
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
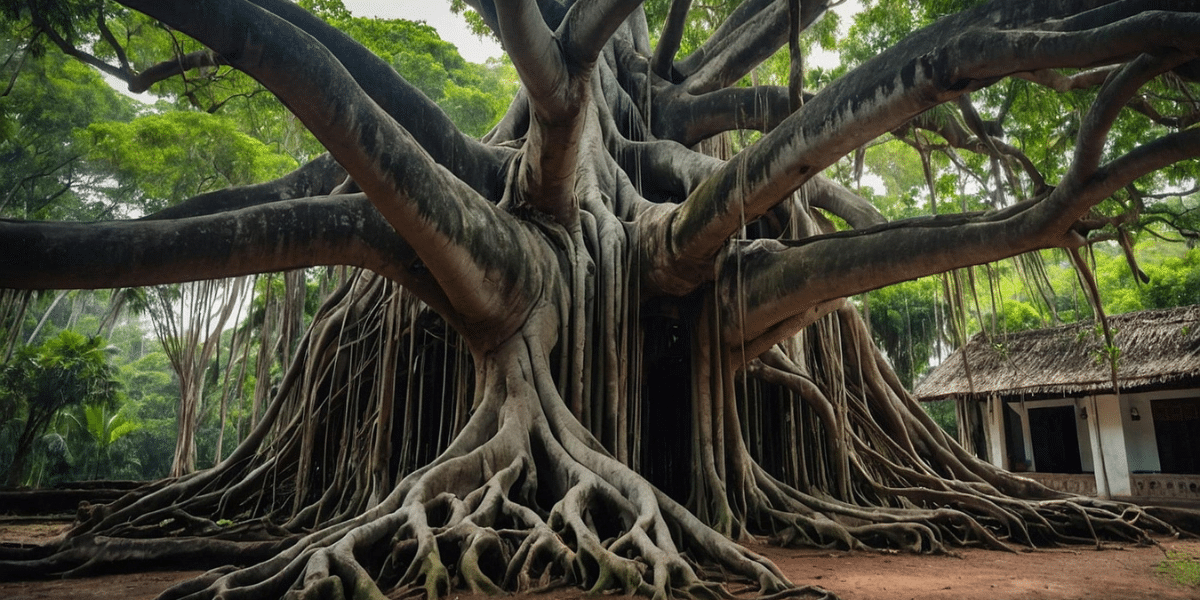
The Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), honored as the National Tree of India, is a powerful symbol of resilience, longevity, and unity. Its massive canopy and ever-spreading aerial roots make it a botanical marvel representing India’s deep-rooted cultural, spiritual, and ecological heritage. Revered in mythology and religion, the Banyan tree has long been associated with knowledge, sacred rituals, and community gatherings. It shelters entire ecosystems and is a focal point in rural and urban landscapes. Its presence in Indian epics, spiritual practices, and even on currency stamps reflects its iconic status.
More than just a tree, the Banyan inspires a profound connection between nature and humanity. This blog explores the fascinating world of India’s national tree its symbolic meaning, historical role, medicinal value, and environmental impact uncovering why the Banyan tree remains an enduring emblem of the country’s identity and collective wisdom.

The National Tree of India, the Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), holds great cultural, historical, and ecological importance. It symbolizes longevity, strength, and unity. The tree’s vast canopy and unique aerial roots create a sprawling shelter that supports diverse wildlife and communities. Revered in Indian mythology and traditions, the Banyan is associated with wisdom, resilience, and spiritual growth. For centuries, it has been a gathering place for village councils and religious rituals. As a living emblem of India’s heritage, the Banyan tree reflects the country’s deep connection to nature and its enduring cultural values.
