Quick Summary
Detailed list of India’s Vice Presidents from 1952 to 2025.
Insights into their terms, contributions, and historical significance.
Easy-to-understand language suitable for readers of all ages.
Table of Contents
The Vice President of India holds the second-highest constitutional position in the country, acting as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). Understanding the list of Vice Presidents of India provides valuable insights into the nation’s political evolution and governance.
In the big mosaic of India’s democratic shape, the list of vice president of India holds an important place. Often called the second-in-command, the vice president’s role exceeds formal duties. Its constitutional duties affect government operations. As the President’s deputies, they maintain democracy, government honor, and essential services. The job of the Vice President is sometimes the most symbolic but additionally important for ensuring the smooth operation of the government.
The Vice President of India chairs the Rajya Sabha. This function endows them with the power to rule over its meetings and manual talks and make sure that parliamentary procedures adhere to set guidelines. It manages chaos, solves issues, and promotes constructive dialogue. Indian Vice Presidents promote India abroad and boost its presence in addition to politics. The list of Vice Presidents of India provides insight into the individuals who have contributed to the nation’s governance over the decades.
The Vice President’s constitutional duties include other domain names. The vice president takes over when the president is away. Keeps the government stable during change by continuing executive duties. The Vice President helps the National Development Council plan and improve. A comprehensive list of Vice President of India can be found on government websites and educational platforms.
These sections examine India’s past Vice Presidents’ political impact by reviewing major events, trends, and presidents.
Examining the list of Vice Presidents of India through a historical lens, we can see famous, interesting trends and styles that have grown over time. Vice Presidents with academic backgrounds have advanced intellectual discourse, while those with political or legal backgrounds have passed laws. Analyzing these traits reveals each vice president’s skills and experiences.
Beyond their legal duties, vice presidents shape kingdom politics. The public, policy debates, and the direction of the government are all susceptible to their leadership, words, and deeds throughout their term. Policy, government, and social issues can show how vice presidents shape kingdom governance.
who is the 14 vice president of India list encompasses all the individuals who have served in this capacity throughout history. Every Indian vice president was successful and shaped politics.
Here is a table of the tenure vice president list of India:
| S. No. | Vice-President | Tenure (From) | Tenure (To) | President |
| 1 | Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan | 13 May 1952 | 12 May 1962 | Dr. Rajendra Prasad |
| 2 | Dr. Zakir Hussain | 13 May 1962 | 12 May 1967 | Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan |
| 3 | Varahagiri Venkata Giri | 13 May 1967 | 20 July 1969 | Dr. Zakir Hussain |
| 4 | Gopal Swarup Pathak | 31 August 1969 | 30 August 1974 | V. V. Giri |
| Dr. Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed | ||||
| 5 | Basappa Danappa Jatti | 31 August 1974 | 30 August 1979 | Dr. Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed |
| Neelam Sanjiva Reddy | ||||
| 6 | Justice Muhammad Hidayatullah | 31 August 1979 | 30 August 1984 | Neelam Sanjiva Reddy |
| Giani Zail Singh | ||||
| 7 | Ramaswamy Venkataraman | 31 August 1984 | 24 July 1987 | Giani Zail Singh |
| 8 | Shankar Dayal Sharma | 7 September 1987 | 24 July 1992 | Ramaswamy Venkataraman |
| 9 | Kocheril Raman Narayanan | 21 August 1992 | 24 July 1997 | Shankar Dayal Sharma |
| 10 | Krishan Kant | 21 August 1997 | 27 July 2002 | Kocheril Raman Narayanan |
| A. P. J. Abdul Kalam | ||||
| 11 | Bhairon Singh Shekhawat | 19 August 2002 | 21 July 2007 | A. P. J. Abdul Kalam |
| 12 | Mohammad Hamid Ansari | 11 August 2007 | 10 August 2017 | Pratibha Patil |
| Pranab Mukherjee | ||||
| Ram Nath Kovind | ||||
| 13 | M Venkaiah Naidu | 11 August 2017 | 11 August 2022 | Ram Nath Kovind |
| 14 | Jagdeep Dhankhar | 11 August 2022 | Incumbent | Droupadi Murmu |
The Vice President of India holds a significant position in the Indian political system. As per the Constitution of India, the Vice President’s powers and functions are defined in various articles, particularly Article 63 to 71. The Vice President is the second-highest constitutional authority in India, directly following the President, and performs crucial roles in both the executive and legislative branches of government.
