
Quick Summary
India is home to over 43 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, both cultural and natural.
These sites include famous landmarks like the Taj Mahal, Qutub Minar, and Kaziranga National Park.
UNESCO sites in India are a must-visit for anyone interested in exploring the country’s rich heritage and history.
Table of Contents
India is home to a rich and diverse heritage, and its UNESCO World Heritage Sites are a testament to the country’s historical and cultural significance. As of now, India boasts over 43 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, which include some of the world’s most important cultural and natural landmarks. In this article, we will explore these sites, categorizing them by type and significance, and provide you with detailed information about each one.
It’s a great honor to see how many UNESCO World Heritage Site India has. The country is rich in cultural and natural wonders that have fascinated the world with their deep historical significance and breathtaking beauty. Among these treasures, 43 have earned the prestigious title of UNESCO World Heritage Site India. India is home to 43 world heritage sites in India, showcasing its rich cultural heritage and natural beauty. Iconic landmarks like the Taj Mahal, Ajanta and Ellora Caves, Sun Temple at Konark, and the group of monuments at Hampi highlight its historical splendor. The Moidams of Assam, added in 2024, reflects the Ahom dynasty’s cultural significance.
Other notable sites include Jaipur City, a planned urban marvel; Kaziranga National Park, renowned for its biodiversity; and the Valley of Flowers, famous for breathtaking landscapes. These 43 world heritage sites in India collectively symbolize the nation’s legacy of art, history, and ecological wealth.
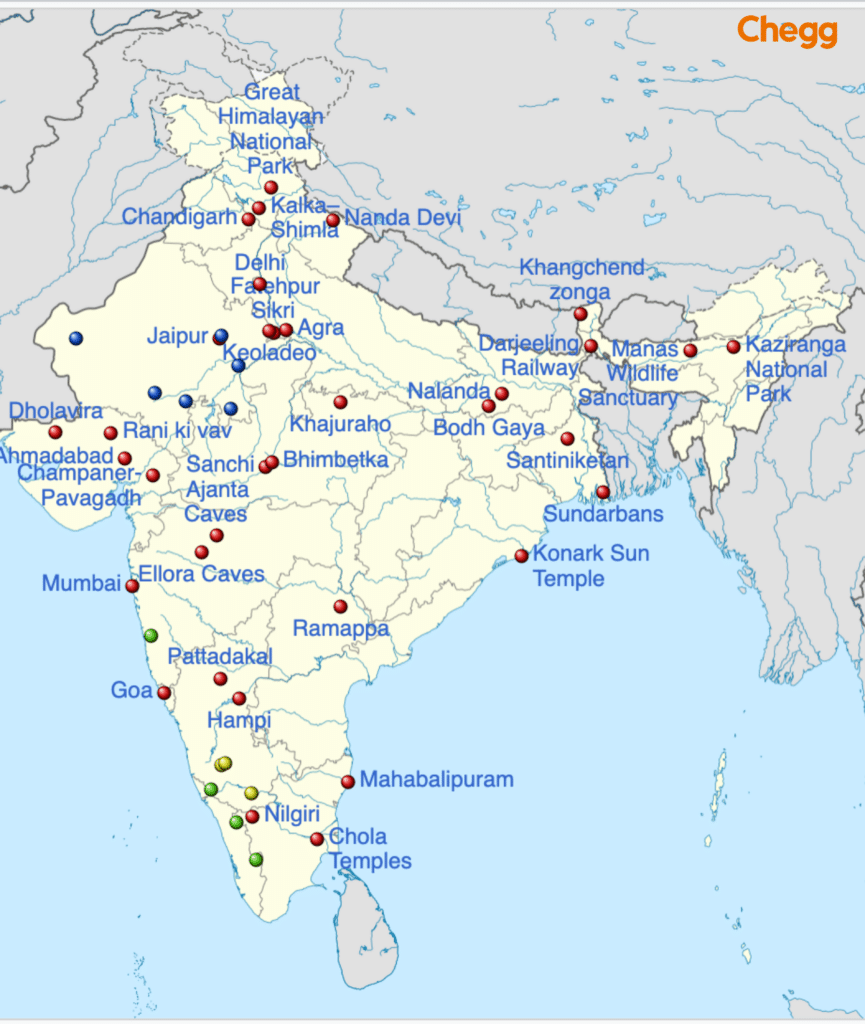
India is home to 43 UNESCO World Heritage Sites as of 2025, showcasing its rich cultural and natural heritage. These include iconic landmarks like the Taj Mahal, Ajanta and Ellora Caves, Sun Temple at Konark, and Hampi. The Moidams of Assam, inscribed in 2024, is the latest addition.
