
Whether you’re a student preparing for a geography quiz, a trivia enthusiast, or simply curious about the U.S., knowing the states and capitals is essential to understanding the country’s structure. This knowledge helps you grasp geographic locations and the political and historical significance of each state and its capital. In this post, we’ll provide a complete list of U.S. states and capitals, share fun facts about them, and explain the importance of state capitals. We’ll also offer helpful learning tips to make memorizing states and capitals easier.
Knowledge of the states and capitals of India, along with the union territories, is necessary for preparing for several Government exams. For students who are wondering about how many states are in India, let us clear away the doubts.

India’s states and capitals have a rich history, shaped by colonial rule, the post-independence restructuring, and the cultural and political evolution of the country. Below is an overview of the key milestones in the history of India’s states and capitals:
Before independence in 1947, India was under British colonial rule and was divided into provinces and princely states. The capitals during this time were primarily British-controlled cities like Calcutta (now Kolkata), which was the capital of British India, and Bombay (now Mumbai), Madras (now Chennai), and Delhi, which served as important administrative centers for the British colonial government.
Upon gaining independence in 1947, India was initially divided into 29 states and 7 union territories, each with its own administrative structure. The capital of India remained New Delhi, which was already an established center of governance during British rule.
The States Reorganization Act of 1956 was a significant turning point in the history of India’s states and capitals. The goal was to reorganize the states based on linguistic lines, which led to the creation of several new states, including Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, and Karnataka, and their respective capitals were defined.
In the years following 1956, several states and union territories were formed due to various political and social reasons:
The concept of union territories (UTs) was introduced to manage regions that were not part of any state but were of national importance. These territories were directly governed by the central government, and each has its own administrative structure:
In the 21st century, new states were created, leading to new capitals being formed:
In 2019, the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act led to the formation of two new Union Territories — Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh. This change came after the abrogation of Article 370, which granted special status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
Additionally, the two Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli were merged into one entity in 2020.
India has 8 union territories as of January 26, 2020. The two union territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli have been merged into a single union territory.
Jammu and Kashmir, which was previously a state, has been reorganized into two Union Territories—Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh. This change was implemented through a reorganization act passed by Parliament on August 5 and 6, 2019. The restructuring also impacts the India States and Capitals Map, as the alteration in administrative divisions influences the governance and territorial organization of the country.
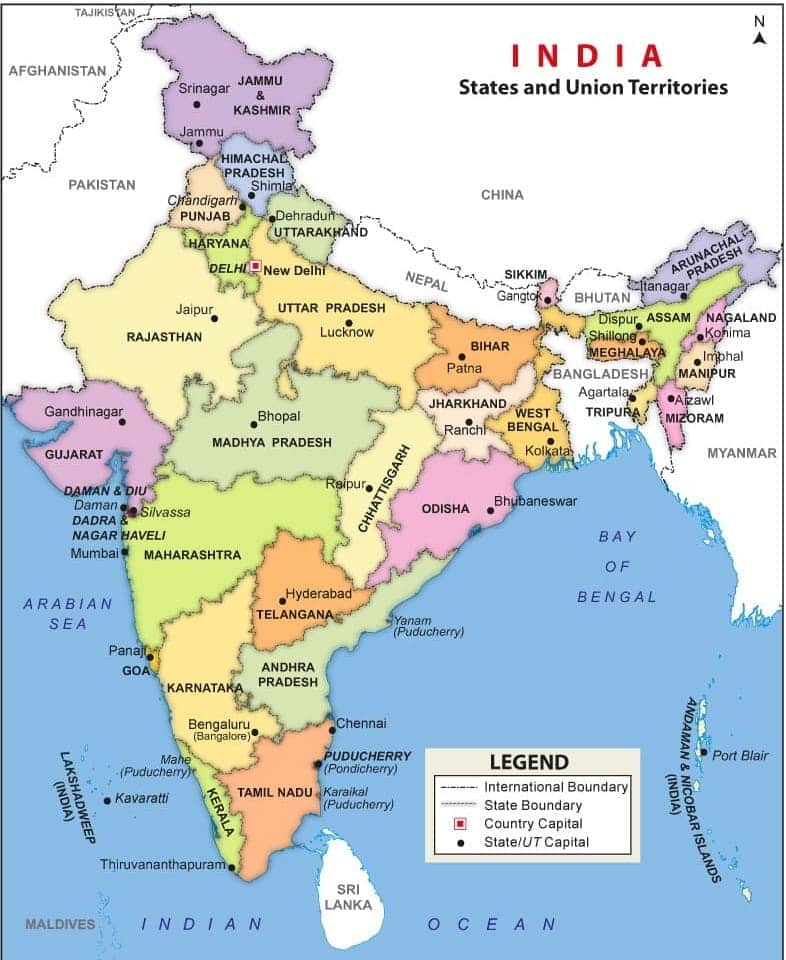
There are a total of 28 Indian states and capitals. Rajasthan is the largest state in India in terms of area, and Goa is the smallest state. All of these states have been given the status of State in stages over the years. News states have been added in batches during the years 1950, 1956, 1960, 1963, 1966, 1972, 1982, 1987, 2000, and 2014. The last states that made the list were Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Uttarakhand in the year 2000, and thereafter, Telangana took shape in the year 2014. The full list of all states and capitals has been, for reference, prepared in a table.
