
Quick Summary
Table of Contents

It’s a joint forum that brings together the Center and the States to make pivotal decisions about the GST. It is the cornerstone of the GST system in India, playing a significant role in shaping our economy.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the workings of the GST Council, its composition, and its impact on the Indian taxation system. Stay tuned as we unravel the intricacies of this influential body.
Before the Goods and Services Tax (GST), India had a complicated tax system with various indirect taxes like VAT, Service Tax, and Excise Duty. This tangled web made business operations challenging and resulted in extra financial burdens due to layered taxes.
In what is GST Council, the council plays a vital role in deciding GST-related matters, ensuring a cooperative federal system. By replacing the older tax regime, the GST Council signifies a commitment to making India’s tax system more transparent, business-friendly, and adaptable to the changing economic landscape. It reflects a significant step toward a simpler and more efficient taxation framework in the country.
The GST Council wants to make India’s tax system more uniform, open, and straightforward. Its objectives are to balance tax laws, promote economic growth, enhance compliance, and foster an environment that benefits businesses and taxpayers.
The main objective of the GST Council is to simplify the indirect tax framework in India. Its goals are to simplify taxes, do away with tax cascades, and promote a smooth national market. It seeks to improve the ease of conducting business, guarantee equitable and effective revenue collection, and minimize tax evasion.
The GST Council hopes to accomplish these objectives by promoting economic expansion, leveling the playing field for companies, and advancing India’s economy into a strong and competitive one.

