

Quick Summary
- To become a doctor in India, one has to complete 12th grade with science, clear NEET, do MBBS, & pursue PG courses.
- Types of doctors are cardiologists, psychiatrists, orthopaedic surgeons, gynecologists, & dermatologists.
- The salary of a doctor ranges from 0.8 lakh to 10.8 lakh annually in India.
Table of Contents
India’s healthcare system relies heavily on skilled and compassionate medical professionals. The journey to becoming a doctor in India is a marathon, not a sprint, requiring sustained effort and passion. This guide simplifies the complex process of how to become a doctor in India, making it accessible to everyone. So, if you’re asking yourself, “How to become a doctor in India?”, you’ve come to the right place. We’ll explore in detail how to become a doctor in India.
Step-by-Step Guide to How to Become a Doctor in India
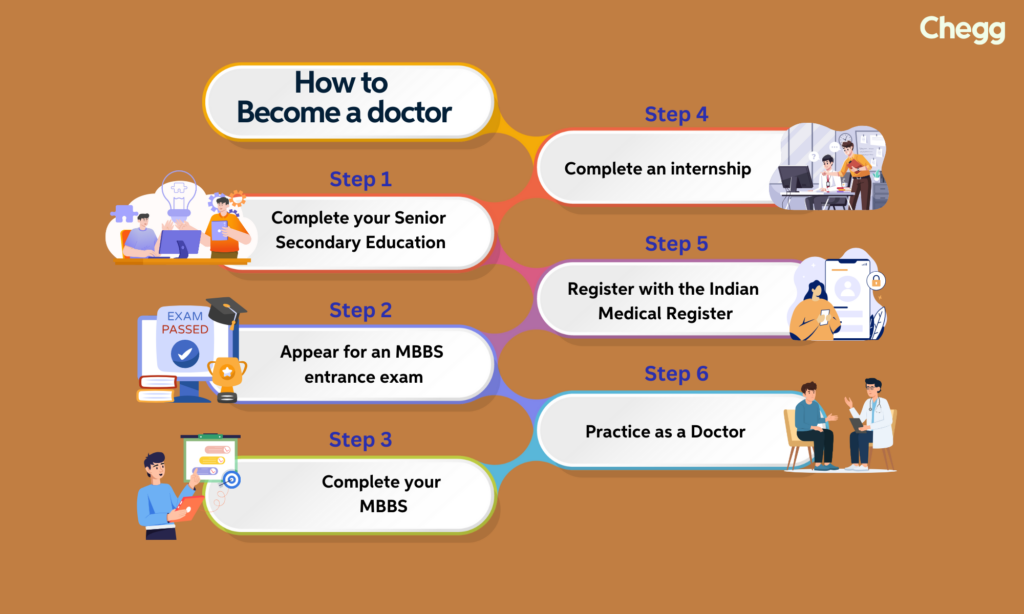
To become a doctor in India it requires developing strong problem-solving and critical thinking skills. You must always think, how many years does it take to become a doctor after 12th? The duration of becoming a doctor after completing the 12th grade varies. It depends on the country and the educational system. Here are the steps to becoming a doctor in India.
Step 1: Complete 10+2 (Higher Secondary Education) with PCB:
The very first step on how to become a doctor in India is your higher secondary education (11th and 12th grades). You must opt for the Science stream and choose Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (PCB) as your core subjects. These subjects form the bedrock of medical knowledge. A strong foundation in PCB is essential for understanding complex medical concepts later on. Aim for excellent grades in these subjects, as they directly impact your eligibility for NEET. This is the foundational step in how to become a doctor in India.
- Subject Combinations: While PCB is mandatory, you can also have optional subjects like English, Mathematics, or Computer Science.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Ensure a thorough understanding of the NCERT syllabus for these subjects, as it forms the basis of the NEET exam.
- Board Exams: You’ll need to pass your 12th board exams with the required minimum percentage to be eligible for NEET.