Functions of the Vice President as Chairman:
Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan was the first Vice President of India and a prominent figure in philosophy and education. His tenure from 1952 to 1962 was a significant period for India’s developing democracy. Dr. Radhakrishnan’s role went beyond just a formality; it reflected his intellectual capacity and profound understanding of the country’s cultural ethos. His influence as a scholar and philosopher added a unique dimension to his position.
Beyond being Vice President, Dr. Radhakrishnan had an impact. Knowledge is essential to a healthy society, so he promoted education and culture. He dedicated himself to becoming India’s president. Dr. Radhakrishnan said the vice president shaped national values. By examining the list of Vice Presidents of India, one can appreciate the evolution of the role and its impact on Indian democracy.

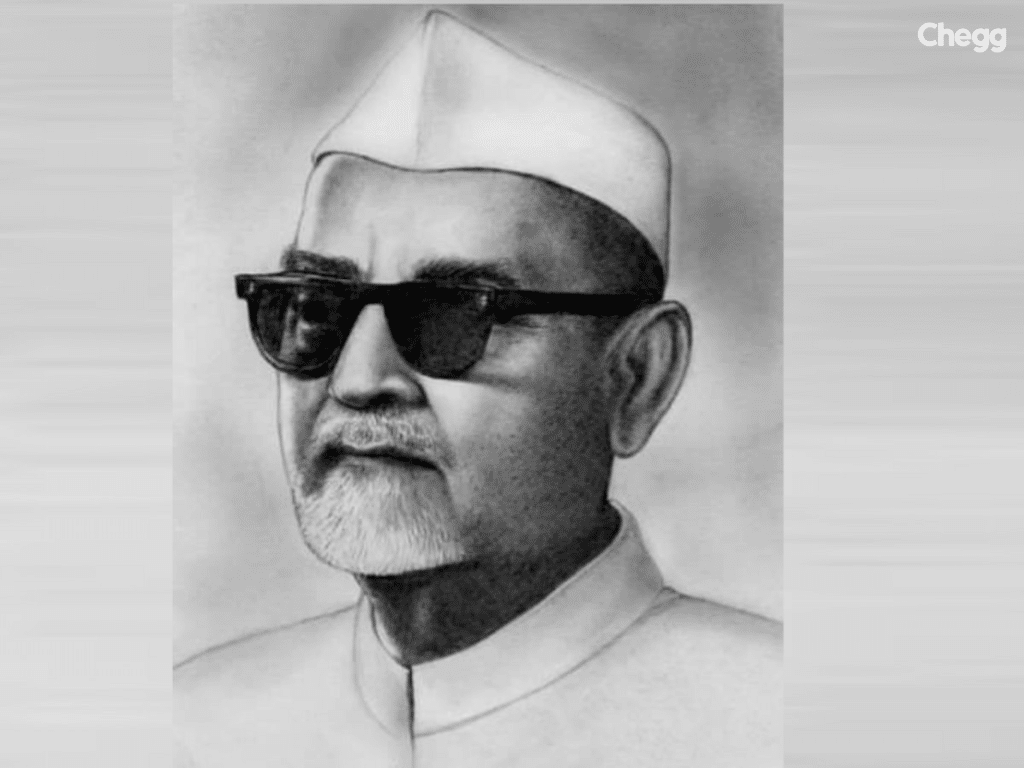
One of the most well-known figures in Indian history was Dr. Zakir Husain, who was born on February 8, 1897, and died on May 3, 1969. He made a big impact on the nation while holding several prestigious positions that made history in 1967 when he became the first Muslim to lead India as president. He was the governor of the state of Bihar from 1957 until this point. Furthermore, Dr. Husain’s election as India’s vice president in 1962 demonstrated the public’s broad recognition and confidence in him.
His influence went beyond the politics. In the field of education, Dr. Husain was important in the founding of the Muslim National University in Aligarh, which subsequently moved to New Delhi. He acted as its vice-chancellor from 1926 until 1948, directing and influencing its expansion. The list of Vice Presidents of India highlights how the position has been filled by distinguished individuals from various fields.