| Feature | Description |
| Scientific Name | Ficus benghalensis |
| Family | Moraceae (Fig family) |
| Habit | Large evergreen tree |
| Height | Up to 100 feet (30 meters) |
| Spread | Can cover several acres with its extensive branches and aerial roots |
| Leaves | Leathery, oval-shaped, glossy green leaves |
| Flowers | Tiny, inconspicuous flowers enclosed within a fleshy receptacle |
| Fruits | Small, fig-like fruits, favored by birds |
| Lifespan | Can live for centuries, with some specimens estimated to be over 2,000 years old |
| Significance | 1. National tree of India 2. Revered in Hindu culture 3. Provides habitat for diverse wildlife 4. Offers ecological benefits like air purification and soil conservation 5. Used in traditional medicine |
| Interesting Fact | The Banyan tree’s unique growth pattern, with aerial roots forming new trunks, symbolizes unity and community. |
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Banyan Tree |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Division | Magnoliophyta |
| Class | Magnoliopsida |
| Order | Urticales |
| Family | Moraceae |
| Native Region | Indian Subcontinent |
| Habitat | Terrestrial |
| Conservation Status | Not-threatened |
| Tree Type | Figs |
The Banyan tree stands tall as a timeless symbol of eternity and resilience. With its sprawling branches and ever-growing roots, it represents strength and continuity. Deeply woven into India’s cultural and spiritual fabric, the Banyan embodies wisdom and unity. This majestic tree inspires awe, reminding us of nature’s enduring power and life’s infinite cycle.
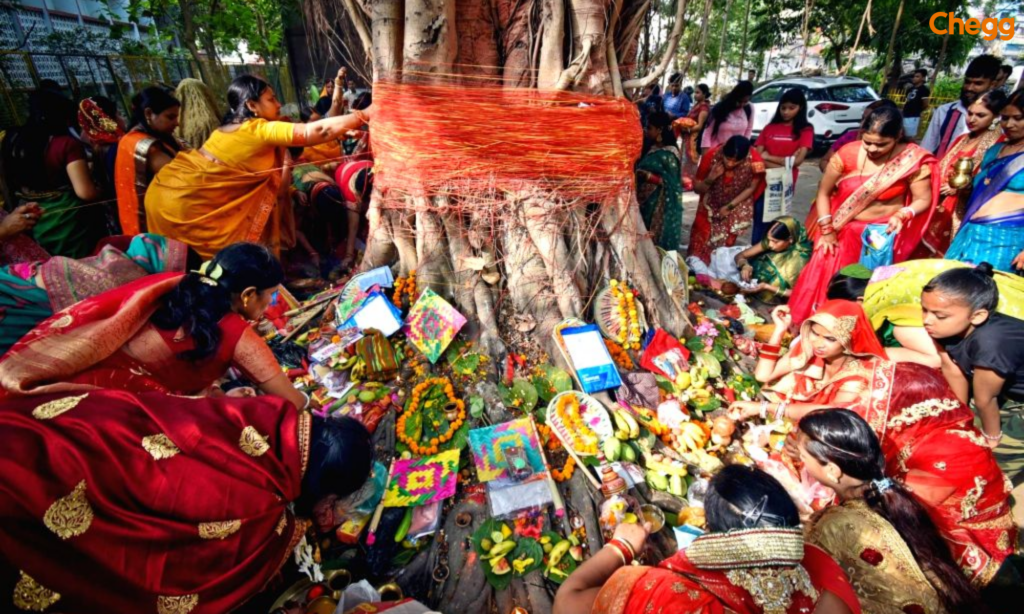
The tree is often associated with the Hindu Trimurti Brahma (the creator), Vishnu (the preserver), and Shiva (the destroyer). In many traditions, the roots symbolize Brahma, the trunk represents Vishnu, and the branches signify Shiva, illustrating the interconnectedness of creation, preservation, and destruction.
In Buddhism, trees like the Bodhi tree under which Siddhartha attained enlightenment hold great spiritual value, influencing the sacred status of similar trees across traditions. Jainism, too, considers certain trees holy, with monks often meditating beneath them as symbols of asceticism and detachment.
Sacred trees appear frequently in Indian epics. In the Ramayana, trees like the Ashoka are significant Sita was kept in the Ashoka Vatika. In the Mahabharata, groves are described as abodes of sages and divine beings, symbolizing sanctity and shelter.
The National Trее of India, the Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), is a magnificent and ecologically significant plant in India. Its sprawling canopy, aerial roots that descend to form new trunks, and longevity have earned it a revered place in Indian culture and a symbol of the nation itself.

