Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Nuclear Power Plants in India generate nuclear reactions by splitting uranium atoms in nuclear fission. Steam can power turbines connected to generators to generate electricity from this reaction. These reliable, low-carbon plants must be operated carefully due to radioactive materials. If you wondered how many nuclear power plants are in India? Then the answer is that India currently has 22 nuclear power reactors with an installed capacity of 6780 MegaWatt electric (MWe) operational in 7 states. Keep reading to find out exactly what is a nuclear power plant.
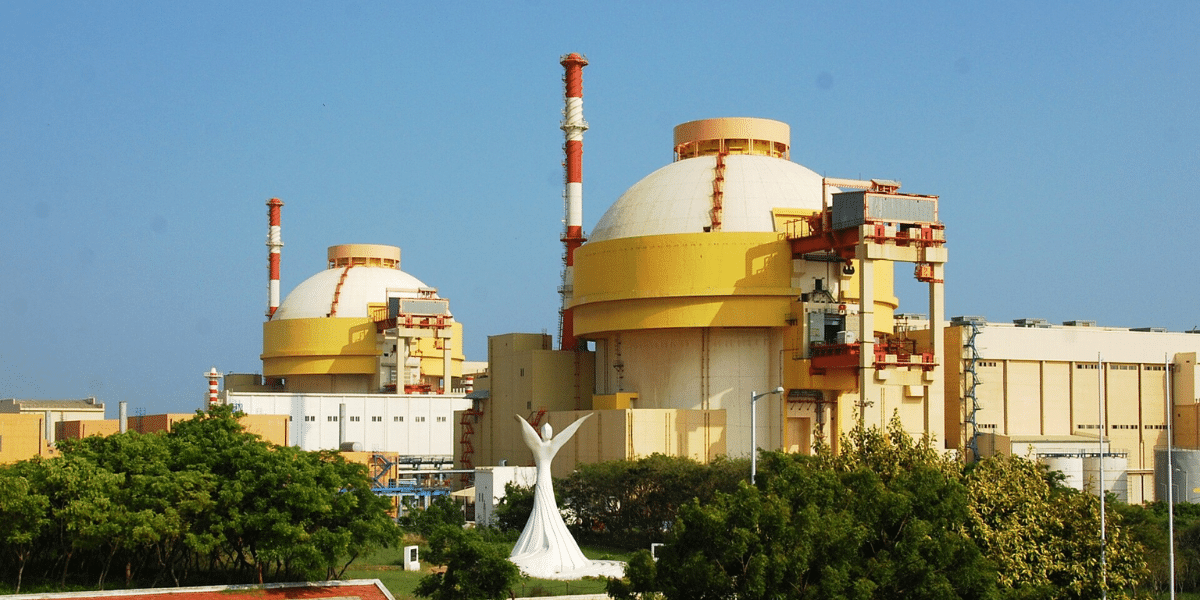
India’s first nuclear power plant was the Tarapur Atomic Power Station (TAPS), which began operations in 1969. Located in Maharashtra, it consists of two reactors and was initially designed to generate 160 MW of electricity. TAPS marked the beginning of India’s journey into nuclear energy, laying the foundation for its growing nuclear power sector.
The first nuclear power plant changed the global energy landscape. Nuclear fission generated electricity—a breakthrough. Beyond technology, this milestone affected geopolitics, energy security, and the environment.
The first power plant provided a powerful fossil fuel alternative and showed countries’ technological prowess. The pioneer plant showed peaceful nuclear reactions could generate power.
The first nuclear power plant introduced a new energy era with safety, security, and sustainability concerns.
Indian energy has been greatly affected by nuclear power. India uses nuclear power for lighting and more.
Energy diversification in India matters. Nuclear energy reduces national vulnerability to fossil fuel supply disruptions and price fluctuations. Businesses, homes, and critical infrastructure gain energy stability.
| Nuclear power plant | Location | Number of reactors | Total installed capacity (MW) |
| Tarapur | Maharashtra | 4 | 1400 |
| Rawatbhata | Rajasthan | 6 | 1180 |
| Kundankulam | Tamil Nadu | 2 | 2000 |
| Kaiga | Karnataka | 4 | 880 |
| Kakrapar | Gujarat | 3 | 1140 |
| Narora | Uttar Pradesh | 2 | 440 |
| Kalpakkam | Tamil Nadu | 2 | 470 |
| Gorakhpur | Haryana | Under construction | Planned capacity |
A global nuclear powerhouse, India has 7 nuclear power plants. Plants with small to large reactors are strategically located nationwide.
