
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
Are you a student looking to enhance your general knowledge about international organizations? If so, you’ve come to the right place! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the objectives of SAARC, exploring its functions, member countries, and much more. Whether preparing for a class 12 exam or simply curious about this substantial regional body, this article will provide all the necessary information.

Before we delve into the objectives of SAARC, let’s start with the basics. SAARC Full Form is South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. It’s a regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of South Asian nations. Founded in 1985, SAARC aims to promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in various fields among its member states.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is a group of eight countries in South Asia that work together on economic and political issues. SAARC was created in 1985 when the leaders of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka agreed to form this organization. Afghanistan joined later, in 2007, as the eighth member.
Since its formation, SAARC has held 18 meetings, during which the leaders of these countries discuss important matters. The person in charge of SAARC, called the Secretary-General, is a former foreign secretary from Nepal. The 19th meeting was planned to take place in Pakistan in 2016.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is a regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union in South Asia. Here’s a brief history of SAARC:
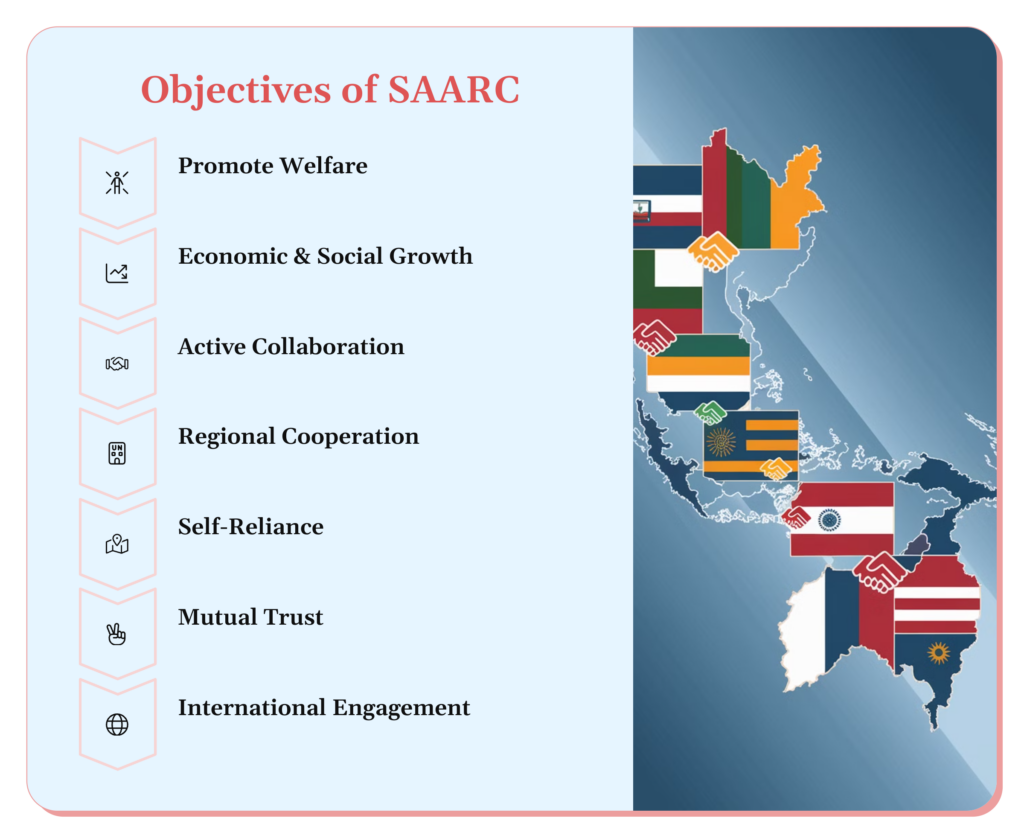
Now, let’s focus on the main topic of our discussion: SAARC’s objectives. These objectives form the foundation of the organization’s activities and guide its efforts towards regional cooperation and development.
