
Quick Summary
Tehri Dam, the Largest dam in India, stands at 260.5 meters on the Bhagirathi River in Uttarakhand. This massive rock and earth-fill embankment dam serves multiple purposes, including hydropower generation (1,000 MW), irrigation, and drinking water supply. Known for its engineering marvel, Tehri Dam plays a vital role in flood control and supports regional development. As a popular tourist attraction, it showcases India’s infrastructure prowess while contributing significantly to renewable energy goals.
Table of Contents
Hey there, young explorers! Are you ready to dive into an exciting journey to discover the largest dam in India? Buckle up, because we’re about to embark on an adventure that’ll make your next science project or general knowledge quiz a breeze!

The largest dam in India, Tehri Dam, is located on the Bhagirathi River near Tehri in Uttarakhand. It is a significant structure in terms of height and the volume of water it holds. The Tehri Dam is not only the largest in India but also one of the tallest dams in the world, standing at a height of 260.5 meters (855 feet). It plays a crucial role in hydroelectric power generation, irrigation, and flood control in the region.
Dams are crucial structures for water management and come in various types based on their construction and function. Here’s a breakdown:
Based on Structure
The story of the largest dam in India, Tehri Dam, begins in the mid-20th century. The initial idea of constructing a dam on the Bhagirathi River was proposed in the 1950s. However, the actual construction work began much later, in 1978. The project faced numerous challenges, including technical difficulties, financial constraints, and environmental concerns. Despite these hurdles, the determination to harness the river’s potential for irrigation and power generation kept the project moving forward.
After years of relentless effort and overcoming various obstacles, the Tehri Dam was finally completed in 2006. This monumental project was undertaken by the Tehri Hydro Development Corporation (THDC) and stands as a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance.
Tehri Dam, the largest dam in India and the fourth highest dam in the world, is a multi-purpose rock and earth-fill embankment dam on the Bhagirathi River, a tributary of the Ganges River. Here are some key structural features and specifications:
The dam’s height makes it the highest dam in India and one of the highest in the world. The vast reservoir created by the dam, known as the Tehri Lake, stretches over 42 square kilometers, providing water storage for irrigation, municipal supply, and hydroelectric power generation.
The Tehri Dam, being the largest dam in India, holds immense significance in various aspects:
The construction of the largest dam in India has had significant environmental implications. While the Tehri Dam provides numerous benefits, it has also brought about several environmental challenges:
The Tehri Dam has had profound economic and social impacts:
When discussing the largest dam in India, it’s important to understand how Tehri Dam compares to other major dams in the country:
Tehri Dam and the surrounding areas offer a unique blend of natural beauty and engineering marvels. Here are some tips for those interested in visiting:
The Tehri Dam, a marvel of engineering, offers a multitude of interesting facts:
The Tehri Dam is not just a structure; it is a symbol of India’s progress and its ability to harness its natural resources for the benefit of its people. It stands as a testament to the country’s engineering prowess and its commitment to sustainable development.
India, a land of diverse landscapes, relies heavily on dams for water management. These giants of civil engineering serve multiple purposes, including irrigation, flood control, and hydropower generation. Let’s explore the top 10 largest dams in India, marvels of human ingenuity that play a vital role in the nation’s development.
| Rank | Dam Name | Location | State | Height (m) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tehri Dam | Bhagirathi River | Uttarakhand | 260.5 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 2 | Bhakra Dam | Sutlej River | Himachal Pradesh | 225.6 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 3 | Sardar Sarovar Dam | Narmada River | Gujarat | 163 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 4 | Indira Sagar Dam | Narmada River | Madhya Pradesh | 92 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 5 | Nathpa Jhakri Dam | Satluj River | Himachal Pradesh | 67.5 | Hydroelectric |
| 6 | Srisailam Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 145 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 7 | Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 124 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 8 | Hirakud Dam | Mahanadi River | Odisha | 60.96 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 9 | Tungabhadra Dam | Tungabhadra River | Karnataka/Andhra Pradesh | 49.5 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 10 | Maithon Dam | Barakar River | Jharkhand | 50 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
These top 10 largest dams in India are just a glimpse into India’s vast network of dams. They stand as testaments to the country’s commitment to water management and infrastructure development.
