
Quick Summary
Table of Contents
India has several notable plateaus, each with unique characteristics and formation processes. The central plateaus in India include the Deccan Plateau, Marwar Plateau, Central Highland, Bundelkhand Upland, Malwa Plateau, Baghelkhand Plateau, Chota Nagpur Plateau, Meghalaya Plateau, and Maharashtra Plateau. Plateaus are unique geographical features covering significant surface areas of the Earth. They are often referred to as tablelands or mesas due to their extensive, flat tops and steep sides. Plateaus in India are formed through various geological processes, including the collision of two continental plates, which causes the land to be pushed upward, and volcanic eruptions, where lava flows build up over time to create a flat, elevated surface.
These plateaus are rich in minerals, making them crucial for mining activities. Their fertile soils also support extensive agriculture and are home to diverse ecosystems contributing to biodiversity. Understanding the formation and importance of plateaus helps us appreciate these unique landforms and their contributions to India’s geography and economy.
A plateau is a flat-topped landform that rises sharply above the surrounding area. Due to its extensive, leveled surface, it is often referred to as a tableland. Plateaus in India are formed through various geological processes, including volcanic activity, tectonic movements, and erosion.
Volcanic activity involves repeated lava flows that build up over time, creating a flat, elevated surface. Tectonic movements occur when the Earth’s crust is pushed upward due to the collision or separation of tectonic plates, resulting in elevated landforms. Erosion, caused by wind, water, and ice, gradually wears away the surrounding land, leaving the higher land intact as a plateau. Plateaus in India are rich in minerals, making them crucial for mining activities.
Plateaus are created through a variety of geological processes. One typical method is tectonic uplift, in which the Earth’s crust is pushed upward, resulting in elevated landforms. Plateaus can also be generated by volcanic activity, in which successive lava eruptions accumulate over time, resulting in a level or gradually sloping surface. Erosion and weathering also contribute to the formation of plateaus. The surrounding lands are steadily eroded by wind, water, and ice, but the elevated plateau remains largely intact.
India has several breathtaking plateaus with unique geological features, climate, and cultural significance. These elevated landforms are crucial in shaping the country’s geography and supporting diverse ecosystems. From the vast Deccan Plateau to the rugged Ladakh Plateau, there are seven excellent types of plateaus in India that showcase the nation’s natural beauty and rich heritage.
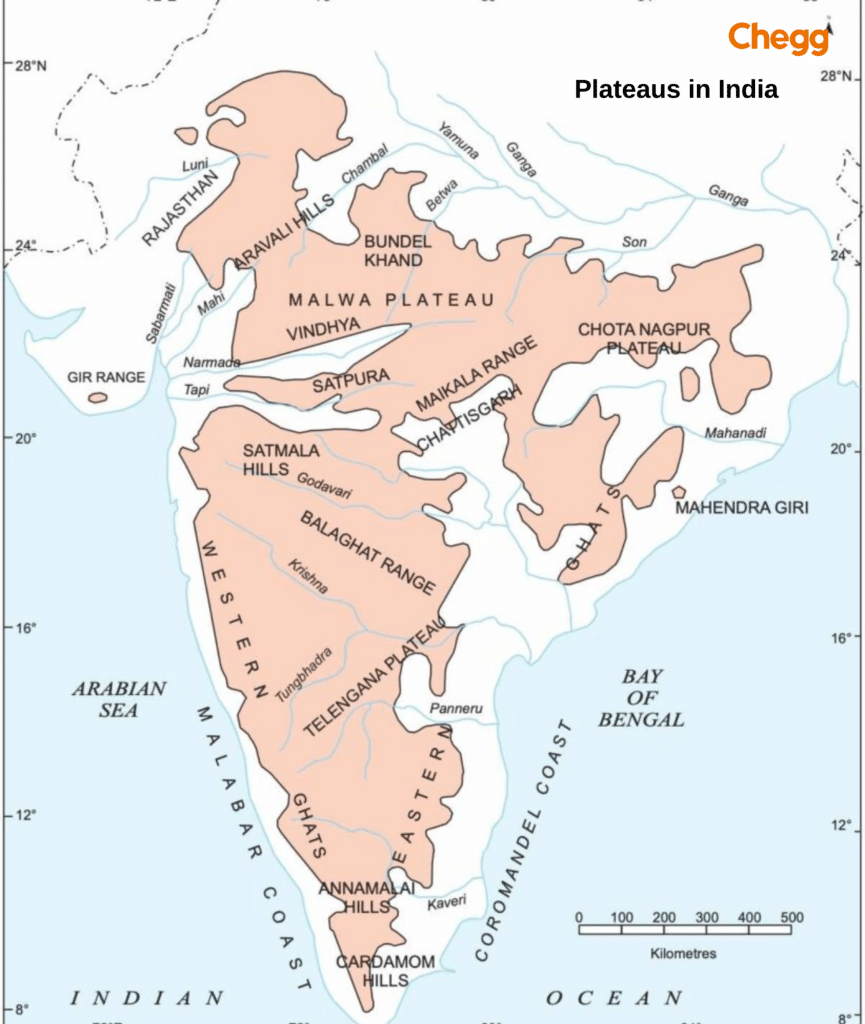
The Deccan Plateau is the most extensive plateau in India, covering much of central and southern India. It spans several states, including Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. Formed by ancient volcanic activity, the Deccan Plateau is rich in minerals like coal, iron ore, and manganese.
The Malwa Plateau is in central India, primarily in Madhya Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan. It was formed by ancient lava flows and is known for its fertile black soil, ideal for growing cotton.
The Chota Nagpur Plateau is in eastern India, spanning Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal. Formed through tectonic activity, it is rich in minerals such as coal, iron ore, and mica, making it a major mining hub.