One of the primary objectives of SAARC is to improve the quality of life for South Asian people. This broad goal encompasses various aspects, including:
SAARC aims to create programs and initiatives that directly benefit the citizens of its member countries, addressing their basic needs and enhancing their overall well-being.
Economic development is a crucial objective of SAARC. The organization works towards:
By focusing on these areas, SAARC aims to boost the economies of its member countries and improve their citizens’ living standards.
SAARC recognizes the importance of cooperation across multiple sectors. The objectives of SAARC include fostering collaboration in:
This multifaceted approach ensures that the benefits of regional cooperation extend to various aspects of society and governance.
Building strong relationships between member countries is another key objective of SAARC. This involves:
By strengthening these ties, SAARC aims to create a more cohesive and harmonious South Asian community.
SAARC strives to reduce the dependence of its member states on external assistance. The objectives of SAARC in this regard include:
This self-reliance focus helps build a more resilient and independent South Asian region.
Fostering peace and stability in the region is a crucial objective of SAARC. This involves:
SAARC aims to create a more secure and harmonious South Asia by working together on these issues.
SAARC recognizes the importance of engaging with the global community. Its objectives include:
This outward-looking approach helps to integrate South Asia into the global community and amplify its voice in international affairs.
Also Read 👇:
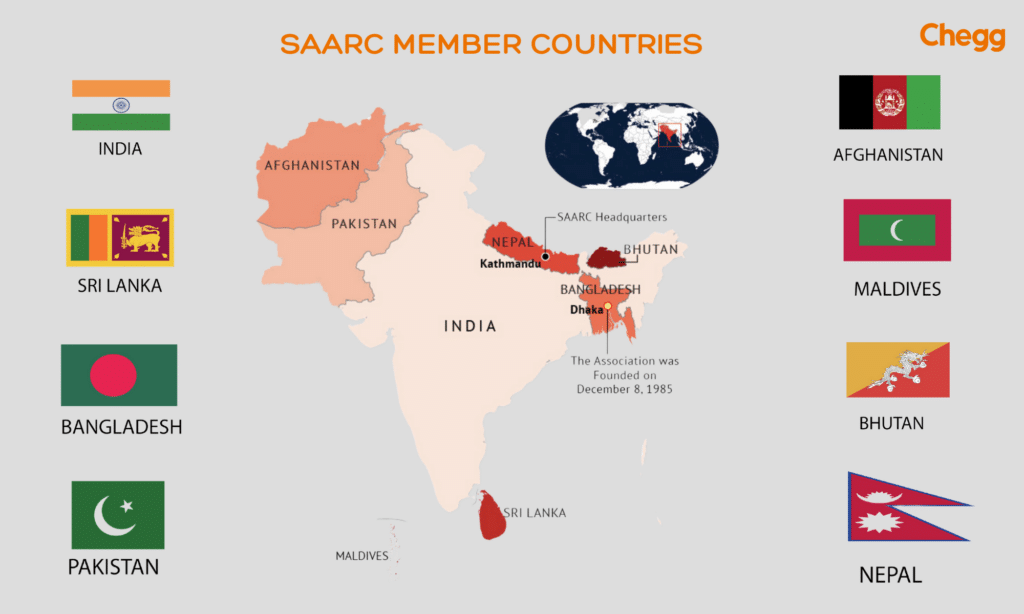
SAARC comprises eight member countries. These nations work together to achieve the common goals outlined in the SAARC charter.
The SAARC Secretariat, the organization’s headquarters, is in Kathmandu, Nepal. Here, the Secretary-General of SAARC and other staff members coordinate the organization’s activities and initiatives.
The headquarters of SAARC, or the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, is located in Kathmandu, Nepal. It was established to promote regional integration and cooperation among its member countries.
Key Information about SAARC:
To achieve its objectives, SAARC carries out various functions. These include:
These functions help translate the objectives of SAARC into concrete actions and initiatives that benefit the region.