The Goods and Services Tax Council is the central body overseeing India’s GST regime. Understanding its composition is crucial for anyone interested in the system’s functioning. Here’s a breakdown:
This two-tier structure fosters collaboration between the central government and the states. It allows for:
While the official list of GST Council members isn’t readily available on a single government webpage, here are some resources to help you stay updated:
The GST Council serves as the cornerstone of India’s tax system, promoting a uniform and streamlined tax structure via its well-structured decision-making procedure. The Goods and Services Tax Council actively shapes the tax environment through regular meetings. Decisions are made through consensus whenever possible. However, a voting mechanism exists to resolve disagreements.
To promote economic openness and harmonization, this dynamic body determines tax rates, threshold limits, exclusions, and taxation concerns.
The Goods and Services Tax Council actively ensures consistent implementation of decisions across all states and union territories, fostering a smooth national market.
Representatives from the federal and state governments collaborate to develop and carry out tax policy through the GST Council. It is a collaborative mentality that feeds off of obtaining choices by agreement to balance the interests of all parties involved.
The council supports a clear and straightforward tax system and harmonizes tax policy through this cooperative approach. Its emphasis on governance, economic efficiency, and conflict resolution guarantees that the framework of tax policy supports India’s economic stability and prosperity.
| Position | Details |
|---|---|
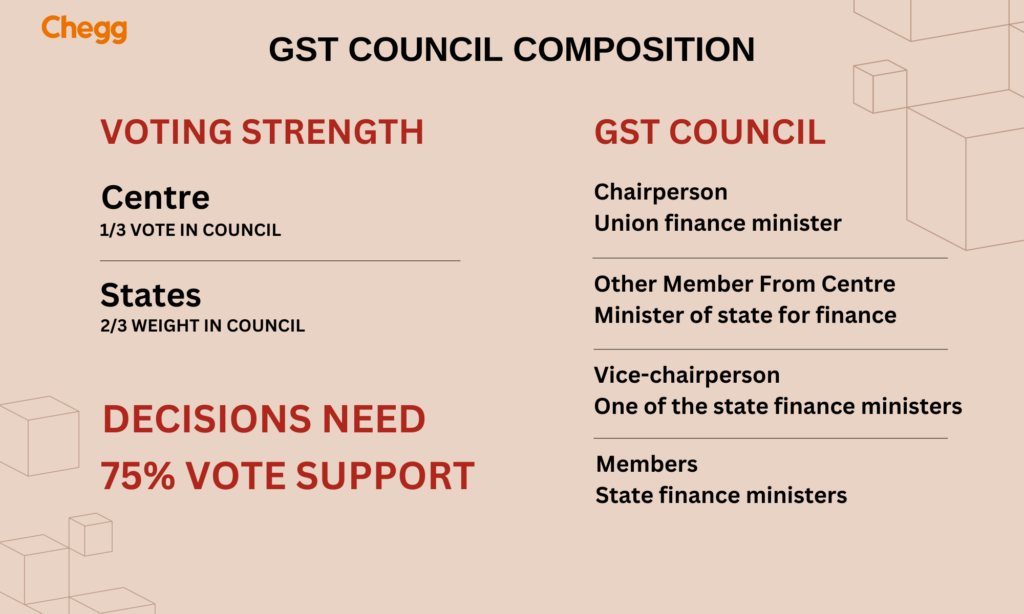
| Chairperson | The Union Finance Minister |
| Vice-Chairperson | Selected by the Members of the Goods and Services Tax Council from the States among themselves. |
| Members can also determine their term. | |
| Members | – The Union Minister of State for Revenue or Finance. |
| – State Ministers responsible for Finance, Taxation, or other Ministers nominated by the State Government. | |
| – The Chairperson of the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) as a permanent non-voting invitee. | |
| – The Union Revenue Secretary (Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance) serves as the ex-officio Secretary. |
A key player in India’s tax system, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council carries out a variety of tasks to optimize and control the GST system. Here are the functions of the GST Council:
The Goods and Services Tax Council (What is GST Council) is a vital cog in India’s taxation machinery. This federal body, comprising the Union Finance Minister and representatives from all states, wields significant powers in shaping the GST regime. Here’s a breakdown of its key authorities:
In India, the GST Council is charged with vital responsibilities meant to guarantee the smooth operation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, and those are:
Understanding these powers highlights the GST Council’s significance in:
By effectively utilizing its powers, the GST Council in (What is GST Council) plays a critical role in streamlining India’s tax structure and promoting a more efficient indirect tax system.
The GST Council in India is a hierarchical organization consisting of members from the national and state governments. The Indian Union Finance Minister, who is the council’s chair, is crucial to the decision-making process. Each state and union territory’s minister or deputy minister of taxes and finance is a member of the council. This ensemble functions as a cooperative platform by guaranteeing balanced representation and dynamics of decision-making.
One important organization in India’s tax system, the GST Council (What is GST Council?), has unique characteristics that are vital in determining the indirect tax environment of the country.
These characteristics make it easier to use a flexible and dynamic taxing strategy, which helps India’s tax system become more unified and effective.
Constitutional provisions and a strong legislative framework provide the foundation for the formation of the GST Council in India. The 101st Constitutional Amendment Act, 2016, which imposed the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on India, also created it. This legislation outlined the council’s duties and responsibilities and gave the organization a legal foundation. It is protected by Article 279A of the Indian Constitution.
The Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers’ discussions, which prepared the way for the implementation of the GST, were among the historical turning points that paved the way for the creation of What is GST Council. September 2016 saw the official formation of the council, which was a major step toward the implementation of a unified and streamlined indirect tax system in the country.
The Goods and Services Tax revolutionized India’s indirect tax system, aiming for a seamless flow of goods and services across the nation. While it has brought significant advantages, some challenges remain. Here’s a breakdown of both:
The Goods and Services Tax Council is a crucial topic for UPSC Civil Services Examination aspirants. Understanding its role in India’s economic and fiscal landscape demonstrates a strong grasp of current affairs and inter-governmental dynamics. Here’s a breakdown to equip you for success:
Now you know about What is GST Council. Active members of the council, representing both federal and state governments, collaborate to make important decisions about tax rates, exemptions, and compliance guidelines, aiming to provide a straightforward and standardized tax system.
With the council’s formation, India’s economic history underwent a sea change, and a new era of streamlined taxes began. The council, with its robust decision-making framework and supportive secretariat, dedicates itself to promoting economic viability, reducing tax avoidance, and ensuring a clear and consistent tax system across the nation.
Also Read:-
A Complete Note on Per Capita Income of Indian States
Constituent Assembly of India: An Overview
Juvenile Justice Act: An Overview
Along with the “What is GST Council,” Read the related articles by visiting the above links.
There is only 1 GST Council in India. However, it comprises 33 members, including two from the Union and the remaining 31 from the States and Union Territories.
It’s a joint body of India’s central and state governments that decides on all aspects of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Led by the Union Finance Minister, it includes finance ministers or tax representatives from each state.
The head of the GST Council is the Union Finance Minister of India. As of the latest information, the position is held by Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
People often refer to the former Prime Minister of India, Atal Bihari Vajpayee, as the “Father of GST” in India. He set up a committee to design a GST model, which the government later implemented in 2017.
The Full Form of GST is Goods and Services Tax.
Article 279A of the Indian Constitution establishes the GST Council as a constitutional body. The Constitution’s One Hundred and First Amendment is the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
GST Amount = (Original Cost* GST Rate Percentage) / 100.
Net Price = Original Cost + GST Amount.
The first Chairman of the GST Council was Arun Jaitley. Arun Jaitley served as the Union Finance Minister of India.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) was implemented in India on July 1, 2017.

Authored by, Amay Mathur | Senior Editor




Amay Mathur is a business news reporter at Chegg.com. He previously worked for PCMag, Business Insider, The Messenger, and ZDNET as a reporter and copyeditor. His areas of coverage encompass tech, business, strategy, finance, and even space. He is a Columbia University graduate.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.