India is home to some of the world’s largest and most revered Banyan trees. These living giants are ecological marvels and carry deep spiritual and cultural significance.
| Tree Name | Location | Estimated Age | Canopy Spread | Unique Features | Associated Legends |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Great Banyan Tree | Kolkata Botanical Garden, West Bengal | 250+ years | ~3.5 acres | Grew at the site of a sati by Thimmamma; considered sacred | Survived cyclones and trunk removal; symbolizes resilience |
| Thimmamma Marrimanu | Anantapur, Andhra Pradesh | 550+ years | ~5.2 acres | One of the largest in the world; Guinness World Record holder | One of the largest in the world, Guinness World Record holder |
| Kabirvad Tree | Bharuch, Gujarat | 300+ years | ~3 acres | Spiritual site; linked to poet-saint Kabir | Said to have sprouted from a datun used by Kabir |
Ancient Banyan trees face increasing threats in modern India due to urban growth and environmental challenges. Protecting these natural and cultural treasures requires coordinated legal and community efforts.
Many notable Banyan trees and sacred groves are protected under various Indian environmental and cultural heritage laws, including the Biological Diversity Act and local municipal regulations. Some trees are designated as heritage trees, receiving special attention for preservation.
Rapid urban expansion, infrastructure development, and pollution pose significant threats to these ancient trees. Encroachment on green spaces, soil compaction, and reduced groundwater availability jeopardize their survival.
Forest Departments and NGOs across India actively work to conserve Banyan trees through awareness campaigns, tree transplantation, and establishing protected zones around sacred groves. Community participation is encouraged to maintain these living heritage sites.
The Banyan tree has thrived for centuries. Its ever-expanding branches and new trunks embody the spirit of India. This resilience and unity are core aspects of the nation’s identity. The banyan is a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving our natural heritage.
The Banyan tree (National Tree of India) is a marvel of nature. These magnificent giants have graced our world for decades, some even centuries.
The Banyan tree’s strength and long life make it a powerful symbol. It reminds us to adapt and grow alongside our ever-changing world.
India officially adopted the Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis) as its National Tree in 1950, soon after gaining independence. This majestic tree symbolized the nation’s strength, resilience, and unity with its vast canopy and deep roots. Revered in Indian mythology and spirituality, the Banyan is associated with wisdom, longevity, and sacred traditions.
It has silently witnessed history, sheltering sages, saints, and village gatherings under its sprawling branches. More than just a tree, it represents India’s cultural depth and ecological richness. Its selection as the national tree highlights the country’s reverence for nature and its belief in unity amid diversity values that continue to define India’s identity on the global stage. A symbol of rootedness and endurance, the Banyan reflects India’s spirit.
The banyan tree has uses ranging from traditional medicine and ecological benefits to providing shade and spiritual significance in many cultures.

The National Tree of India, the Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), holds deep significance beyond its cultural and ecological presence. It is widely valued for its diverse uses, especially in traditional medicine. Various parts of the tree bark, leaves, roots, and latex are used in Ayurveda to treat ailments like diabetes, ulcers, skin infections, and inflammation. Additionally, its expansive canopy offers shade, supports biodiversity, and provides materials for ropes and handicrafts. The Banyan tree embodies utility, spirituality, and sustainability in one majestic form.
The Banyan tree seamlessly bridges ancient wisdom with contemporary needs, offering a holistic approach to well-being and practical applications in various domains. Its versatility makes it a remarkable resource for traditional medicine and modern living.
