Quick Summary
Table of Contents
The List of prime minister of India who were great visionaries in power, supporters of amazing initiatives, and more has been extensive. The Prime Minister holds one of the most important positions in India, as they bear the responsibility for the nation’s overall administration and future development. They represent the country in international organizations, delegations, etc., as the political leader of the government.
Some of the Indian Prime Ministers, as highlighted in the list of Prime Minister of India, have achieved numerous goals and helped develop our country. The first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, helped India gain independence. The current Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, has helped establish great foreign relationships.
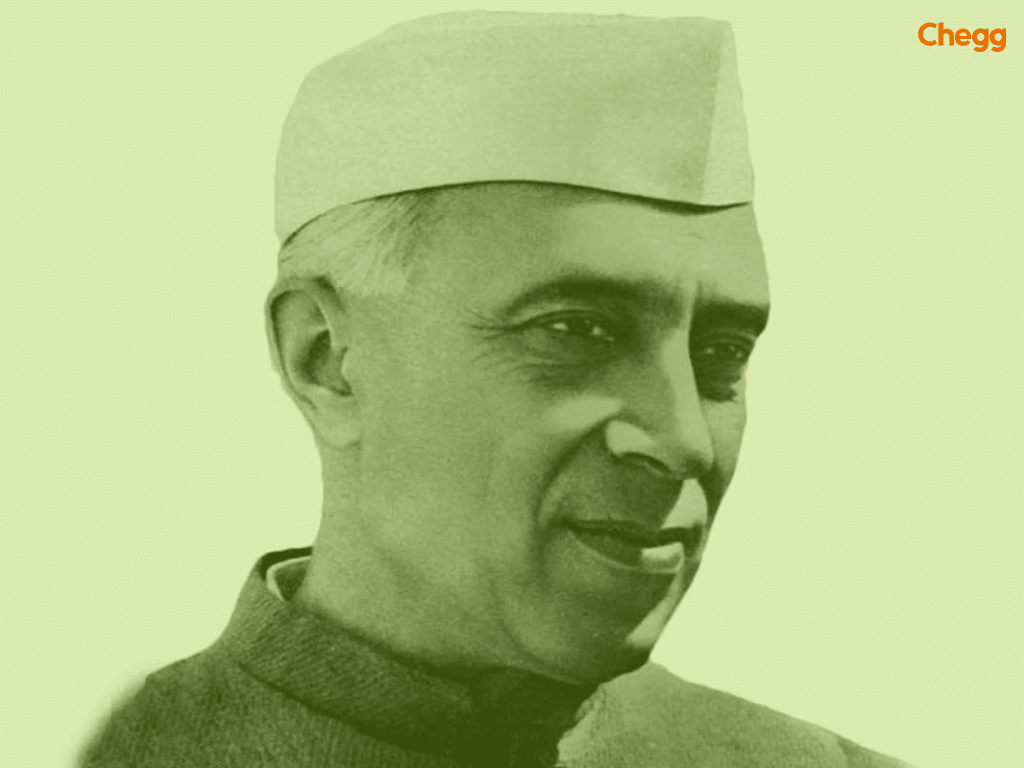
Jawaharlal Nehru was the first prime minister of India in the List of prime minister of India. He left for England when he was fifteen. Nehru eventually received an Inner Temple Bar admissions letter. In 1912, he relocated back to India and immediately entered politics. After returning, he became a delegate for the 1912 Bankipore Congress and then the Secretary of the Home Rule League in 1919.
He organized the first Kisan March in the Pratapgarh District. He was also incarcerated twice during the Non-Cooperation Movement from 1920 to 1922. In 1926, the Congress adopted independence as one of its aims, which Nehru influenced. He signed the Nehru Report in 1928 on Indian Constitutional Reform. This organization worked hard for India’s separation from the British Empire, as reflected in the list of Prime Minister of India and their contributions to the nation’s freedom struggle.
He played an important role in fighting for the country’s independence. However, his goals for India went beyond just independence. He focused on modernization with the help of scientific and technical progress. His Five-Year Plans for improving infrastructure and increasing employment established him as India’s founding father, a key figure in the list of Prime Minister of India who shaped the nation’s future.