Additionally, six sites have been added to India’s tentative list for UNESCO recognition in 2025. These include the Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs in Telangana, Kanger Valley National Park in Chhattisgarh, Ashokan Edict Sites, Chausath Yogini Temples, Gupta Temples, and the Palace-Fortresses of the Bundelas.
The criteria for UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India follow the global UNESCO guidelines. To qualify, a site must meet at least one of these ten criteria:
The first UNESCO World Heritage Site in India is the Ajanta Caves, which were inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1983.
India has a remarkable list of 43 UNESCO World Heritage Site India total, celebrated for their cultural and natural significance.
| S.No | Name of Sites | Year | Location |
| 1 | Ajanta Caves | 1983 | Maharashtra |
| 2 | Ellora Caves | 1983 | Maharashtra |
| 3 | Agra Fort | 1983 | Agra |
| 4 | Taj Mahal | 1983 | Agra |
| 5 | Sun Temple | 1984 | Orissa |
| 6 | Mahabalipuram Monuments | 1984 | Tamil Nadu |
| 7 | Kaziranga National Park | 1985 | Assam |
| 8 | Keoladeo National Park | 1985 | Rajasthan |
| 9 | Manas Wildlife Sanctuary | 1985 | Assam |
| 10 | Churches and Convents of Goa | 1986 | Goa |
| 11 | Monuments of Khajuraho | 1986 | Madhya Pradesh |
| 12 | Monuments of Hampi | 1986 | Karnataka |
| 13 | Fatehpur Sikri | 1986 | Agra |
| 14 | Elephanta Caves | 1987 | Maharashtra |
| 15 | Great Living Chola Temples | 1987 | Tamil Nadu |
| 16 | Pattadakal Monuments | 1987 | Karnataka |
| 17 | Sundarbans National Park | 1987 | West Bengal |
| 18 | Nanda Devi & Valley of Flowers National Park | 1988 | Uttarakhand |
| 19 | Monuments of Buddha | 1989 | Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh |
| 20 | Humayun’s Tomb | 1993 | Delhi |
| 21 | Qutub Minar and its Monuments | 1993 | Delhi |
| 22 | Mountain Railways of Darjeeling, Kalka Shimla & Nilgiri | 1999 | Darjeeling |
| 23 | Mahabodhi Temple | 2002 | Bihar |
| 24 | Bhimbetka Rock Shelters | 2003 | Madhya Pradesh |
| 25 | Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus | 2004 | Maharashtra |
| 26 | ChampanerPavagadh Archaeological Park | 2004 | Gujarat |
| 27 | Red Fort | 2007 | Delhi |
| 28 | Jantar Mantar | 2010 | Delhi |
| 29 | Western Ghats | 2012 | Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra |
| 30 | Hill Forts | 2013 | Rajasthan |
| 31 | Rani Ki Vav (The Queen’s Stepwell) | 2014 | Gujarat |
| 32 | Great Himalayan National Park | 2014 | Himachal Pradesh |
| 33 | Nalanda | 2016 | Bihar |
| 34 | Khangchendzonga National Park | 2016 | Sikkim |
| 35 | Architectural Work of Le Corbusier (Capitol Complex) | 2016 | Chandigarh |
| 36 | The Historic City | 2017 | Ahmedabad |
| 37 | Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles | 2018 | Mumbai |
| 38 | The Pink City | 2019 | Jaipur |
| 39 | Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple | 2021 | Telangana |
| 40 | Dholavira | 2021 | Gujarat |
| 41 | Santiniketan | 2023 | West Bengal |
| 42 | Hoysala temples of Belur, Halebid and Somananthpura | 2023 | Karnataka |
| 43 | Moidams – the Mound-Burial system of the Ahom Dynasty | 2024 | Assam |
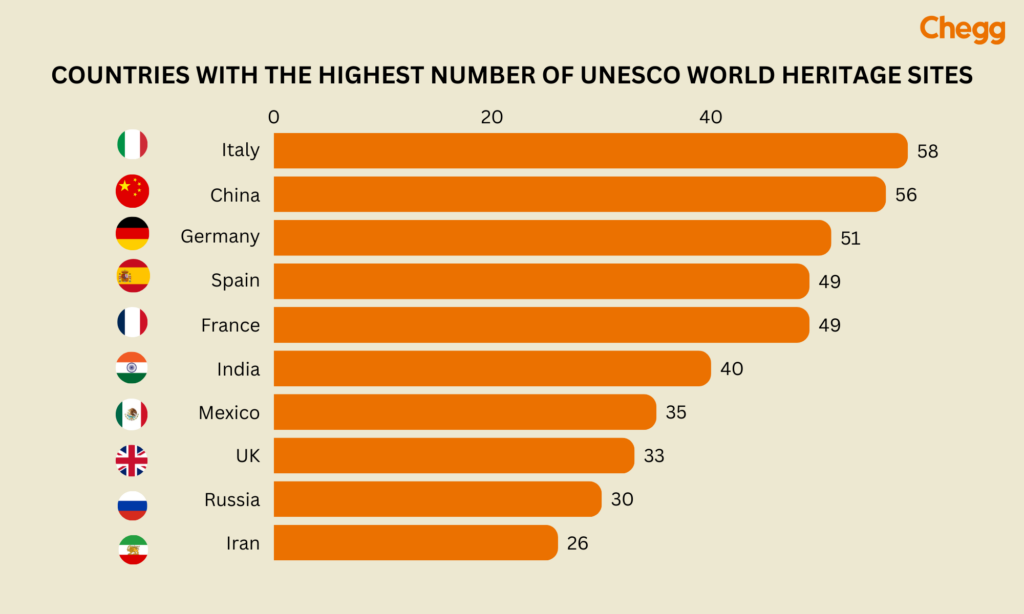
India holds the sixth-highest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites globally. The countries with 42 or more such sites include Italy, Spain, Germany, China, and France. Notably, since 2014, India has added 12 new World Heritage Sites, showcasing the nation’s commitment to preserving and promoting its cultural and natural treasures.