| State | Capital | Date of Formation |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati | November 1, 1956 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | February 20, 1987 |
| Assam | Dispur | November 26, 1966 |
| Bihar | Patna | January 26, 1950 |
| Chhattisgarh | Raipur | November 1, 2000 |
| Goa | Panaji | May 30, 1987 |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar | May 1, 1960 |
| Haryana | Chandigarh | November 1, 1966 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla | January 25, 1971 |
| Jharkhand | Ranchi | November 15, 2000 |
| Karnataka | Bengaluru | November 1, 1956 |
| Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram | November 1, 1956 |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | November 1, 1956 |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai | May 1, 1960 |
| Manipur | Imphal | January 21, 1972 |
| Meghalaya | Shillong | January 21, 1972 |
| Mizoram | Aizawl | February 20, 1987 |
| Nagaland | Kohima | December 1, 1963 |
| Odisha | Bhubaneswar | April 1, 1936 |
| Punjab | Chandigarh | November 1, 1966 |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur | March 30, 1949 |
| Sikkim | Gangtok | May 16, 1975 |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai | January 14, 1969 |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | June 2, 2014 |
| Tripura | Agartala | January 21, 1972 |
| Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | January 26, 1950 |
| Uttarakhand | Dehradun | November 9, 2000 |
| West Bengal | Kolkata | January 26, 1950 |
India currently has a total of 8 Union Territories (UTs). Jammu & Kashmir was reorganized into two separate Union Territories—Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh. Additionally, the Union Territories of Daman and Diu, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli were merged into a single entity. On August 5, the central government revoked the special status granted to Jammu & Kashmir under Article 370 and officially divided it into two UTs. With the merger of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, the total number of Union Territories was reduced to eight. Below is a detailed list of India’s Union Territories along with their respective capitals.
| Union Territory | Capital | Date of Formation |
|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair | 1st Nov 1956 |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1st Nov 1966 |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Daman | 26th Jan 2020 |
| Delhi | New Delhi | 9th May 1905 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer), Jammu (Winter) | 31st Oct 2019 |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti | 1st Nov 1956 |
| Puducherry | Pondicherry | 1st Nov 1954 |
| Ladakh | Leh | 31st Oct 2019 |
Each of these Union Territories has a unique administrative structure and plays a crucial role in India’s governance system.
India is a diverse country with 28 states, each having its own unique culture, traditions, languages, and states and capitals. The constitution of India recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule, with each state often having its own official language(s). For instance, Hindi is widely spoken in states like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, while Tamil is the official language of Tamil Nadu, and Bengali is spoken in West Bengal. Other languages, such as Telugu, Marathi, Gujarati, and Kannada, represent the regional identity and linguistic heritage of their respective states. This linguistic diversity adds to the rich cultural fabric of India, making it one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world.