The diversity of locations and capacities
India’s nuclear power plant locations and capacities support a diverse energy portfolio. Nuclear fission plants efficiently generate electricity in multiple states. From the iconic Tarapur Atomic Power Station in Maharashtra to the cutting-edge Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in Tamil Nadu, geographical distribution ensures energy accessibility nationwide.
| Year | Installed Nuclear Capacity | Key Developments & Projects |
| 2010 | 4,780 MW | – Existing plants: Tarapur, Rawatbhata, Kakrapar, Kalpakkam, Narora. |
| 2011-2015 | 4,780 MW | – Kudankulam Unit 1 begins generating power (2014). |
| 2016 | 5,780 MW | – Kudankulam Unit 2 becomes operational (2016). |
| 2017-2020 | 6,780 MW | – Ongoing construction of Kudankulam Units 3 & 4. – Agreements with international partners (U.S., Russia, France) for new reactors. |
| 2021 | 6,780 MW | – Kaiga Unit 5 and Kaiga Unit 6 expected to contribute to nuclear capacity. – Continued work on Jaitapur Nuclear Power Plant (9,900 MW capacity). |
| 2022-2025 | 7,000 MW – 9,000 MW | – Kudankulam Units 3 & 4 expected to become operational, adding 2,000 MW. – Jaitapur and Kaiga expansion projects under construction. |
| 2025 (Projected) | 7,000 MW – 9,000 MW | – Expected to meet or exceed 7,000 MW nuclear power capacity. – Jaitapur (9,900 MW) and Kudankulam expansion (Units 3 & 4) will significantly contribute to growth. |
India’s nuclear power generates 3-4% of electricity. In Tamil Nadu, it dominates energy. Several reactors generate 6,000 megawatts of power for India. Indian nuclear energy sustainability is shown by the plant’s advanced technology and strict safety measures.
India’s largest nuclear power plant is in Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu. This India-Russia mega-complex has six reactors and 6,000 MW. India’s energy security and power generation depend on the plant. Advanced PWR technology meets international safety and efficiency standards. The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in India promotes nuclear energy for sustainable development, but safety, environmental, and public concerns remain.
Indian energy relies on nuclear plants. The nation’s energy comes from large power plants. Nuclear power is important because controlled reactions generate lots of electricity. This efficient energy source cuts India’s fossil fuel and greenhouse gas use.
Discover the Narora Nuclear Power Plant in India. Uttar Pradesh generates power with it. Learn its operation, safety, and energy security.
If you come across a question like Narora nuclear power plant in which state, this is what you need to know. The Uttar Pradesh Bulandshahr Narora Nuclear Power Plant is well-positioned. This vital facility is 68 km west of Lucknow, the state capital, on the Ganges. Because it uses a lot of water to operate and regulate reactor temperatures, its location cools it. The strategic location of Narora Nuclear Power Plant streamlines resource and personnel transport.
Narora Nuclear Power Plant is in Uttar Pradesh. The northern state’s history, culture, and landscapes are famous. Uttar Pradesh’s population impacts India’s economy and politics.
Uttar Pradesh is spiritually significant because the Ganges River flows through its center, drawing millions of pilgrims to Varanasi. After learning which state has the Aurora nuclear power plant, we can discuss nuclear power’s pros and cons.
Read More:-
Nuclear fuel refers to materials that can be used in nuclear reactors to produce energy through nuclear fission. The most commonly used nuclear fuels are isotopes of uranium and plutonium. Here’s an overview of nuclear fuel:
India’s nuclear power industry faces a challenge due to limited domestic uranium reserves, which are insufficient to meet the growing energy demands. Although India has some uranium deposits, they are not enough to sustain long-term nuclear power generation at the scale needed for the country’s energy goals. As a result, India relies significantly on uranium imports from countries like Canada, Australia, and Kazakhstan.
Since the early 1990s, India has sought to diversify its sources of uranium through international agreements and collaborations, enabling the country to secure a steady supply for its nuclear reactors. This dependency on imports has driven India to explore alternative sources of uranium and even consider nuclear fuel reprocessing, in which spent nuclear fuel is recycled to extract usable material.