Seven natural wonders in India that are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Famous for the world’s 2/3rd population of Great One-Horned Rhinoceroses. The park holds the record for the highest density of tigers in the world, as well as wild water buffalo, elephants, and swamp deer. Additionally, it has gained recognition as an Important Bird Area.
A UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1985, Manas National Park is a protected area covering 284 sq km in Assam, India. Its rich biodiversity and endangered species like the Assam roofed turtle, pygmy hog, hispid hare, golden langur, and Bengal florican are well-known.
This former hunting ground of the Maharajas of Bharatpur is now a bird sanctuary that is home to over 230 species of birds, including the Asian koel, from which it gets its name.
This UNESCO World Heritage Site encompasses two national parks, Nanda Devi National Park and Valley of Flowers National Park. The second-highest mountain in India, Nanda Devi, lends its name to Nanda Devi National Park. The meadows filled with wildflowers make Valley of Flowers National Park renowned.
This park is home to the Royal Bengal tiger, the largest tiger population in the world. It is also the largest mangrove forest in the world.
The Western Ghats is a mountain range that runs along the western coast of India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its rich biodiversity and unique ecosystems.
This park is located in the Himalayas and is home to a variety of mountain animals, including snow leopards, bears, and ibex.
34 wonders that are considered UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India.
Khangchendzonga National Park: In the UNESCO list, experts consider the national park a mixed type. It earns fame for its fauna and flora, with occasional sightings of snow leopards.

Various UNESCO World Heritage Sites exhibit India’s rich history and culture, which are well-recognized. These locations are examples of architectural and cultural marvels, ranging from the towering Taj Mahal, a representation of eternal love, to the breathtaking temples of Khajuraho, renowned for their elaborate sexual carvings. Names like Jaipur’s Amer Fort and the spiritual importance of Varanasi’s ghats enhance the heritage of India.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India represent the country’s rich and diverse cultural and natural heritage. Whether you are a traveler, historian, or student, exploring these iconic sites is an enriching experience. Be sure to visit these extraordinary landmarks to understand and appreciate the depth of India’s history and its contributions to the world.
forty-two World Heritage Sites. India is home to 43 World Heritage Sites. 34 of these are cultural, 7 are natural, and one is a mixed type, which is Khangchendzonga National Park.
Karnataka’s Hoysala dynasty temples from the 13th century have been added to UNESCO’s World Heritage list, bringing the total number of these sites in India to 42. and with the recent inclusion of Assam’s Charaideo Moidams, total unesco world heritage sites in India is now 43.
There were about 40 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India as of 2022.
Yes, the Red Fort in Delhi is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Recognized in 2007, it is an iconic symbol of Mughal architecture and India’s history. This majestic fort, built by Emperor Shah Jahan, is a prime attraction and a significant cultural heritage landmark.
India’s 43rd UNESCO World Heritage Site is the Moidams of Assam, inscribed in 2024. These mound-burial systems of the Ahom dynasty reflect unique funerary traditions and architectural brilliance. Located in Charaideo, they symbolize India’s rich cultural heritage.
Also Read:-

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.