| Indian State | Specialization | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Known for its spicy cuisine, historical landmarks like Charminar and Golconda Fort, and rich cultural heritage in art, music, and dance. | Amaravati |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Renowned for its breathtaking landscapes, diverse tribal cultures, and the Tawang Monastery, one of India’s largest. | Itanagar |
| Assam | Famous for its tea plantations, Kaziranga National Park (home to the one-horned rhinoceros), Bihu dance, and traditional silk weaving. | Dispur |
| Bihar | Known for its historical significance, including the ancient city of Patliputra, Buddhist pilgrimage sites like Bodh Gaya, and Madhubani art. | Patna |
| Chhattisgarh | Recognized for its tribal heritage, abundant mineral resources, and the Chitrakote Waterfall, often called the “Niagara of India.” | Raipur |
| Delhi | Famous for iconic landmarks like India Gate and the Istana, symbolizing the country’s historical struggles and future aspirations. | New Delhi |
| Goa | Renowned for its beautiful beaches, vibrant nightlife, unique blend of Indian and Portuguese cultures, and delicious seafood cuisine. | Panaji |
| Gujarat | Celebrated for its industrial and business prowess, the Rann of Kutch desert, vibrant festivals like Navaratri and Diwali, and the Sabarmati Ashram linked to Mahatma Gandhi. | Gandhinagar |
| Haryana | Known for its agricultural productivity, thriving industries, and Chandigarh, a city recognized for its architecture and urban design. | Chandigarh |
| Himachal Pradesh | Famous for picturesque hill stations, adventure tourism, serene landscapes, and the Dalai Lama’s residence in Dharamshala. | Shimla |
| Jharkhand | Rich in mineral resources, known for its tribal culture, and home to Betla National Park. | Ranchi |
| Karnataka | Known as the “Silicon Valley of India,” with a thriving IT industry, historical landmarks like Hampi, and traditional dance forms like Bharatanatyam. | Bengaluru |
| Kerala | Renowned for its backwaters, Ayurvedic practices, lush greenery, and the highest literacy rate in India. | Thiruvananthapuram |
| Maharashtra | Known as the financial and entertainment capital, with Bollywood, historical landmarks like the Gateway of India, and culinary delights like Vada Pav. | Mumbai |
| Manipur | Famous for traditional dance forms like Manipuri dance, Loktak Lake, and vibrant cultural festivals. | Imphal |
Knowing the states and capitals of India holds significant value for several reasons. Whether for educational purposes, competitive exams, general knowledge, or even professional growth, understanding the geographical and political structure of India is crucial. Here’s why it’s important:
The difference between a state and a union territory is that the latter is under the direct control of the central Government. There is also a Lieutenant Governor in the role of an Administrator, while for the states, the head is a Chief Minister. To keep understanding the 28 states and capitals and 8 union territories, we will know in-depth about the differences between them.
| Aspect | States | Union Territories |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Head | President | Lieutenant Governor |
| Management | Managed by the State Government | Managed by the Central Government |
| Actual Head | Chief Minister | Lieutenant Governor |
| Election of Head | Elected by the public | Appointed by the President of India |
| Area Comparison | Generally larger in area | Generally smaller in area |
India’s vastness and diversity are reflected in its 28 states and 8 union territories, each with its own unique culture, history, and governance structure. While states are managed by state governments with elected Chief Ministers, union territories are directly governed by the central government, with a Lieutenant Governor overseeing administration. Understanding the relationship between states and capitals, union territories, and their significance is essential for both academic purposes and competitive exams. For more information about India’s states and capitals, as well as its union territories, visit Chegg India.
Recommended Reads:
Ans. India is a federal union that has 28 states, with each state having its capital.
Ans. At present, India has 8 union territories. They are: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Ladakh.
Ans. Jammu and Kashmir is divided into two union territories: 1. Jammu & Kashmir and 2. Ladakh
Ans. Delhi (Union Territory) is the Capital of India
Ans. Telangana became the 29th state of India, formed in 2014. Telangana was formed after the reorganization of Andhra Pradesh state. Hyderabad is the capital of Telangana.

Authored by, Shivam Singh
Competitive Exam Strategist
Shivam specializes in breaking down complex academic and technical concepts into engaging, student-friendly formats. From curriculum-aligned blogs to explainer content, his goal is to make learning both accessible and enjoyable.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.