Here are the top 10 longest dams in India based on their length:
| Rank | Dam Name | Location | State | Length (m) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hirakud Dam | Mahanadi River | Odisha | 4,800 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 2 | Bhakra Dam | Sutlej River | Himachal Pradesh | 4,250 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 3 | Sardar Sarovar Dam | Narmada River | Gujarat | 2,723 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 4 | Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 2,414 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 5 | Indira Sagar Dam | Narmada River | Madhya Pradesh | 2,240 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 6 | Srisailam Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 2,138 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 7 | Tehri Dam | Bhagirathi River | Uttarakhand | 1,750 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 8 | Nathpa Jhakri Dam | Satluj River | Himachal Pradesh | 1,536 | Hydroelectric |
| 9 | Tungabhadra Dam | Tungabhadra River | Karnataka/Andhra Pradesh | 1,389 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 10 | Maithon Dam | Barakar River | Jharkhand | 1,315 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
Here are the top 10 largest dams in India based on their reservoir capacity:
| Rank | Dam Name | Location | State | Capacity (MCM) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indira Sagar Dam | Narmada River | Madhya Pradesh | 12,220 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 2 | Bhakra Dam | Sutlej River | Himachal Pradesh | 9,670 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 3 | Hirakud Dam | Mahanadi River | Odisha | 8,135 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 4 | Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 7,449 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 5 | Srisailam Dam | Krishna River | Telangana | 6,760 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 6 | Tehri Dam | Bhagirathi River | Uttarakhand | 6,330 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 7 | Sardar Sarovar Dam | Narmada River | Gujarat | 6,320 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 8 | Nathpa Jhakri Dam | Satluj River | Himachal Pradesh | 4,600 | Hydroelectric |
| 9 | Maithon Dam | Barakar River | Jharkhand | 4,500 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
| 10 | Tungabhadra Dam | Tungabhadra River | Karnataka/Andhra Pradesh | 4,380 | Hydroelectric, Irrigation |
Creating a visual representation of the largest dams in India on a map can be a helpful way to understand their geographical distribution and significance
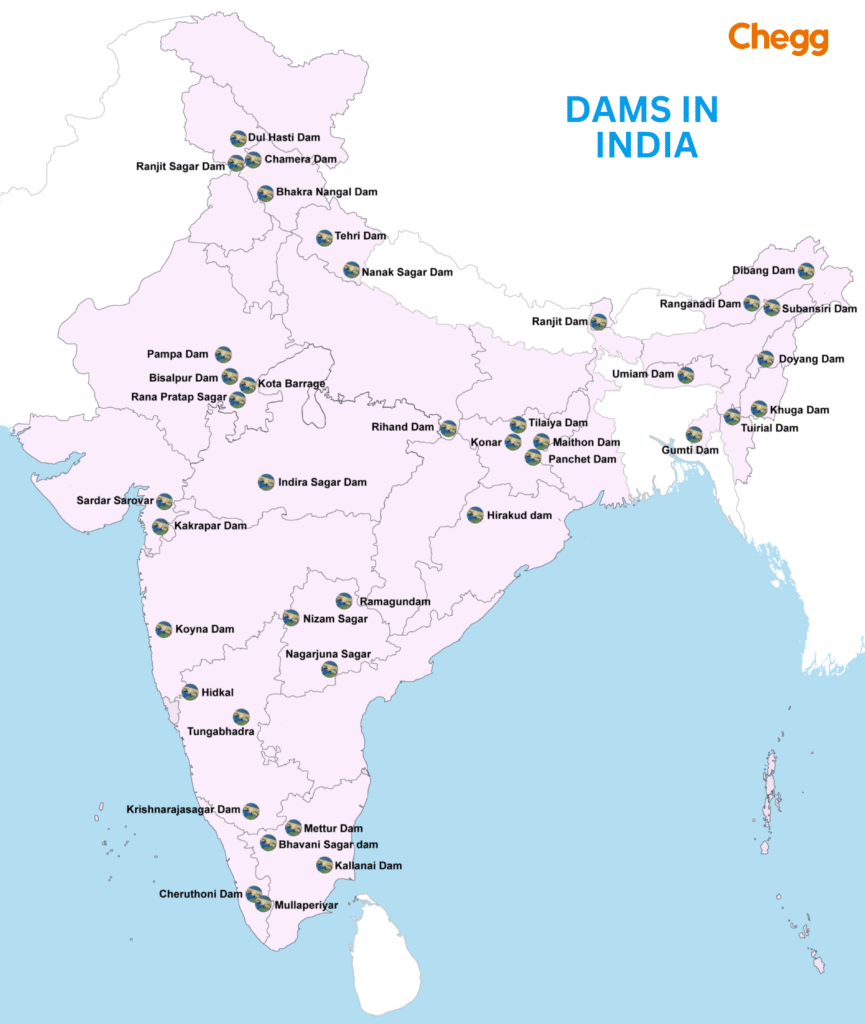
The major dams in India have benefited inhabitants in several ways, including:
Below is a list of some major dams in India, along with their respective states and rivers:
| Dam | State | River |
| Bhavani Sagar Dam | Tamil Nadu | Bhavani |
| Tungabhadra Dam | Karnataka | Tungabhadra |
| Rihand Dam | Uttar Pradesh | Rihand |
| Maithon Dam | Jharkhand | Barakar |
| Koyna Dam | Maharashtra | Koyna |
| Bisalpur Dam | Rajasthan | Banas |
| Mettur Dam | Tamil Nadu | Kaveri |
| Krishnarajasagar Dam | Karnataka | Kaveri |