The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an organization made up of eight South Asian countries. Its main goal is to help these countries work together to improve their economies, social progress, and cultural growth.
SAARC has several levels, each with a specific role:
This structure and process ensure that all SAARC member countries have a say in the organization’s activities and that they work together for the benefit of the entire region.
The adoption of the SAARC Declaration marked the end of the 18th SAARC Summit, which took place in Kathmandu in 2014. The Declaration acknowledges labor migration as a problem requiring group effort. According to Article 21, SAARC nations pledge to work together to guarantee the safety of South Asian migrant laborers. Leaders of the SAARC also urged authorities to combat and stop the trafficking of women and children during the summit. Participating nations seek to launch an intergovernmental process to suitably contextualize the Sustainable Development Goals at the regional level to the Post-2015 Development Agenda.
In 2023, SAARC has seen a gradual resumption of activities after a period of inactivity due to bilateral tensions. Key developments include the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with IRENA to enhance regional cooperation in sustainable energy and the introduction of revised currency swap frameworks by the Reserve Bank of India to support member nations.
If you’re a 12th-standard student, understanding what are the objectives of SAARC class 12 is crucial for several reasons:
By familiarizing yourself with the objectives of SAARC, you’ll be better equipped to analyze and discuss regional issues in your academic pursuits.
While SAARC has made progress in many areas, it faces several challenges in fully realizing its objectives:
Despite these challenges, SAARC continues to work towards its objectives, adapting its strategies and approaches as needed.
As the global landscape changes, the objectives of SAARC continue to evolve. Some emerging focus areas include:
These new directions reflect the changing needs and priorities of the South Asian region, demonstrating SAARC’s commitment to remaining relevant and effective in the 21st century.
In conclusion, SAARC’s objectives play a vital role in shaping the future of South Asia. SAARC aims to create a more prosperous, peaceful, and interconnected region by promoting cooperation, economic growth, and mutual understanding. As students and future leaders, understanding these objectives is crucial for appreciating the complexities of regional development and international relations.
Whether preparing for an exam or simply expanding your knowledge, the objectives of SAARC offer valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing South Asia. By working together towards these common goals, the SAARC countries strive to build a brighter future for all their citizens.
As we look to the future, the objectives of SAARC will continue to guide the organization’s efforts, adapting to new challenges and seizing new opportunities. By staying informed about these objectives and the work of SAARC, you’ll be better equipped to understand and engage with the dynamic landscape of South Asian cooperation and development.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) was established to promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development in South Asia. Its main objectives include:
1. Improving the quality of life of the people of South Asia.
2. Accelerating economic growth through regional cooperation.
3. Promoting social progress and cultural development.
4. Strengthening collective self-reliance among member states.
5. Fostering mutual trust, understanding, and cooperation.
The original seven countries that formed SAARC in 1985 are:
1. Bangladesh
2. Bhutan
3. India
4. Maldives
5. Nepal
6. Pakistan
7. Sri Lanka
Afghanistan later joined in 2007, making it eight member countries.
India collaborates with other SAARC nations in various areas, including trade, energy, security, and cultural exchanges.
Golam Sarwar of Bangladesh has served as SAARC’s Secretary General since March 4, 2023.
Ziaur Rahman is credited as the founder of SAARC.
SAARC summits are currently held biennially, but there are suggestions to increase the frequency of annual meetings.
SAARC has faced several challenges in achieving its objectives, such as political tensions between member countries, especially India and Pakistan, which have hindered practical cooperation. Additionally, the organization has struggled with inadequate resources, a lack of strong enforcement mechanisms, and differing economic and political priorities among its members. These factors have limited SAARC’s effectiveness in achieving its broader goals.
The SAARC logo features two hands representing goodwill and friendship, with seven doves symbolizing the original seven member countries pursuing peace.
The primary objectives of SAARC are to promote regional cooperation, economic growth, social progress, cultural development, poverty alleviation, mutual assistance, and collective self-reliance among South Asian nations while fostering peace and stability.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.