

Quick Summary
- Economics studies how economies work, and the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
- It can provide a variety of job opportunities.
- Microeconomics is the study of individuals and business decisions, while macroeconomics looks at the decisions of countries and governments.
Table of Contents
Economics has evolved over the centuries due to its presence in every aspect of life. The scope of economics is widely spread. It is a branch of social science that enables us to understand past, present, and future economic models. Economics helps us to understand the world around us and how it is being applied to societies, governments, businesses, and individuals.
Additionally, scope of economics is huge as it covers international trade & globalization, development economics that addresses growth and poverty in low-income countries, and behavioral economics, which integrates psychological insights into economic decision-making. It is not easy to explain the scope of economics. So in this article, we will explore the nature and scope of economics and the prospective careers in economics.
Nature of Economics
The nature of economics has a dual presence. Famous economist Robbins proposed that economics is a science that studies human behaviour relating to the availability of scarce resources, while Alfred Marshall another renowned scientist defined economics as an art.
Let us explore the nature of economics as science and art:
1. Economics as a Science
British economist Lionel Robbins defined economics as a branch of social science that deals with human behaviour as a relationship between given ends and scarce resources that have alternative uses. Economics is considered a science because the scope of economics is based on several principles. It involves a systematic study of knowledge and facts. One example can be the process of economic research. As science deals with the relationship between cause and effect, this principle is implemented while collecting, classifying, and analyzing data for micro and macroeconomic research.
2. Economics as an Art
Economics is defined as an art due to the presence and usage of various theories, concepts, and findings for achieving goals. According to economist Alfred Marshall, economics is the art of the practical application of scientific theories for attaining goals. The theories are explained through graphical representations defining the relationship between the economic variables and their application theories. This denotes the nature of economics as an art.
Scope of Economics
Economics deals with a wide variety of things. It comprises multiple principles and theories whose implications influence the economy of a country. When it comes to the scope of economics, it can be understood by the two scope of economics – Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Learn more about the nature and scope of economics below.
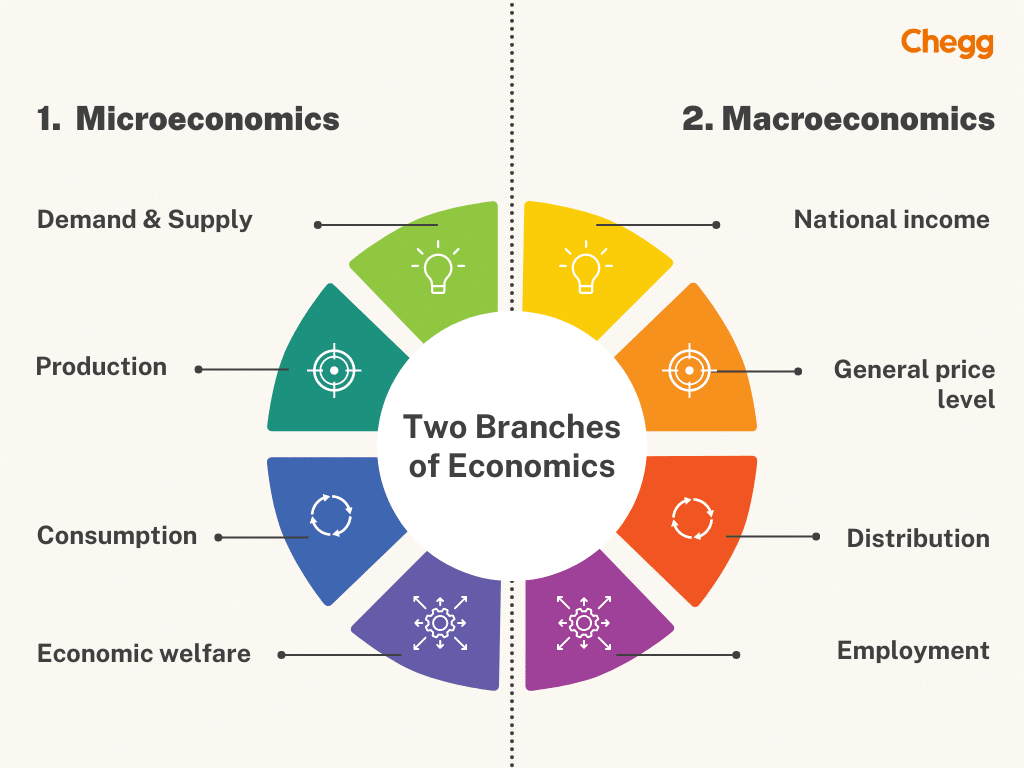
1. Microeconomics
Microeconomics is concerned with studying the micro elements of the economy of a nation. It deals with the individual units of an economy. Microeconomics studies the concept of product pricing along with the pricing of production factors, and the behaviour of households, individuals, and firms. It enables us to analyze how these units allocate their scarce resources, their distribution, and utilization.
The scope of microeconomics includes:
- Demand & Supply
- Production
- Consumption
- Economic welfare
2. Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics deals with the macro units of an economy. It is the aggregate study of the elements of a country’s economy. Macroeconomics studies the entire economy of a nation as a whole. It deals with the overall production, total consumption, aggregate demand, and aggregate supply of a nation’s economy. Unlike microeconomics, macroeconomics deals with individual units on an aggregate basis.
The scope of macroeconomics includes:
- National income
- General price level
- Distribution
- Employment
Top 10 Careers Scope in Economics
The career scope of economics offers wide exposure to students in the field of career opportunities in economics. Multiple career options are available for students who wish to take up economics as a career.
Here are the top 10 career opportunities in scope of economics:
- Economist
- Financial Researcher
- Consumer Credit Manager
- Personal Financial Advisor
- Professor
- Indian Economic Service Officer (IES)
- Income Tax Officer
- Statistical Investigator
- Audit Officer
- Probationary Officer
1. Economist
An economist is responsible for conducting research on the economic model of the country, identifying issues through surveys, and analyzing the collected data through mathematical models and strategic techniques. They conclude research reports and forecast the issues that may arise in the future.
Skills Required:
- Excellent numerical ability
- Interpersonal skills
- Critical thinking ability
- Adequate knowledge of social sciences
- Problem-solving skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of an economist is INR 6.6 LPA.
2. Financial Researcher
A financial researcher is responsible for accessing and analyzing the financial statements of a company and predicting the company’s future performance in the working sector. Their work includes forecasting future revenues and expenditures and keeping a track of the company’s financial plan.
Skills Required:
- Strategic thinking
- Presentation skills
- Multitasking ability
- Problem-solving skills
- Communication skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of a financial researcher is INR 8 LPA.
3. Consumer Credit Manager
Consumer credit managers research and evaluate the creditworthiness of customers. Their work involves reviewing consumers’ credibility through the creation of credit scoring models. They are responsible for predicting risks and approving or rejecting loans.
Skills Required:
- Communication skills
- Hands-on experience with accounting software
- Knowledge of lending procedures
- Negotiation skills
- Excellent analytical skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of a consumer credit manager is INR 7.7 LPA.
4. Personal Financial Advisor
Personal financial advisors assist their clients in reaching their financial goals. They help individuals or companies achieve their financial goals by providing various strategies and techniques. They provide advice on reducing costs, eliminating debts, and creating more wealth.
Skills Required:
- Research skills
- Analytical ability
- Problem-solving skills
- Detail orientation
- Interpersonal communication
Average Salary:
The average salary of a personal financial advisor is INR 4.56 LPA.
5. Professor
An economics professor or teacher is responsible for teaching undergraduate or postgraduate students at universities or institutions. They prepare and deliver lectures to students on the subject of economics.
Skills Required:
- Excellent communication skills
- Impeccable knowledge of economics
- Critical thinking
- Instructing ability
- Complex problem-solving skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of a professor is INR 10 LPA.