Step 2: Prepare for and Qualify NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test):
NEET is the single national-level entrance examination for admission to all MBBS and other undergraduate medical courses in India. It’s conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA). Qualifying NEET is absolutely essential for anyone aspiring to know how to become a doctor in India. This exam evaluates your understanding of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology at the 11th and 12th-grade levels. Rigorous preparation and consistent study are key to scoring well in NEET. Understanding NEET is crucial for how to become a doctor in India.
What is NEET?
NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is the gateway to medical education in India. It’s the only way to secure admission to MBBS, BDS (Bachelor of Dental Surgery), AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy), and other related courses. This is a crucial aspect of how to become a doctor in India.
Important details about NEET:
- Exam Pattern: NEET is a pen-and-paper-based test with multiple-choice questions (MCQs).
- Syllabus: The syllabus comprises topics from Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (Botany and Zoology) of classes 11th and 12th.
- Marking Scheme: Each correct answer carries 4 marks, and there is a negative marking of 1 mark for each incorrect answer.
- Eligibility Criteria: There are certain eligibility criteria related to age, nationality, and qualifying exams, which are updated regularly on the NTA NEET website.
- Preparation Strategies: Many resources are available for NEET preparation, including coaching institutes, online courses, and self-study materials.
Step 3: Participate in NEET Counselling and Secure Admission to a Medical College:
After the NEET results are declared, the Medical Counselling Committee (MCC) conducts online counselling for All India Quota seats (15% of total seats in government colleges and 100% in central universities), while state authorities conduct counselling for state quota seats (85% in state government colleges). Based on your NEET score, rank, and preferences, you can participate in the counselling process and secure admission to a medical college. This step is a critical part of how to become a doctor in India.
- Counselling Process: The counselling process usually involves registration, choice filling (selecting preferred colleges), seat allotment, and reporting to the allotted college.
- Types of Colleges: Medical colleges in India can be broadly classified into government colleges, private colleges, and deemed universities.
- Cut-off Scores: The NEET cut-off scores vary each year depending on factors like the difficulty level of the exam and the number of applicants.
Step 4: Complete MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery):
Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS Full Form) is the primary undergraduate medical degree required to become a doctor in India. The MBBS. course is a 4.5-year program, followed by a mandatory one-year internship. The curriculum is divided into preclinical, paraclinical, and clinical subjects. This is the core educational component of how to become a doctor in India.
- Preclinical Subjects: Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry.
- Paraclinical Subjects: Pathology, Microbiology, Pharmacology, Forensic Medicine, Community Medicine.
- Clinical Subjects: Medicine, Surgery, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics, Ophthalmology, ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat).
- Examinations: Regular examinations are conducted throughout the MBBS course to assess students’ understanding of the subjects.
Step 5: Complete Internship:
After completing the 4.5 years of MBBS coursework, you’ll undertake a compulsory one-year rotating internship in a hospital affiliated with your medical college. During this internship, you’ll gain hands-on experience by working in various departments under the supervision of experienced doctors. The internship is an invaluable part of how to become a doctor in India.
- Clinical Rotations: You’ll rotate through different departments like Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology, and others.
- Practical Skills: You’ll learn essential clinical skills like history taking, physical examination, diagnosis, and treatment planning.
Step 6: Register with the National Medical Commission (NMC):
After successfully completing your MBBS and internship, you must register with the National Medical Commission (NMC) or the State Medical Council. This registration grants you the license to practice medicine legally in India. This is a formal and essential requirement in how to become a doctor in India.
Step 7 (Optional): Pursue Postgraduate Studies (MD/MS/Diploma):
After obtaining your MBBS degree, you can choose to specialize in a particular medical field by pursuing postgraduate studies like MD (Doctor of Medicine) or MS (Master of Surgery). Admission to postgraduate courses is through the NEET PG (Postgraduate) exam. This is an important step for those looking for specialized knowledge after they learn how to become a doctor in India generally.