India’s nuclear fuel strategy also includes efforts to develop its own indigenous technology for thorium-based reactors, as thorium is considered an alternative to uranium with more abundant reserves in India. The country has made strides toward this with its Fast Breeder Reactor and thorium reactor programs, which are intended to reduce reliance on imported uranium in the future. However, until these technologies become more widespread, India will continue to depend on uranium imports to fuel its nuclear power plants.
Indian nuclear power plants have many benefits, including low emissions. India uses nuclear reactor electricity to fight climate change and reduce its carbon footprint because it emits no greenhouse gases or air pollutants. This aids India’s carbon reduction goals.
Nuclear power plants provide reliable energy and grid protection. A little nuclear fuel generates a lot of electricity, reducing refueling time and energy reliability. Rising energy needs in India require this.
Nuclear power creates jobs and advances technology. They need skilled operators, maintainers, and researchers to promote nuclear expertise. Nuclear technology could improve medicine and materials.
Nuclear Power Plants in India supply a large portion of the country’s electricity. Safety, waste disposal, and environmental impact are concerns despite their benefits.
Accidents like Chornobyl and Fukushima make safety a top priority. Although strict safety measures and protocols prevent such incidents, the risk remains. They produce radioactive waste that is hard to store and manage. Clean disposal reduces illness and contamination.
India’s nuclear energy sector operates under strict government policies aimed at expanding clean energy while ensuring safety and sustainability. The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) oversee the development and regulation of nuclear power plants.
The era of nuclear fission discoveries and advancements is known as the modern “Atomic Age.” India’s first nuclear power plant was put into service in Tarapur, Maharashtra, following the country’s three-stage nuclear power program, which was developed shortly after independence to meet security and energy demands. Pupils studying for the IAS Exam must know about this and associated subjects.
A key idea in science and technology, a nuclear reactor is a component of a nuclear plant and is covered in General Studies Paper 3 of the UPSC Syllabus. This article explains the different kinds of nuclear reactors and how they operate. For the UPSC 2022 Exam, we have also covered subjects that may be connected to nuclear reactors.
In conclusion, India’s nuclear energy journey, beginning with the first nuclear power plant in India—the Tarapur Atomic Power Station commissioned in 1969—demonstrates significant advancements in nuclear fuel technology and infrastructure. The expansion of the Nuclear Fuel Complex in Hyderabad has ensured a reliable supply of fuel bundles and reactor components, strengthening the country’s domestic capabilities. Leading this progress is the largest nuclear power plant in India, the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in Tamil Nadu, which currently generates about 2,000 MWe and is poised for further expansion. These achievements underscore India’s transformation from its early nuclear endeavors into a key global player in safe and large-scale nuclear power generation.
India operates 22 nuclear power reactors with a total installed capacity of 6,780 MWe across 7 states. Of these, 18 are Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) and 4 are Light Water Reactors (LWRs).
The Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) is in charge of all nuclear power plants in India. Established in 1987, this corporation is owned by the state.
Nuclear power’s contribution to India’s electricity capacity remains modest at 1.6 percent.
Occupational and Industrial Health doctors staff fully equipped Personnel Decontamination Centers for periodic medical exams, dosimetry, and bioassays at NPPs. All operating plants are ISO 14001/IS 18001 certified.
Waste management, greenhouse gas reduction, and ecological protection are environmental benefits and drawbacks of nuclear energy.
Spent reactor fuel and uranium mill tailings pose a significant threat to the environment. These radioactive materials pose a threat to human health for millennia to come.
India’s largest nuclear power plant is the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, located in Kudankulam, Tamil Nadu. It has an installed capacity of 2,000 MWe from two operational units, with additional units under construction to further increase capacity.
India’s first nuclear power plant is the Tarapur Atomic Power Station in Maharashtra, which started operations in 28 oct 1969.
The largest nuclear power plant in the world is the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant, located in Japan. It has a total electrical generation capacity of about 7,965 MW.
India’s current installed nuclear capacity is over 7,000 MW. The government has set an ambitious target to significantly increase this to 22,480 MW by 2031 by commissioning new plants and reactors.
No, nuclear power generation in India is exclusively under the central government. Private sector participation is not permitted in this sector. NPCIL is the sole body responsible for designing, constructing, and operating all nuclear power reactors.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.