The Bundelkhand Plateau is located in northern-central India, covering parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. It was formed through tectonic upliftment and features rugged terrain and rocky outcrops.
The Meghalaya Plateau is located in northeastern India, primarily in Meghalaya. It is part of the larger Shillong Plateau and is known for its scenic beauty, with rolling hills, deep valleys, and numerous waterfalls.
The Kathiawar Plateau is located in western India, primarily in Gujarat. It is volcanic and rich in minerals such as limestone and bauxite. The plateau supports various industries, including cement production and aluminum manufacturing.
The Ladakh Plateau is located in northern India, primarily in the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. Formed through tectonic upliftment, it features high-altitude desert landscapes with stunning mountains, valleys, and lakes.
These plateaus in India showcase the country’s diverse geological features and rich natural resources. Understanding their formation and importance helps us appreciate the varied landscapes and their contributions to India’s economy and culture.
Here is the list of Plateaus in India with states:
| Name | States |
| Deccan Plateau | Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu |
| Chota Nagpur Plateau | Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh |
| Malwa Plateau | Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan |
| Karnataka Plateau | Karnataka |
| Meghalaya Plateau | Meghalaya, Assam, parts of Nagaland |
| Bundelkhand Plateau | Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh |
| Marwar Plateau | Rajasthan |
Plateaus in India play a crucial role in various aspects of the country’s geography, economy, and ecology. These elevated flatlands, known as plateaus, are significant for several reasons:
Many plateaus in India are abundant in minerals such as coal, iron, copper, and mica. These minerals are essential for various industries and mining activities. For example, the Chota Nagpur Plateau is known for its rich coal and iron ore deposits, making it a significant mining hub. The extraction and processing of these minerals contribute significantly to India’s industrial growth and economic development.
The fertile soils found in some plateaus, like the Malwa Plateau, are ideal for agriculture. These regions support cultivating various crops, providing food and livelihood for many people. The black soil of the Malwa Plateau is particularly suitable for growing cotton. Additionally, plateaus offer grazing lands for cattle and sheep, supporting pastoral communities and contributing to the rural economy.
Plateaus in India are home to diverse flora and fauna, making them essential for biodiversity. They support central wildlife reserves such as the Gir Forest and Satpura National Park. These protected areas are crucial for conserving various species, including the Asiatic lion in Gir Forest. The unique ecosystems on plateaus contribute to India’s rich natural heritage and ecological balance.
Many rivers originate from plateaus, providing essential water resources for irrigation and drinking. For instance, the Godavari and Krishna rivers, originating from the Deccan Plateau, are vital for agriculture and water supply in the surrounding regions. These rivers help sustain the livelihoods of millions of people and support agricultural productivity.
Plateaus in India have significant historical and cultural importance. Sites like Hampi on the Deccan Plateau and Ujjain on the Malwa Plateau are rich in cultural heritage and attract numerous tourists. These regions’ scenic beauty, waterfalls, and caves also draw visitors, boosting tourism and contributing to the local economy. The cultural landmarks and natural attractions on plateaus help preserve India’s heritage and promote tourism.
Understanding the importance of plateaus in India helps us appreciate their multifaceted contributions to the country’s geography, economy, and ecology. These unique landforms, known as plateaus, are essential for mineral resources, agriculture, biodiversity, water supply, and tourism, making them vital to India’s overall development and prosperity
The Indian Peninsular Plateau, also known as the Deccan Plateau, is marked by ancient rock formations and unique hill ranges that have shaped its geography, climate, and cultural heritage.
Plateaus in India play a crucial role in the nation’s economy and geography. They offer rich mineral deposits—such as coal and iron on the Chota Nagpur Plateau—and fertile soils, like the black soil of the Malwa Plateau, ideal for cotton cultivation. Additionally, these flatlands provide grazing lands and support diverse ecosystems, including wildlife reserves like Gir Forest and Satpura National Park. The expansive Deccan Plateau, the most extensive plateau in India, further enriches the landscape with its vast stretch and abundant natural resources. With significant historical and cultural sites such as Hampi and Ujjain, plateaus also boost tourism and local livelihoods.

Ans. The Peninsular Plateau, formed from the drifting of the Gondwana land, is India’s oldest landmass. Broad valleys and rounded hills characterize it.
Ans. The Deccan Plateau in southern India, situated between the Western and Eastern Ghats, is the country’s most renowned plateau. It encompasses the peninsular region south of the Narmada River and is bordered by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges to the north.
Ans. A plateau is a level stretch of raised land with at least one side that rises sharply above the surrounding area.
Ans. There are a total of 7 Platues in India:
1. Marwar Plateau
2. Central Highland
3. Bundelkhand Upland
4. Malwa Plateau
5. Baghelkhand
6. Chota Nagpur Plateau
7. Meghalaya Plateau
8. Deccan Plateau (This is often referred to as the Maharashtra Plateau as well)
Ans. The Deccan Plateau is the most extensive plateau in India. It is a triangular landmass south of the river Narmada.
Ans. The Tibetan Plateau is the world’s highest, largest, and most famous. It stretches through Tibet, China, and India in South-Central Asia.
Ans. The ten notable plateaus in India include:
1. Marwar Plateau
2. Central Highland
3. Bundelkhand Upland
4. Malwa Plateau
5. Baghelkhand Plateau
6. Chota Nagpur Plateau
7. Meghalaya Plateau
8. Deccan Plateau
9. Maharashtra Plateau
10. Karnataka Plateau
Ans. Largest Plateau in India: The Deccan Plateau is the most extensive plateau in India, covering a vast area in southern India
Smallest Plateau in India: The Sigur Plateau in Tamil Nadu is considered one of the smallest plateaus in India
Also Read:-

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.