- Specializations: Numerous specializations are available, including Cardiology, Neurology, Oncology, Pediatrics, Psychiatrists, and many more.
- Super Specialization: After MD/MS, you can further specialize in a sub-specialty through DM (Doctor of Medicine) or MCh (Master of Chirurgiae) courses.

Eligibility Criteria to Become a Doctor in India
To become a doctor in India, you must meet specific eligibility criteria at different stages of your education and career. Here is a detailed look at the requirements:
1. Educational Qualification
High School (10+2) Requirements:
| Subjects | You must have completed your high school education with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (PCB) as your main subjects. Mathematics is optional but can be helpful. |
| Minimum Marks | You need to secure a minimum of 50% marks in PCB subjects in your 12th standard exams. For reserved category students (SC/ST/OBC), the minimum required marks are usually 40-45%. Some top medical colleges may have higher cut-off marks. |
2. Entrance Exam – NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test)
Exam Eligibility:
| Educational Background | You must have completed 10+2 with PCB subjects from a recognized board. |
| Age Limit | Minimum Age: You must be at least 17 years old on or before December 31st of the year of admission. Maximum Age: There is no upper age limit as per the current regulations, allowing all aspiring candidates to apply. |
| Number of Attempts | As per current regulations, there is no limit on the number of attempts for NEET. |
Exam Details:
| Subjects | NEET exam covers Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (Botany and Zoology). |
| Exam Pattern | The exam consists of 180 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) – 45 questions each from Physics and Chemistry, and 90 questions from Biology. |
| Duration | The exam duration is 3 hours. |
| Marking Scheme | Each correct answer earns 4 marks, and each incorrect answer deducts 1 mark. |
3. MBBS Course Admission
Admission Process:
| NEET Score | Your NEET score is crucial for securing admission into MBBS courses. Top medical colleges have high cut-off scores, so aim for the best possible score. |
| Counseling | After the NEET results are declared, you need to participate in the counseling process conducted by the Medical Counseling Committee (MCC) or the respective State Counseling Authorities. Based on your rank, you will be allocated a seat in a medical college. |
| Document Verification | During counseling, you will need to provide various documents, including your 10th and 12th mark sheets, NEET scorecard, birth certificate, identity proof, and other relevant certificates. |
Reservation Criteria:
| Reserved Categories | There are specific reservations for SC, ST, OBC, EWS, and PwD candidates. Each category has a designated percentage of seats reserved in government medical colleges. |
4. Postgraduate (MD/MS) Eligibility
Educational Qualification:
| MBBS Degree | You must have completed your MBBS degree from a recognized medical college in India. |
| Internship | You must have completed a mandatory one-year rotating internship after your MBBS. |
Entrance Exam – NEET-PG:
| Exam Eligibility | To apply for NEET-PG, you must have a valid MBBS degree and have completed your internship. |
| Subjects | The NEET-PG exam covers various subjects studied during the MBBS course. |
| Exam Pattern | The exam consists of 300 multiple-choice questions (MCQs). |
| Duration | The exam duration is 3 hours and 30 minutes. |
| Marking Scheme | Each correct answer earns 4 marks, and each incorrect answer deducts 1 mark. |
5. Licensing and Registration
Medical Licensing:
| Medical Council Registration | After completing your MBBS and internship, you need to register with the Medical Council of India (MCI) or the respective State Medical Council to obtain a license to practice. |
| Documents Required | You will need your MBBS degree certificate, internship completion certificate, identity proof, birth certificate, and other relevant documents. |
Licensing Exam (if applicable):
| Foreign Graduates | If you have obtained your medical degree from a foreign university, you may need to clear the Foreign Medical Graduates Examination (FMGE) conducted by the National Board of Examinations (NBE) to practice in India. |
By meeting these eligibility criteria, you can embark on your journey to becoming a doctor in India. It is essential to stay updated with the latest regulations and requirements as they may change over time.
