jobs and technology to every corner of the country. This helps ensure all districts can thrive and contribute to India’s progress. Understanding “How Many District in India” is essential. By focusing on equitable development across all districts, the government seeks to enhance economic opportunities and improve living standards, ultimately fostering a more inclusive and prosperous nation.
Kutch in Gujrat is the largest district in India, with an area of 45,674 square kilometers.
As of 2025 data, there are 28 states in India and 8 union territories.
Mahe in Puducherry is the smallest district in India in terms of area. The district occupies an area of 9 square kilometers.
There are around 800 total district in India as of 2025 in 29 states of India.
The first district formed in India was Salem district in Tamil Nadu, established on April 4, 1792.
Uttar Pradesh has the most districts, with 75 districts as of 2025.
Districts in India are organized by state and union territories, each having its administrative division.
Yes, the number of districts in India has gradually increased as new districts are created for better administrative management and governance.
Delhi has 11 districts. Each district is further subdivided into subdivisions for administrative purposes.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.