| Indira Sagar Dam | Madhya Pradesh | Narmada |
| Cheruthoni Dam | Kerala | Cheruthoni |
| Sardar Sarovar Dam | Gujarat | Narmada |
| Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | Telangana | Krishna |
| Hirakud Dam | Odisha | Mahanadi |
| Bhakra Nangal Dam | Punjab-Himachal Pradesh Border | Sutlej |
| Tehri Dam | Uttarakhand | Bhagirathi |
भारत में सबसे बड़ा बांध टिहरी बाँध है। यह बांध उत्तराखंड राज्य में भागीरथी नदी पर स्थित है। टिहरी बाँध की ऊंचाई 260.5 मीटर है, जिससे यह भारत का सबसे ऊंचा बांध है। इस बांध का निर्माण 1978 में शुरू हुआ और 2006 में पूरा हुआ। टिहरी बाँध, जल विद्युत उत्पादन, सिंचाई और बाढ़ नियंत्रण जैसे कई उद्देश्यों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
Click here to read: Largest Dam in India in Hindi.

For UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) exams, it’s important to understand significant infrastructure projects in India, including dams. The UPSC syllabus covers a wide range of topics, and knowledge about the largest dams in India can be relevant for both the Prelims and Mains exams, especially under the sections related to Indian geography, economy, and environment.
When preparing for UPSC, it’s crucial to not only know which dam is the largest based on specific criteria (like height, length, or reservoir capacity) but also to understand the dam’s significance in terms of its purpose, impact on the environment and society, and its role in India’s development.
Here are some key points to remember about India’s largest dams for UPSC preparation:
For UPSC preparation, candidates should focus on understanding these dams’ geographical, economic, and environmental significance. It’s also important to stay updated with any recent developments, policies, or debates related to these dams, as they can be potential topics for UPSC questions.
Click here to read about the Largest Dam in India on Wikipedia.
The Tehri Dam, the largest dam in India, stands as a symbol of human achievement in harnessing natural resources for sustainable development. Its contributions to hydroelectric power generation, irrigation, flood control, and water supply are invaluable. However, it is essential to balance such large-scale projects with environmental and social considerations to ensure a sustainable future. Through understanding and appreciating the complexities of the Tehri Dam, we can gain insights into the broader challenges and opportunities in the field of water resource management.
The largest dam in India is the Tehri Dam, located in Uttarakhand. It stands at a height of 260.5 meters.
The Three Gorges Dam in China is considered the largest dam in the world. It’s the world’s largest hydroelectric power plant with an installed capacity of 22,500 MW.
The highest dam in India, based on its height, is the Tehri Dam, located in the state of Uttarakhand.
The construction of the Tehri Dam faced several challenges, including environmental concerns, the relocation of thousands of people, and technical difficulties related to building in a seismically active region.
The Bhakra Nangal Dam, located on the Sutlej River in Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, is considered the second largest dam in India in terms of height and capacity.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.