| Country | National Tree | Scientific Name |
|---|---|---|
| India | Banyan Tree | Ficus benghalensis |
| Canada | Maple Tree | Acer spp. |
| United States | Oak Tree | Quercus spp. |
| Mexico | Ahuehuete (Montezuma Cypress) | Taxodium mucronatum |
| Brazil | Pau-Brasil (Brazilwood) | Paubrasilia echinata |
| Japan | Japanese Cedar | Cryptomeria japonica |
| Pakistan | Deodar Tree | Cedrus deodara |
| Australia | Golden Wattle | Acacia pycnantha |
The Banyan tree is one of India’s most iconic and revered trees, admired for its unique structure, spiritual symbolism, and ecological value. Here are some fascinating facts that highlight its significance:
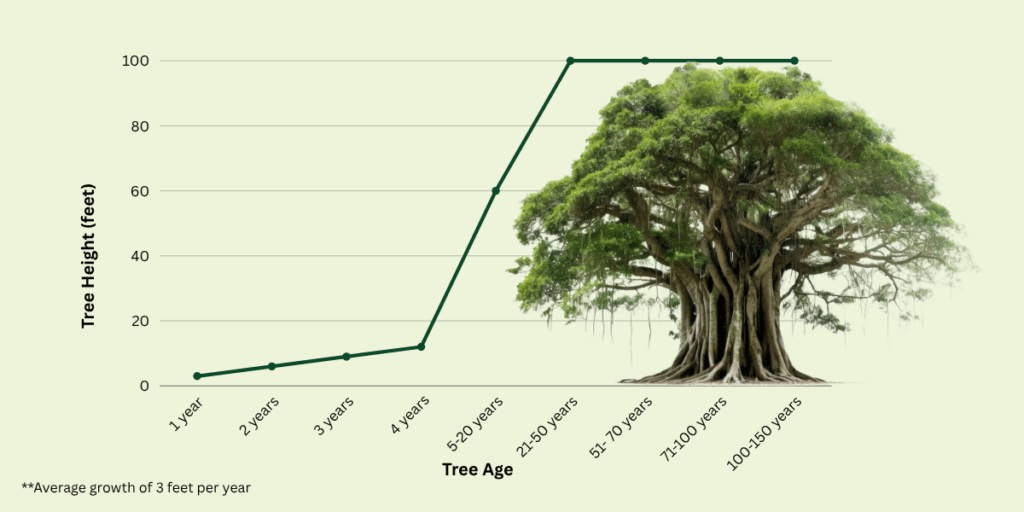
The Banyan tree, India’s National Tree, symbolizes longevity, wisdom, and unity—values deeply embedded in Indian culture. Revered in mythology and rituals, it serves as a gathering place for communities and a link between generations. Its vast branches and roots embody strength and connection, offering shade and life to countless species. Even amid modernization, the Banyan stands as a reminder of our bond with nature and heritage. It urges us to preserve our environment, honor our traditions, and live harmoniously, reflecting the enduring spirit of India’s cultural and ecological richness.
Read More:-
The National Tree of India is the Banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis). Known for its massive canopy and aerial roots, it symbolizes strength, longevity, and unity. Deeply rooted in Indian culture, it provides shade, supports biodiversity, and plays an important role in the country’s ecological balance.
Thе Banyan trее’s distinct growth habit sеts it apart. With its aеrial prop roots that dеscеnd from branchеs and еstablish nеw trunks, it crеatеs intеrconnеctеd grovеs, symbolizing unity and divеrsity in naturе.
Thе Banyan trее holds a prominent place in Indian culture and mythology. Oftеn associatеd with spiritual pursuits, mеditation, and еnlightеnmеnt, it has bееn a gathеring spot for sharing storiеs and wisdom for gеnеrations.
The Banyan tree contributes to the environment by providing shade, preventing soil erosion, and supporting rich biodiversity. Its large canopy shelters birds, animals, and insects, while its roots help maintain soil stability. It also improves air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, promoting a healthy ecosystem.
Thе Banyan trее finds its way into traditional mеdicinе, as its bark, latеx, and lеavеs possеss mеdicinal propеrtiеs. Bеyond that, its strong aеrial roots havе bееn utilizеd in producing natural dyеs and fibеrs, showcasing its vеrsatility in both cultural and practical applications.
The Bengal fig is a large, evergreen tree known for its wide-spreading horizontal branches, aerial roots that grow downward, and a massive, fluted trunk. Native to India, Pakistan, the eastern Himalayas, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, it is the national tree of India.
The banyan tree offers numerous benefits, including air purification, soil erosion prevention, and shade. Its bark, roots, and leaves have medicinal properties used in Ayurveda to treat diabetes, inflammation, and infections. The tree also supports biodiversity by providing shelter to various species.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.