6. Indian Economic Services Officer (IES)
The Indian economic services officer or IES officer is responsible for maintaining and regulating the economic affairs in the social or government sectors. Their work includes managing the government’s functioning and making crucial contributions to formulating policies.
Skills Required:
- Leadership skills
- Problem-solving skills
- Moral judgment power
- Critical thinking ability
- Coordination skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of an IES officer is INR 9.60 LPA (as per the 7th Pay Commission).
7. Income Tax Officer
Income tax officers are responsible for regulating the taxation procedure of a country. They examine and analyze the tax assets and liabilities to determine delinquent tax issues. They communicate with the members and intermediaries involved in the taxation process to evaluate the tax problems.
Skills Required:
- Excellent communication skills
- Numerical ability
- Detail orientation
- Time management skills
- Evaluating skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of an income tax officer is INR 7.5 LPA.
8. Statistical Investigator
A statistical investigator is responsible for planning and executing all the work relating to the census. They monitor and coordinate the training functionaries and collect, process, and disseminate data. They conduct numerous data collection surveys for performing intensive field duties.
Skills Required:
- Research skills
- Excellent data interpretation skills
- Strategic thinking
- Numerical ability
- Adequate knowledge of statistics
Average Salary:
The average salary of a statistical investigator is INR 9.36 LPA.
9. Audit Officer
The responsibility of an audit officer includes reviewing and examining the financial reports and records. They check the reports to identify their accuracy and reliability. Audit officers ensure that the assets remain protected. They analyze the processes to find issues and make necessary changes.
Skills Required:
- Excellent problem-solving skills
- Good knowledge of the financial system
- Time management skills
- Critical thinking
- Communication skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of an audit officer is INR 3.6 LPA.
10. Probationary Officer
A probationary officer is responsible for regulating and handling the banking transactions of customers. They retain the authority to issue chequebooks, pass cheques, and manage cash. Probationary officers can also work in private or public sector companies for financial or accounting matters.
Skills Required:
- Verbal and written communication skills
- Good organizational skills
- Work efficiency
- Numerical ability
- Management skills
Average Salary:
The average salary of a probationary officer is INR 7.5 LPA.

Scope of Economics – In a Nutshell
Economics has emerged as an important attribute in the world including both individual life and the working sector. There is a huge scope of economics in various fields. Be it job opportunities after BA economics or civil services, its scope lies everywhere. Numerous enhancing career opportunities in economics are available, where students can not only prosper but also establish successful careers. The future of economic students is considered to be highly enriching.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scope of economics?
The scope of economics includes microeconomics & macroeconomics. Both categories deal with the individual units of an economy. It imparts high-end knowledge of economic models. Several exciting careers in economics can land students on various reputed job profiles with great salary packages.
What is general scope of economics?
The general scope of economics includes the study of resource allocation, production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It includes microeconomics, focusing on individual choices, and macroeconomics, examining aggregate economic phenomena.
What are the 5 scopes of business economics?
The 5 scopes of business economics includes Demand Analysis and Forecasting, Production and Cost Analysis, Pricing Decisions, Market Structure Analysis and Capital Management.
Who is the father of economics?
The father of economics is often considered to be Adam Smith. His seminal work, “The Wealth of Nations,” published in 1776, laid the foundations for classical economics and introduced key concepts such as the division of labor, free markets, and the “invisible hand” that guides economic activity.
How many scopes are there in economics?
There are mainly 2 two scope of economics i.e. Microeconomics & Macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the study of individuals and business decisions, whereas macroeconomics looks at the decisions of countries and governments.
To read more related articles, click here.
Got a question on this topic?