Top Medical Colleges in India
India is home to several prestigious medical colleges that offer top-notch education and training for aspiring doctors. Here are some of the top medical colleges in India:
| College Name | Rank | Courses Offered | Admission | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi | 1 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh | 2 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore | 3 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore | 4 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry | 5 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore | 6 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS), Lucknow | 7 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Varanasi | 8 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | 9 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
| Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram | 10 (NIRF 2024) | MBBS, MD, MS, DM, MCh, and various other postgraduate and super-specialty courses. | Based on NEET scores. | Approximately INR 1,000 per year for government seats. |
These colleges are renowned for their excellent infrastructure, experienced faculty, and high academic standards. Admission to these institutions is highly competitive and based on NEET scores. The fees for government seats are relatively low, but private medical colleges can have significantly higher fees.
Career Prospects and Salary
Pursuing a career as a doctor in India opens up a world of opportunities and offers a rewarding professional journey. Here’s a detailed look at the various career prospects and potential salary ranges for doctors in India:
Career Prospects
1. Clinical Practice:
- Government Hospitals: Many doctors start their careers in government hospitals, where they gain valuable experience. Opportunities include positions in primary health centers, district hospitals, and large public hospitals.
- Private Hospitals: Private hospitals offer specialized roles and often provide better salaries and working conditions. They include multi-specialty hospitals and clinics.
- Own Practice: With enough experience, many doctors opt to open their own private clinics. This allows them to set their own schedules and potentially earn higher incomes.
2. Specializations:
- After completing an MBBS, doctors can pursue postgraduate studies (MD/MS) in various specializations like General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Orthopedics, Dermatology, Psychiatry, Radiology, and more. Specialists are in high demand and can command higher salaries.
3. Academic and Research:
- Teaching: Doctors can choose to teach at medical colleges, becoming professors or lecturers. This career path allows them to contribute to educating future doctors while conducting research.
- Research: Doctors can work in medical research institutes, contributing to advancements in medical science and technology. Research roles often involve working on clinical trials, developing new treatments, and publishing findings.
4. Healthcare Administration:
- Doctors with an interest in management can move into healthcare administration, taking on roles such as hospital administrators, medical superintendents, or healthcare managers. These roles involve overseeing hospital operations and ensuring efficient delivery of healthcare services.
5. Public Health:
- Working in public health allows doctors to focus on community health and preventive medicine. They may work with government or non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to develop and implement public health programs and policies.
6. International Opportunities:
- With additional certifications and qualifications, Indian doctors can pursue opportunities abroad. Countries like the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia have pathways for foreign-trained doctors to practice.
Salary
Salaries for doctors in India vary based on factors such as specialization, experience, and place of employment. Here’s an overview of potential salary ranges:
1. Government Hospitals:
- Interns: INR 20,000 – 30,000 per month.
- Junior Doctors: INR 50,000 – 80,000 per month.
- Specialists: INR 1,00,000 – 2,00,000 per month.
- Senior Consultants: INR 2,00,000 – 3,00,000 per month.
2. Private Hospitals:
- Interns: INR 25,000 – 35,000 per month.
- Junior Doctors: INR 60,000 – 1,00,000 per month.
- Specialists: INR 1,50,000 – 3,00,000 per month.
- Senior Consultants: INR 3,00,000 – 5,00,000+ per month.
3. Own Practice:
- General Practitioners: Earnings can vary widely, ranging from INR 50,000 to 2,00,000 per month, depending on the location and patient load.
- Specialists: In high-demand specializations, earnings can exceed INR 5,00,000 per month.
4. Academic and Research:
- Lecturers/Professors: INR 60,000 – 1,50,000 per month.
- Researchers: INR 60,000 – 2,00,000 per month, with potential for higher earnings through grants and projects.
5. Healthcare Administration:
- Administrators/Managers: INR 1,00,000 – 3,00,000 per month.
6. Public Health:
- Public Health Officers: INR 50,000 – 1,50,000 per month.