Lal Bahadur Shastri was the Second Prime Minister of India in the List of Prime Minister of India and served the country from 1964 to 1966. He managed to lead our country through very difficult times with ease. His time as prime minister of India is mostly remembered because of the 1965 war with Pakistan. The war formally ended in 1966 when the then-Soviet Union mediated an agreement in Tashkent.
After Pakistan attacked India, his slogan, “Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan,” was first mentioned in 1965 while he was giving a speech in Delhi. It translates to “Hail to the soldier, Hail to the farmer.” This slogan aimed to raise the morale and enthusiasm of soldiers to fight for our country and to inspire farmers to increase food production to help solve the food scarcity problem. He advocated for the Green Revolution in India in 1965 to increase food production. To promote this, he backed Amul milk in Gujarat, making him a prominent figure in the list of Prime Minister of India who worked toward national growth and self-sufficiency.
India’s first female Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi, had a lasting impression on the country’s history. She led India with flair and skill, facing difficult internal and international problems. She declared an Emergency in India every six months for a total of 21 months starting from June 25, 1975. Throughout this period of emergency, she gave her absolute authority over the country’s political situation.
Indira Gandhi’s government played an important role in the Green Revolution. They introduced new hybrid seeds, subsidized farmers, and provided them with water, electricity, and fertilizer. Between 1968 and 1973, the amount of institutional financing available for the agriculture industry was also increased. This was done to ensure food security in India. She also helped with the second phase of Indian Foreign policy from 1966 to 1989. She was known as the “Iron Lady of India” because of her great leadership during the 1971 war and her tough decisions, earning her a place on the list of Prime Minister of India for her remarkable contributions to the nation’s progress.

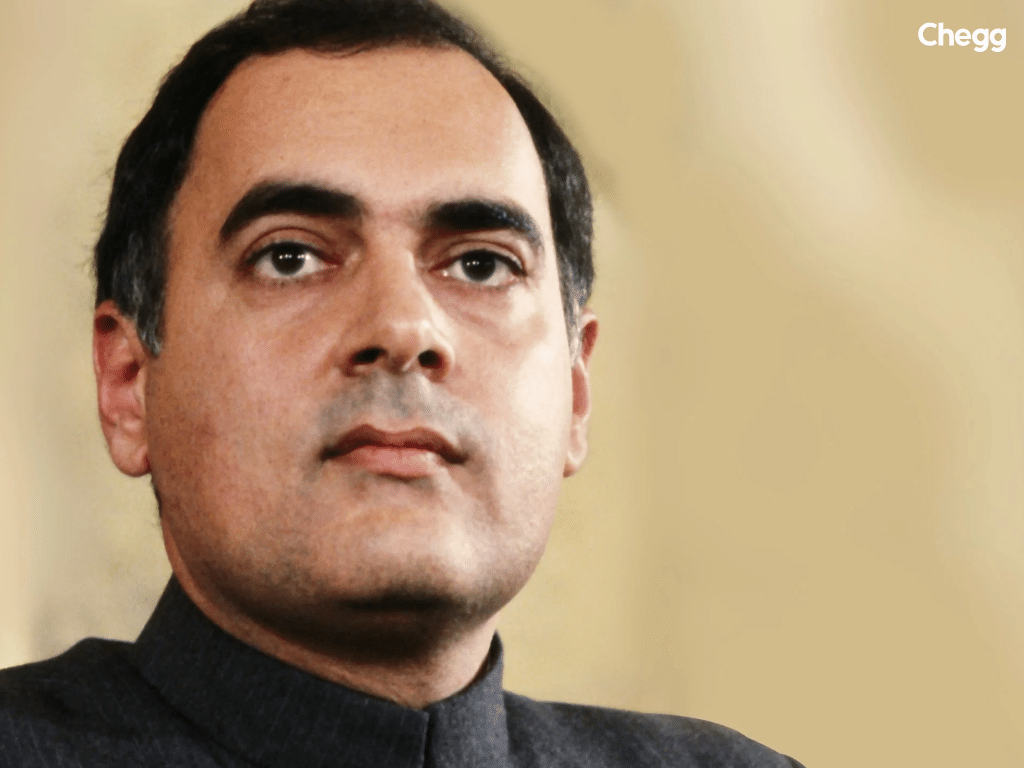
Rajiv Gandhi, at the age of 40, became the youngest Prime Minister in India. He also became the president of the Congress. He was familiar with politics since childhood because he was the son of Indira Gandhi. During his early years, he lived with his grandparents at her official Teen Murti House residence. When he was young, he had no interest in politics. However, he got into politics after his brother passed away, and his leadership later earned him a prominent place on the list of Prime Minister of India.