Furthermore, because of his commitment to education, Dr. Husain accepted Mahatma Gandhi’s 1937 invitation to serve as chair of the National Committee on Basic Education. The goal of this committee was to create a curriculum for schools that prioritized character development and holistic learning, based on Gandhian principles.
Dr. Husain represented India internationally. He further demonstrated his dedication to international collaboration in education and culture by serving on the executive board of UNESCO (the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization) from 1956 to 1958.
Dr. Zakir Husain, known for his vision, leadership, and unwavering efforts toward the progress of India and the world, has left an enduring legacy through his diverse roles in politics, education, and international relations.
The 14th Vice President of India, Venkaiah Naidu, served from August 11, 2017, to May 11, 2022. Born on July 1, 1949, in Andhra Pradesh, he is a senior leader of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). Before becoming Vice President, Naidu held several key positions in the Indian government, including Minister of Urban Development, Minister of Information and Broadcasting, and Minister of Parliamentary Affairs. As Vice President, he also served as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of Parliament. Naidu is known for his oratory skills and has been active in Indian politics for several decades.
In India’s political calendar, the Vice President election is a major event that must be fair and valid. The vice president is elected by The voting method intended to cover the voices of both houses of Parliament: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People).
The election college helps choose the vice president. The vice president is elected by the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha members, and this frame collectively reflects the numerous regions, languages, cultures, and reviews that outline India. The influential electoral college chooses the vice president, who inspires and includes.
The vote-casting device hired in the election is a core process factor. Members of the voting mechanism practice their vote to select the candidate they think is most perfect for the function. Each legislator’s voice in country management is stressed by this balloting method. A state-appointed official’s group is represented by the person with the most votes.
To be eligible for the position of Vice President of India, a candidate must meet the following criteria:
This section covers India’s vice presidents’ notable contributions to various issues. It highlights these leaders’ national growth contributions.
Vice presidents shaped India’s politics, society, and arts. Each Vice President had unique skills, knowledge, and perspectives and left a distinguished record. Vice presidents have promoted education, gender equality, social justice, and sustainability.
Vice presidents shaped many Indian industries and issues. Promoting international relations, culture, history, and marginalized groups is their legacy. Lobbying, legislation, and other vice president efforts improved regional education, healthcare, social welfare, and economic growth.
The office of the Vice President of India is primarily defined by Articles 63 and 64 of the Indian Constitution:
Three Vice Presidents of India have ascended to the presidency, illustrating the dynamic nature of Indian politics and the versatility of its leaders. Let’s explore their remarkable journeys:
These leaders not only fulfilled their roles as Vice Presidents but also made significant contributions as Presidents, shaping India’s development and democratic fabric.
The list of Vice Presidents of India reflects the nation’s rich political heritage and the diverse backgrounds of its leaders. Each individual has contributed uniquely to India’s democratic journey, shaping its policies and governance.
India’s first Vice President was Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan. He served from May 13, 1952, to May 12, 1962, and later became the second President.
Jagdeep Dhankhar is an Indian politician and lawyer, serving as the Vice President of India since 2022. Before this, he was the Governor of West Bengal from 2019 to 2022.
After being sworn in, the vice president serves for five years.
The Vice President of India tenders his resignation to the President of India, as per Article 67(b) of the Indian Constitution. The resignation must be submitted in writing, and it becomes effective upon acceptance by the President.
The Vice President is chosen by an electoral college comprised of Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha members.
Jagdeep Dhankhar is the 14th Vice President of India, having assumed office on August 11, 2022. He succeeded M. Venkaiah Naidu and also serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
India has had 14 Vice Presidents since the inception of the post in 1950. The current Vice President, Jagdeep Dhankhar, is the 15th Vice President of India. There hasn’t been a 22nd Vice President yet. Let me know if you’d like more details!
The US Constitution is the source for the position of Vice President in India.
The 15th Vice President of India is Jagdeep Dhankhar. He assumed office on August 11, 2022, succeeding M. Venkaiah Naidu. As Vice President, he also serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Quite a significant role in India’s governance!
Also Read:-

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.