- Program Managers: INR 1,00,000 – 2,50,000 per month.
The career prospects for doctors in India are diverse and promising, offering opportunities in various fields such as clinical practice, specializations, academia, research, healthcare administration, and public health. Salaries can vary based on experience, specialization, and place of employment, but the medical profession remains one of the most respected and rewarding careers in India.
Related Read :- Highest Paid Doctors in India
Conclusion
Becoming a doctor in India is a demanding but deeply rewarding journey. It requires unwavering commitment, perseverance, and a genuine desire to make a difference in people’s lives. This detailed guide has thoroughly explained the steps involved in how to become a doctor in India. We hope this comprehensive information helps you understand how to become a doctor in India and inspires you to pursue your medical aspirations.
This guide on how to become a doctor in India is designed to be a valuable resource for aspiring medical professionals. Now you have a very detailed understanding of how to become a doctor in India.
Evaluate numerous career choices to choose the right career path for yourself. Dive into our guide on Career Advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How to become a doctor in India after 12th? / How to become a doctor after 12th?
To become a doctor in India after 12th, you need to:
1. Complete 10+2 with PCB subjects.
2. Qualify the NEET exam.
3. Enroll in an MBBS course and complete the 5.5-year program.
4. Complete a one-year internship.
5. Obtain a medical license to practice.
Q2. Can I become a doctor without NEET?
No, qualifying the NEET exam is mandatory for admission to medical colleges in India. It is the gateway to both undergraduate (MBBS) and postgraduate (MD/MS) medical courses.
Q3. What is the salary of MBBS doctor in India?
The salary of an MBBS doctor in India varies widely based on factors like location, experience, etc. On average, a fresh MBBS graduate can earn between ₹40,000 to ₹70,000 per month. With experience, this can rise to ₹1 lakh or more per month, especially in private practice or specialized fields.
Q4. Is MBBS harder than NEET?
MBBS is harder than NEET because its 5.5-year curriculum covers various medical subjects, requiring in-depth knowledge and practical skills. Students face continuous assessments and high-stress environments, making the overall experience more challenging than the focused NEET entrance exam.
Q5. How many years does it take to become a doctor in India? / How many years to become a doctor in India?
It takes around 5.5 years to complete an MBBS degree, which includes a one-year internship. If you pursue postgraduate education, it adds another 3 years, making it a total of 8.5 years.
Q6. Which doctor earns 50 lakhs per month?
Highly experienced specialists like neurosurgeons, cardiologists, or orthopedic surgeons in reputed hospitals or private practice can earn up to 50 lakhs per month, but this is relatively rare and depends on various factors like location, reputation, and years of experience.
Q7. How to become a doctor in India without NEET?
You cannot become a doctor in India without qualifying NEET, as it is a mandatory entrance exam for admission to all medical courses in India.
Q8. How to become a doctor in India after 10th?
After 10th, you need to:
1. Choose the Science stream with PCB subjects in 11th and 12th.
2. Prepare for and qualify the NEET exam.
3. Follow the same steps as becoming a doctor after 12th.
Q9. How to become a doctor with NEET?
To become a doctor with NEET, you need to:
1. Complete 10+2 with PCB subjects.
2. Prepare for and qualify the NEET exam.
3. Enroll in an MBBS course based on your NEET score.
4. Complete the MBBS program and internship.
5. Obtain a medical license to practice.
Q10. What is the cost of becoming a doctor in India?
The cost of becoming a doctor in India varies depending on the college and course. Government colleges may charge around INR 10,000-50,000 per year, while private colleges can charge between INR 10 lakhs to 25 lakhs per year.
Q11. How to become a doctor without MBBS?
In India, you cannot become a certified doctor without completing the MBBS course. However, you can pursue alternative medical courses like BAMS (Ayurveda), BHMS (Homeopathy), or BDS (Dentistry).
To read more related articles, click here.
Got a question on this topic?