After the tragic assassination of his mother, he rose to power as the new prime minister. His main goal as list of prime minister of India was to help India advance technologically. His administration tried to modernize the country’s communication system and build the supporting infrastructure in cities and rural areas. Unfortunately, he was assassinated on May 21, 1991, by a suicide bombing.

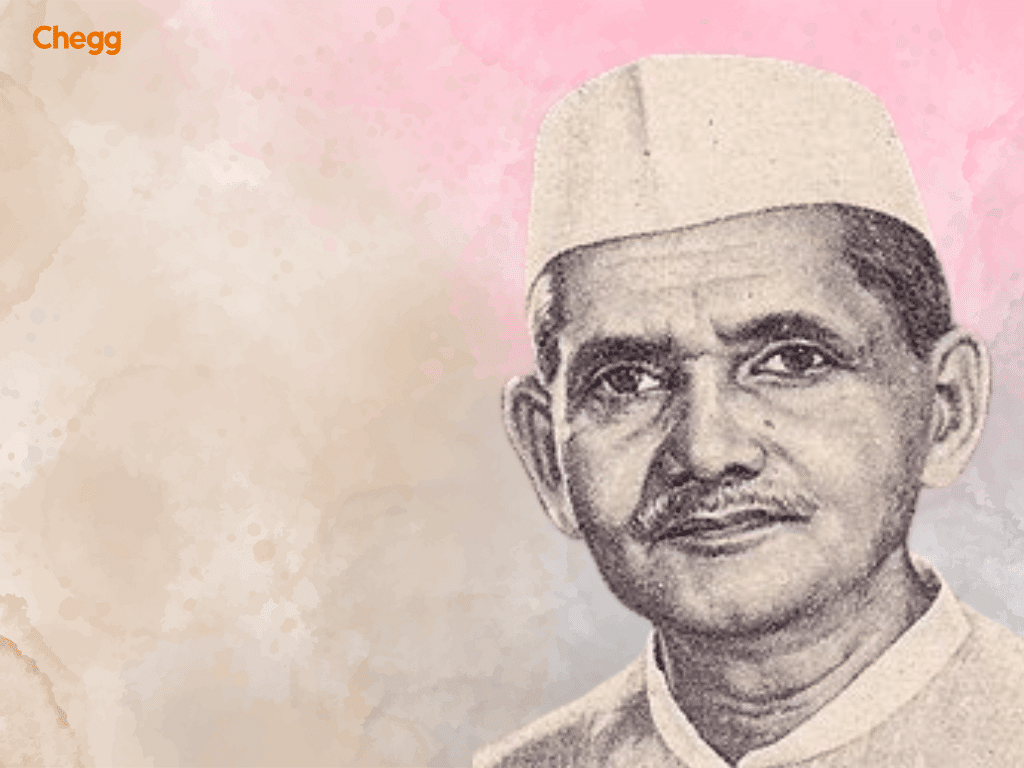
Morarji Desai holds the record of being the oldest among the list of Prime Minister of India, leading the nation from 1977 to 1979. Born on February 29, 1896, in Gujarat, Desai’s journey to the top of Indian politics was long and distinguished. He began his political career in the freedom struggle against British rule and later served as Chief Minister of Bombay State and as Deputy Prime Minister under Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
Desai’s tenure as the list of Prime Minister of India was marked by his commitment to transparency and simplicity in governance. He implemented several reforms aimed at promoting accountability and reducing government corruption. Despite his advanced age, Desai was known for his tireless work ethic and dedication to public service.

Atal Bihari Vajpayee was the 10th in the list of prime minister of India. He was called a statesman because of his efforts to improve our country’s economy. His leadership style was aimed at avoiding conflict. He preferred finding common ground rather than confrontation.
In May 1998, the Indian nuclear tests held in Pokhran succeeded. During Vajpayee’s government, APJ Abdul Kalam oversaw the nuclear tests. Vajpayee had announced that India had conducted 3 underground nuclear tests at Pokhran. However, he also stated that they would follow the “No First Use” policy. He made it clear that nuclear weapons will never be deployed against a non-nuclear state. He also oversaw the Kargil war and the pursuit of peace with Pakistan, securing his place on the list of Prime Minister of India for his strong leadership and pivotal decisions during a critical time.

Manmohan Singh came 13th on the list of Prime Minister of India., He recently passed away on December 26, 2024, at the age of 92 years. He was receiving treatment at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in New Delhi at the time of his death. His tenure was the third-longest in our history, lasting from 2004 to 2014. He took over India’s foreign policies after Vajpayee. His approach, however, remained almost unchanged. He had decided to continue Vajpayee’s strategy and build international relations with the USA, China, and Pakistan.
Under his government, India and the United States signed a civil nuclear deal, which began a new era in their international relations. However, he lost the support of the Indian Left after this deal and India’s consent to place its nuclear plants under IAEA became public. Singh also spoke with three different Pakistani governments and made multiple gestures toward peace during that time, earning him a significant place on the list of Prime Minister of India for his diplomatic efforts and leadership.

Narendra Modi has been India’s Prime Minister since 2014, bringing a dynamic vision for development and transformation. His journey began with the RSS in Gujarat in 1971, and he later joined the BJP in 1985. Rising within the party, Modi became Gujarat’s Chief Minister, where he garnered attention for the Gujarat Model, a development approach he used to propel himself as BJP’s frontrunner in the 2014 elections, earning him a prominent place in the list of Prime Minister of India.

Since becoming Prime Minister, Modi has launched ambitious programs that address India’s core challenges. Initiatives like the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, the world’s largest cleanliness drive, and Digital India have engaged millions and moved India toward becoming cleaner and more digitally connected. His government has also focused on developing infrastructure through the Smart City Mission, Skill India, and the AMRUT Strategy, solidifying his place in the list of Prime Minister of India for his transformative leadership.
Additionally, Modi has strengthened India’s foreign relations, especially with ASEAN and East Asian countries, aligning with India’s Look East strategy.
While Modi’s leadership is marked by his public speaking skills, judgment, and rapport-building, his administration faces challenges, including unemployment, economic concerns, and domestic social issues. Despite these, Modi’s tenure reflects a dedication to building a self-sufficient and progressive India.
Also Read:-
List of Prime Minister of Pakistan
Biography of Jawaharlal Nehru: Family, Wife, and More
The List of prime minister of India list from 1947 to 2025 is given below, showcasing their notable policies, achievements, and challenges:
| Prime Minister | Term | Notable Policies, Achievements, and Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Jawaharlal Nehru | 1947-1964 | Architect of modern India, Five-Year Plans, Non-Aligned Movement |
| Lal Bahadur Shastri | 1964-1966 | “Jai Jawan Jai Kisan,” Green Revolution |
| Indira Gandhi | 1966-1977, 1980-1984 | Emergency, Green Revolution, Pokhran I |
| Morarji Desai | 1977-1979 | Economic reforms, nuclear disarmament |
| Charan Singh | 1979-1980 | Agrarian reforms |
| Rajiv Gandhi | 1984-1989 | IT revolution, Look East Policy |
| V.P. Singh | 1989-1990 | Mandal Commission implementation, economic challenges |
| Chandra Shekhar | 1990-1991 | Short tenure, economic reforms |
| P.V. Narasimha Rao | 1991-1996 | Diplomacy with neighbors, coalition politics |
| Atal Bihari Vajpayee | 1996, 1998-2004 | Nuclear tests, Kargil War, economic reforms |
| H.D. Deve Gowda | 1996-1997 | United Front coalition, economic challenges |
| I.K. Gujral | 1997-1998 | Diplomacy with neighbours, coalition politics |
| Manmohan Singh | 2004-2014 | Economic reforms, nuclear deal, inclusive growth |
| Narendra Modi | 2014-ongoing | Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Digital India, foreign policy initiatives |
This table presents a List of prime minister of India since independence, ranked by the total length of their terms in office:
| Rank | Name | Party | Total Years | Longest Continuous Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jawaharlal Nehru | INC | 16.79 years | 16.79 years |
| 2 | Indira Gandhi | INC/INC(I)/INC(R) | 15.95 years | 11.16 years |
| 3 | Narendra Modi (Current) | BJP | 10.04 years (as of 15/07/2024) | 10.04 years (as of 15/07/2024) |
| 4 | Manmohan Singh | INC | 10 years | 10 years |
| 5 | Atal Bihari Vajpayee | BJP | 6.22 years | 6.27 years |
| 6 | Rajiv Gandhi | INC(I) | 5.08 years | 5.08 years |
| 7 | P. V. Narasimha Rao | INC(I) | 4.92 years | 4.92 years |
| 8 | Morarji Desai | JP | 2.36 years | 2.36 years |
| 9 | Lal Bahadur Shastri | INC | 0.73 years | 0.73 years |
| 10 | Vishwanath Pratap Singh | JD | 0.95 years | 0.95 years |
Notes:
Here are some key facts about the List of Prime Minister of India:
These leaders each left a unique legacy that contributed to shaping the country in significant ways.
The appointment of the Prime Minister of India is governed by the constitutional provisions outlined in the Indian Constitution.
The Prime Minister of India holds a wide array of responsibilities that are critical to the functioning of the government and the nation as a whole. Here’s a detailed overview:
1. Head of Government: The Prime Minister is the head of the government and holds the highest executive authority in India.
2. Leader of the Council of Ministers: The Prime Minister leads the Council of Ministers, which comprises various ministers heading different government departments.
3. Policy Formulation and Implementation: The Prime Minister is responsible for formulating government policies and ensuring their effective implementation across different sectors.
4. Administration and Governance: The Prime Minister oversees the administration and governance of the country, ensuring the smooth functioning of government machinery and efficient delivery of public services.
5. Cabinet Meetings and Decision Making: The Prime Minister convenes and presides over cabinet meetings where important policy decisions are taken collectively by the council of ministers.
6. Coordination among Ministries: The Prime Minister coordinates the activities of various ministries to ensure coherence and synergy in government policies and programs.
7. National Security and Defense: The Prime Minister plays a crucial role in matters of national security and defense, including decision-making during times of crisis or conflict.
8. Foreign Policy and Diplomacy: The Prime Minister represents India on the international stage and formulates the country’s foreign policy objectives. They engage in diplomatic relations with other countries to promote India’s interests globally.
9. Legislation and Parliamentary Affairs: The Prime Minister participates in parliamentary proceedings, introduces important bills and ordinances, and engages in debates on key legislative matters.
10. Economic Management and Development: The Prime Minister oversees economic policies aimed at promoting growth, reducing poverty, and enhancing the overall welfare of the citizens.
11. Social Welfare and Development: The Prime Minister spearheads initiatives for social welfare and development, including poverty alleviation programs, education reforms, healthcare policies, and infrastructure development projects.
12. Crisis Management and Disaster Response: During emergencies, natural disasters, or other crises, the Prime Minister provides leadership and coordinates government efforts to address the situation and ensure the safety and well-being of the populace.
The power and function of the prime minister is quite important. Some of these are:
The Indian prime minister IS also eligible for the services listed below.
Every person in this List of prime minister of India worked hard to ensure India developed socially, politically, and economically. From Nehru’s vision of modernization to Modi’s initiatives for a better tomorrow, they have all left their mark on history. By taking inspiration from one another in foreign policies and initiatives, they have created a standard for political excellence. Hope this article helps you to learn and understand the List of prime minister of India.
Narendra Modi is the 14th and current Prime Minister on the List of prime minister of India. He is currently serving his second term.
Jawaharlal Nehru was the country’s first prime minister in the List of prime minister of India. He led the Dominion of India from August 15, 1947, to January 26, 1950, and the Republic of India from that date until his death in May 1964.
There have been fifteen prime ministers of India since the country’s independence. The first was Indian National Congressman Jawaharlal Nehru. Since 2014, Narendra Modi of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has been as prime minister.
Narendra Modi is currently serving his second term as the Prime Minister of India
Atal Bihari Vajpayee became Prime Minister of India three times. His third term began on October 13, 1999, when he took the oath of office, solidifying his place as a prominent leader.
Manmohan Singh, 13th on the list of Prime Minister of India, passed away on December 26, 2024, at 92. He had been receiving treatment for age-related health issues at the (AIIMS) in New Delhi. Despite efforts to resuscitate him, he was declared dead due to complications related to his health. Singh’s death was met with widespread condolences from both national and international leaders, recognizing his immense contributions to India’s economic and diplomatic landscape.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.